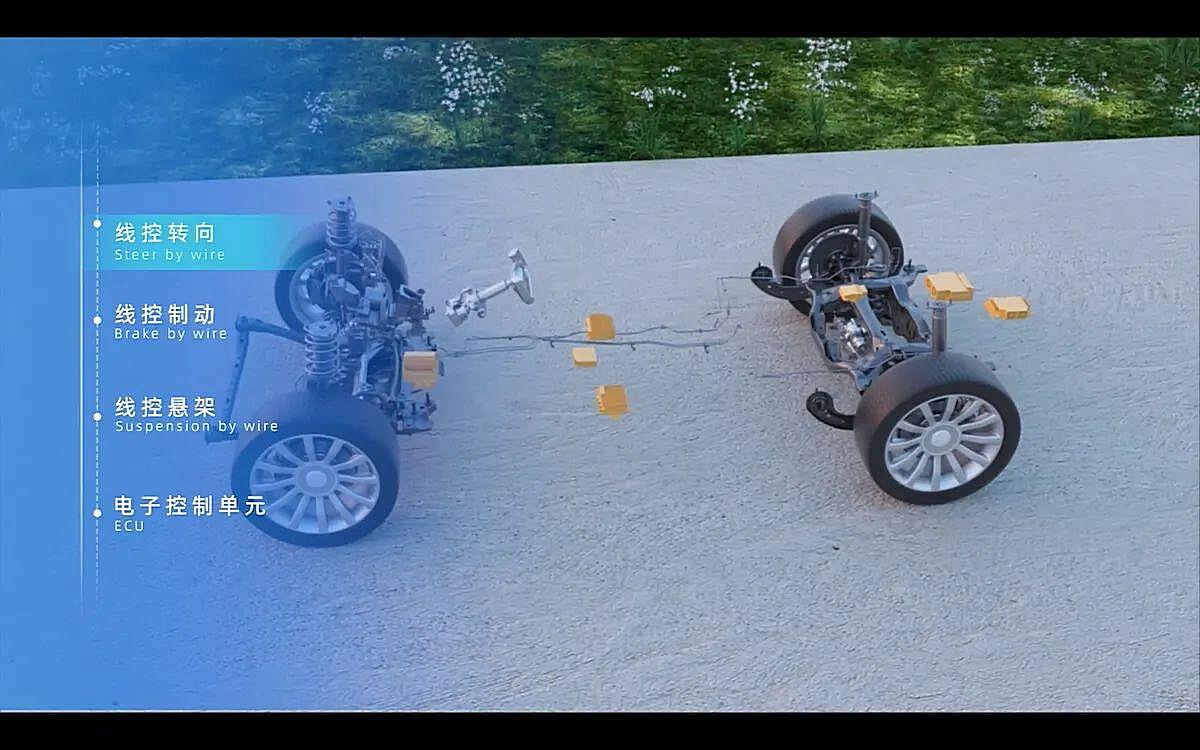
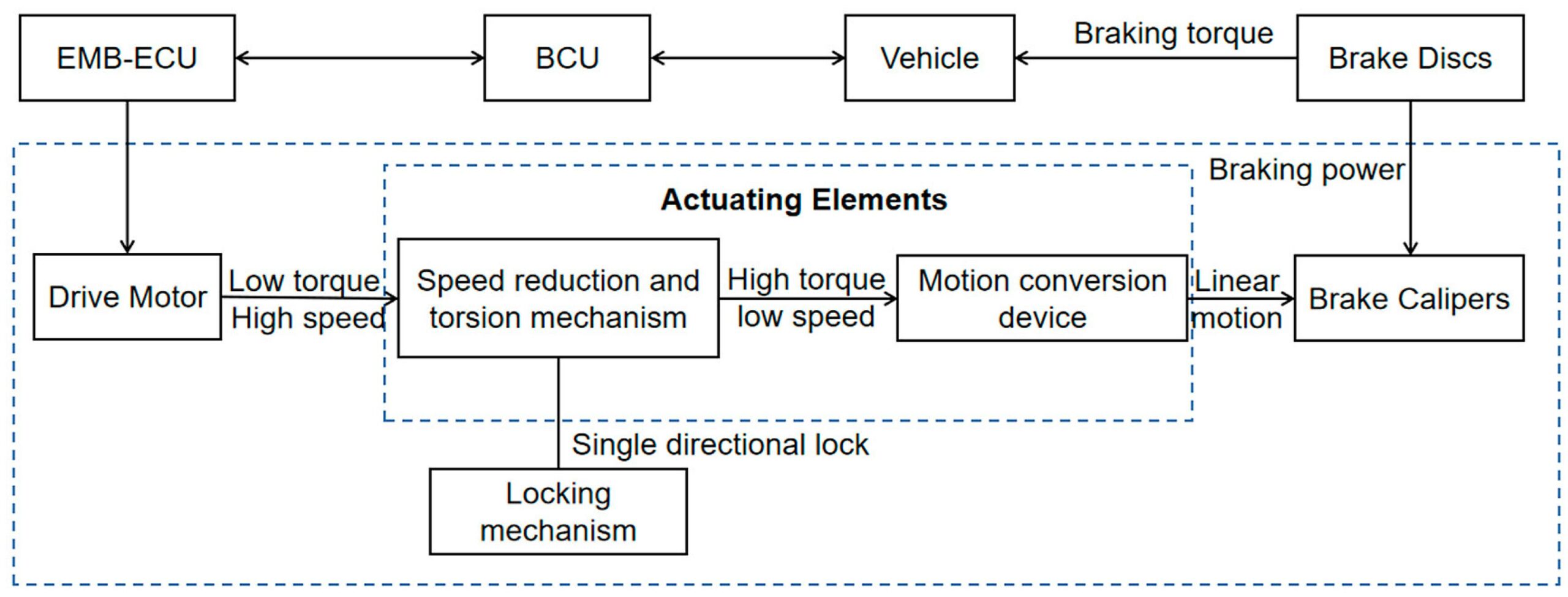
