Understanding the Humble Cable Node
1. What Exactly Is a Cable Node, Anyway?
Ever wondered what makes your internet and cable TV tick? Well, a big part of the answer lies within the unassuming cable node. Think of it as a crucial traffic controller in the vast network that delivers all those cat videos and streaming shows to your screen. It’s not quite the brain, but definitely a major nerve center!
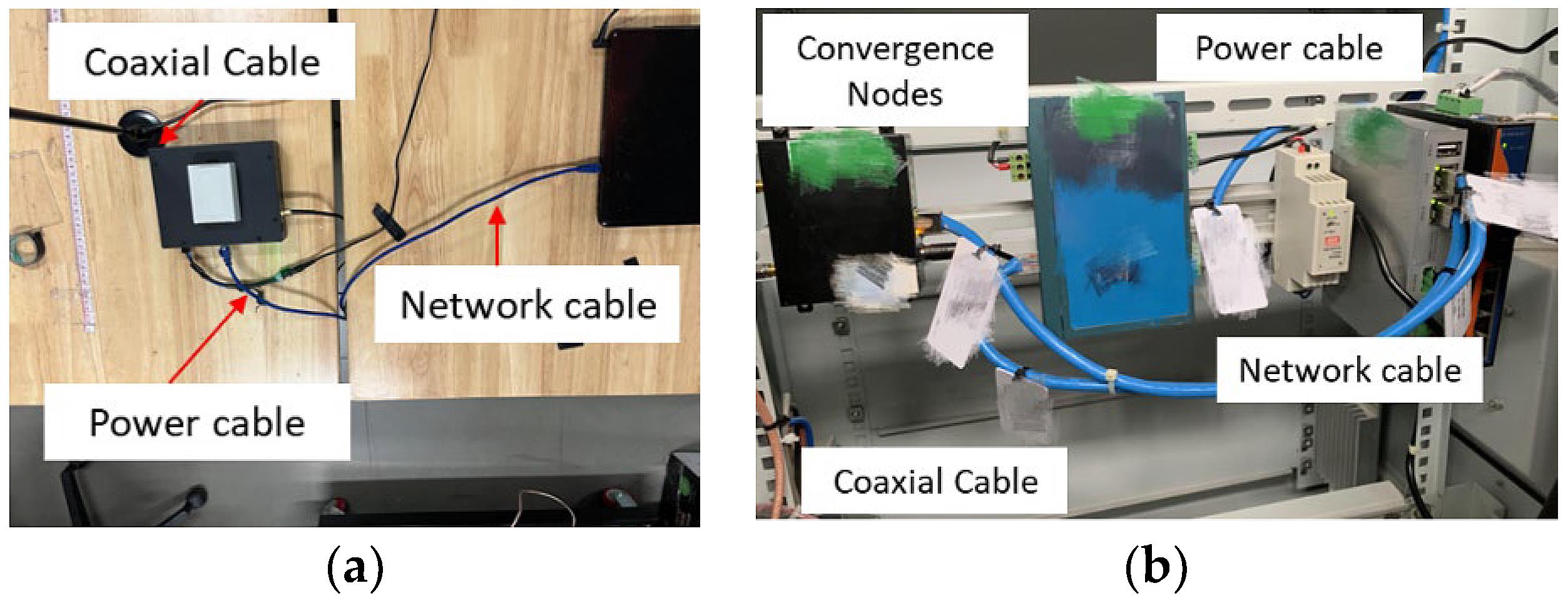
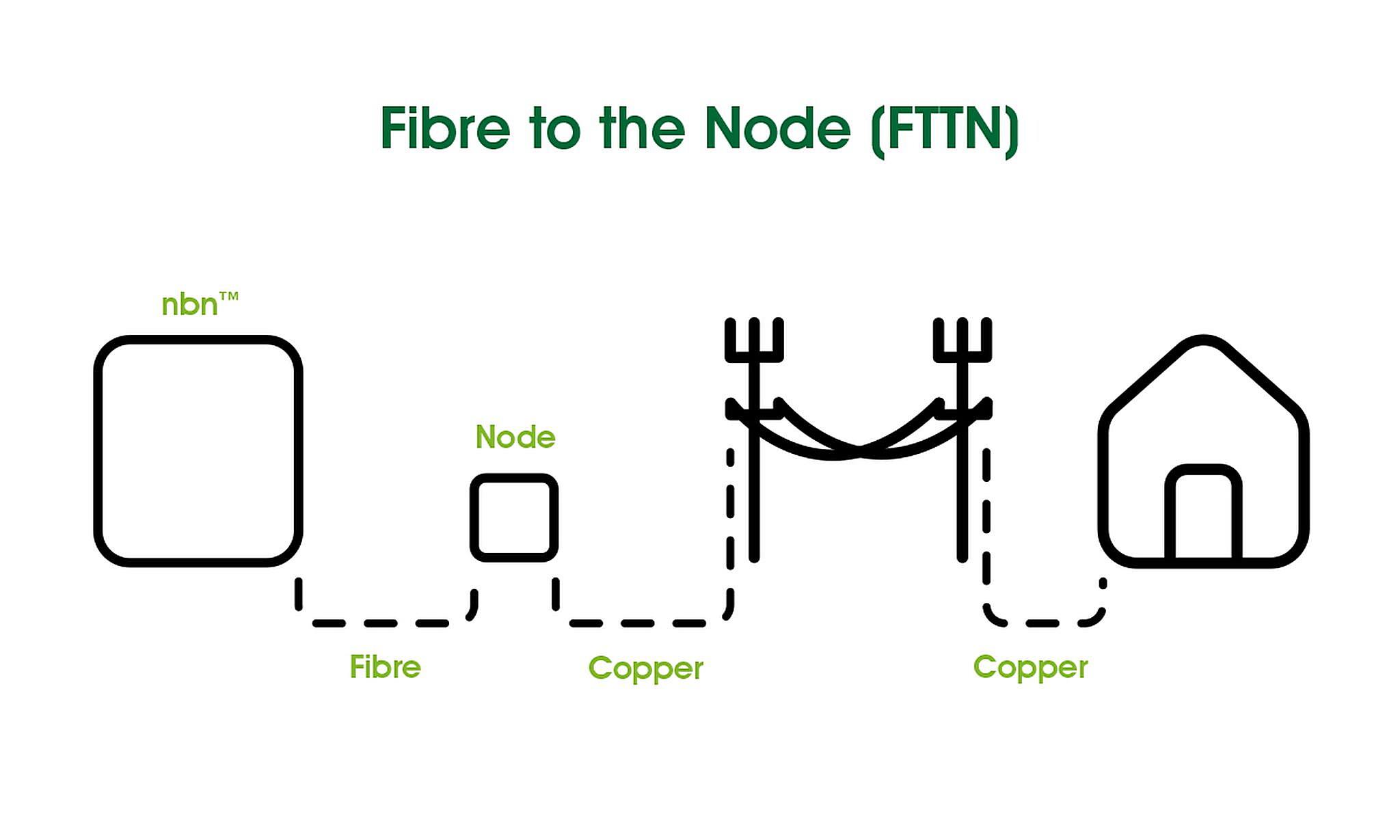
In simple terms, a cable node is a connection point in a cable network. It’s where the optical fiber (the super-fast lane for data) transitions into coaxial cable (the copper wire that probably snakes its way into your home). This transition is essential because, for now, most homes aren’t directly connected to fiber optic lines. The node acts as the translator, taking the light-speed data and converting it into a format your existing cable setup can understand.
Imagine a highway system. The fiber optic cable is like the major highway, carrying massive amounts of traffic quickly across long distances. The cable node is the exit ramp, directing some of that traffic onto smaller local roads (the coaxial cables) that lead to individual houses. Without the exit ramp, everyone would be stuck on the highway forever!
So, next time you’re binge-watching your favorite series, take a moment to appreciate the unsung hero that is the cable node. Its quietly working in the background, ensuring you get your dose of digital entertainment.
Delving Deeper
2. More Than Just a Translator
Okay, so we know the cable node translates fiber optic signals to coaxial cable signals. But that’s not all it does! It’s actually a pretty busy little piece of equipment. Think of it less like a simple translator and more like a mini-distribution center for your digital content.
Besides signal conversion, the node also amplifies the signal to maintain its strength as it travels along the coaxial cables. Coaxial cables are more prone to signal loss than fiber optic, so the node has to give the signal a boost to ensure it reaches your TV or modem without fading out. This amplification is vital for preventing those annoying glitches and buffering issues we all love to hate.
Another important function is signal splitting. A single fiber optic cable carries data for multiple subscribers. The cable node separates this data and directs the appropriate signals to the correct homes. Its like a postal worker sorting mail, making sure everyone gets the right packages. And, like a stressed-out postal worker on December 24th, it has to handle a LOT of information.
Furthermore, modern cable nodes often incorporate sophisticated monitoring and diagnostic capabilities. They can detect signal problems, identify potential faults, and even adjust settings to optimize performance. It’s like having a tiny technician inside the box, constantly tweaking things to keep your connection running smoothly. Pretty neat, huh?
Types of Cable Nodes
3. From Basic to Blazing Fast
Just like cars or smartphones, cable nodes have evolved over time. The technology has improved, leading to different types of nodes with varying capabilities. Understanding these different types can give you a better appreciation for the infrastructure behind your internet and cable service.
Older nodes were primarily designed for analog cable TV signals. They focused on simply amplifying and splitting the signal for distribution. These nodes were relatively simple in design and didn’t have the sophisticated data handling capabilities of modern nodes. Think of them as the Model T Ford of cable technology — reliable in their day, but not exactly cutting-edge now.
Then came the hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) nodes, which are the most common type in use today. These nodes handle both analog and digital signals, allowing for cable TV, internet, and phone services to be delivered over the same network. They’re more complex than the older analog nodes and incorporate more advanced signal processing and management features. They are the workhorses of modern cable networks.
Finally, there are the newer generation of nodes, often referred to as “distributed access architecture” (DAA) nodes. These nodes are designed to push the fiber optic closer to the customer, reducing the length of the coaxial cable run. This results in faster speeds, lower latency, and improved network performance. Think of them as the sleek, electric sports car of cable technology, built for speed and efficiency.
Why Cable Nodes Matter
4. The Node’s Impact
So, why should you care about cable nodes? Well, they have a direct impact on your internet speed, the reliability of your cable service, and the overall quality of your digital experience. They are way more than just a junction box; they are a vital part of the delivery system for all your digital goodies.
A well-maintained and properly functioning cable node ensures you get the speeds you’re paying for. A faulty node can lead to slow internet, pixelated TV, and dropped video calls — all the things that make us want to throw our remotes at the screen. So, reliable nodes mean reliable services.
As technology advances and we demand more bandwidth for streaming, gaming, and other data-intensive activities, the importance of cable nodes only increases. Upgrading to newer, more advanced nodes is crucial for keeping up with the ever-growing demand for speed and bandwidth. Without these upgrades, our networks risk becoming congested and unable to deliver the performance we expect.
Furthermore, the evolution of cable nodes towards DAA is paving the way for even faster and more reliable internet in the future. By pushing the fiber optic closer to the customer, DAA nodes reduce the limitations of coaxial cable and unlock the full potential of fiber optic technology. This means faster downloads, smoother streaming, and a more seamless online experience. So, the cable node is not just about what we have now; it’s about what’s coming next!
Troubleshooting
5. Is It the Node? Common Symptoms & What To Do
Sometimes, things go wrong. If you’re experiencing issues with your internet or cable TV, it might be tempting to blame your service provider immediately. However, before you unleash your inner keyboard warrior on their customer service line, consider that the problem could be related to a cable node issue. But how can you tell?
One common symptom of a node problem is slow or inconsistent internet speeds. If your connection is significantly slower than what you’re paying for, and the problem persists even after restarting your modem and router, there might be an issue with the node serving your area. Packet loss is another signal, leading to frustrating online experiences, especially in gaming or video conferencing.
Pixelation or signal loss on your cable TV can also be a sign of a node-related problem. If you’re seeing a lot of static or the picture keeps cutting out, it’s possible the node is not properly amplifying or distributing the signal. Check if other people in your neighborhood are experiencing similar issues. If so, it strengthens the case for a node problem.
So, what can you do? Unfortunately, not much directly. Cable nodes are typically located outside your home and are maintained by your service provider. The best course of action is to contact your provider and report the issue. Be sure to describe the symptoms you’re experiencing in detail, and mention if you suspect a node problem based on the information you’ve gathered. The more information you can provide, the easier it will be for them to diagnose and fix the problem. And who knows, maybe mentioning that you read an informative article about cable nodes will impress them (or at least make them chuckle)!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Burning Cable Node Questions, Answered!
Let’s tackle some common questions about cable nodes:
Q: How often do cable nodes need to be upgraded?
A: The frequency of upgrades depends on factors like network demand, technology advancements, and the age of the existing infrastructure. Generally, service providers aim to upgrade nodes every few years to keep pace with increasing bandwidth demands and ensure optimal performance.
Q: Can a faulty cable node affect only some subscribers?
A: Yes, it’s possible. Cable nodes serve a specific geographic area, so a problem with a node might only affect subscribers within that area. Also, the specific services affected (internet, TV, phone) can vary depending on the nature of the problem.
Q: Are cable nodes susceptible to weather damage?
A: Absolutely. Like any outdoor equipment, cable nodes are vulnerable to weather-related damage, such as lightning strikes, flooding, and extreme temperatures. Service providers take precautions to protect nodes, but sometimes Mother Nature wins. Hence, maintenance is pretty crucial.
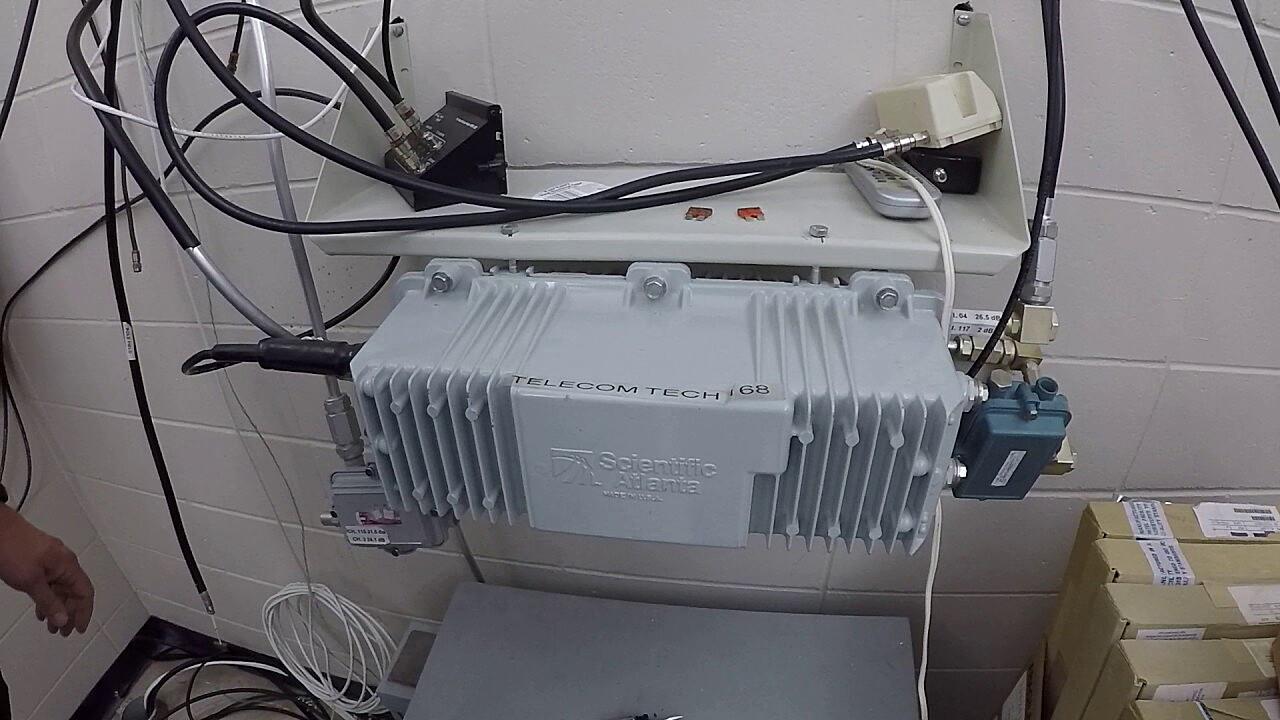
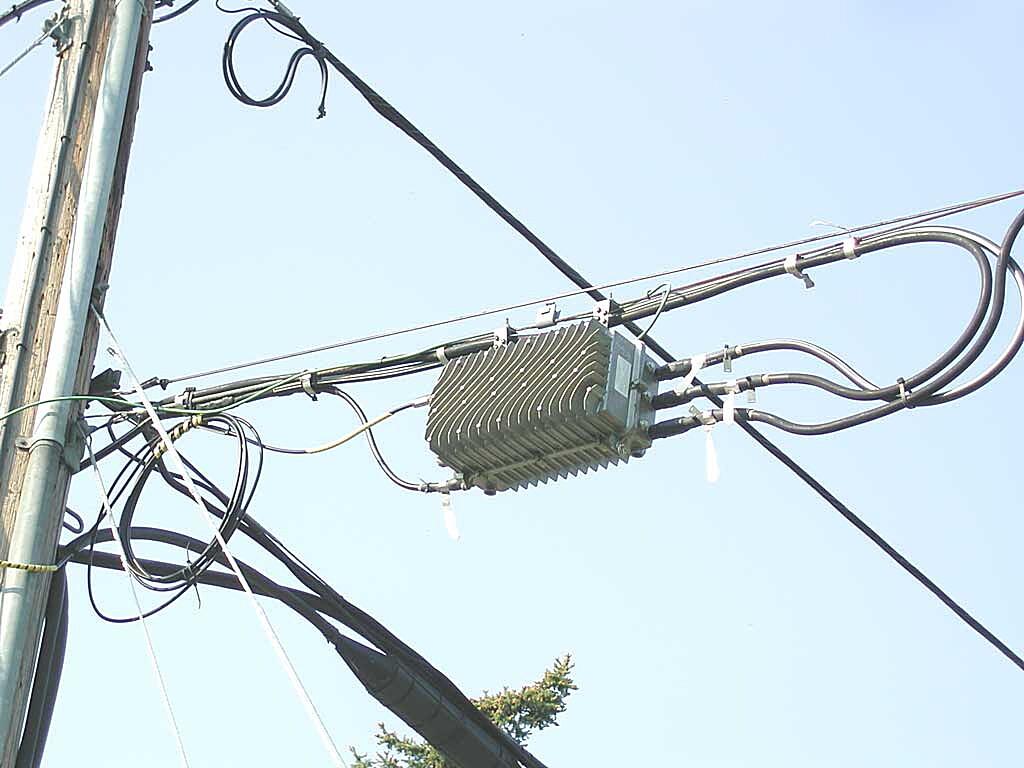
Q: Where are cable nodes usually located?
A: Cable nodes are typically housed in green cabinets or enclosures that you might see along streets or in neighborhoods. They are strategically placed to serve a specific area, ensuring optimal signal distribution.