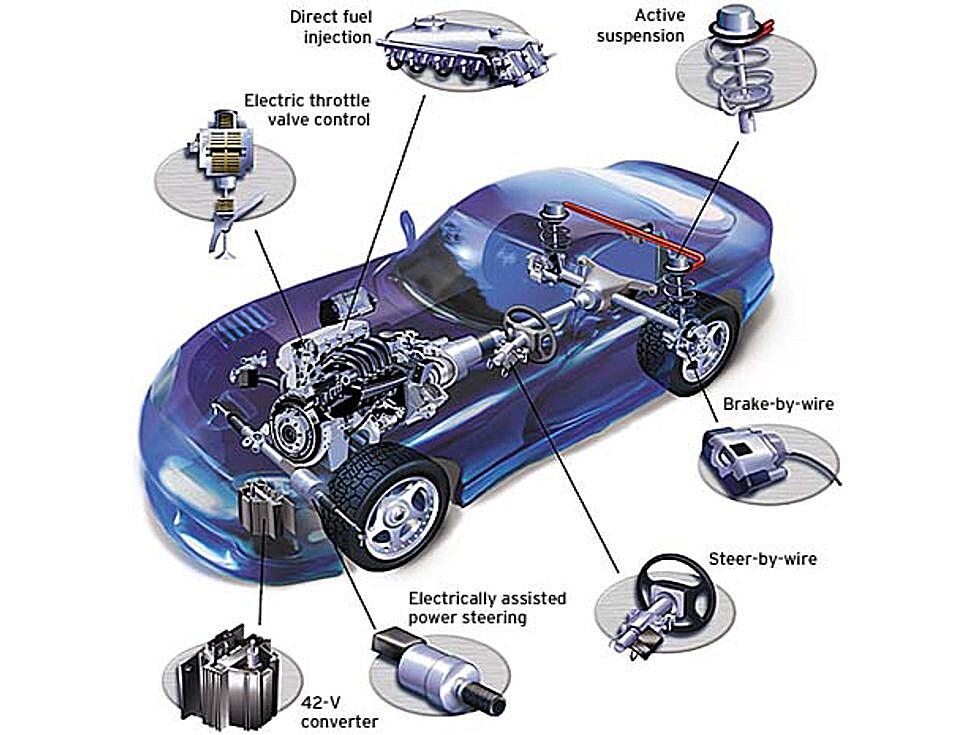
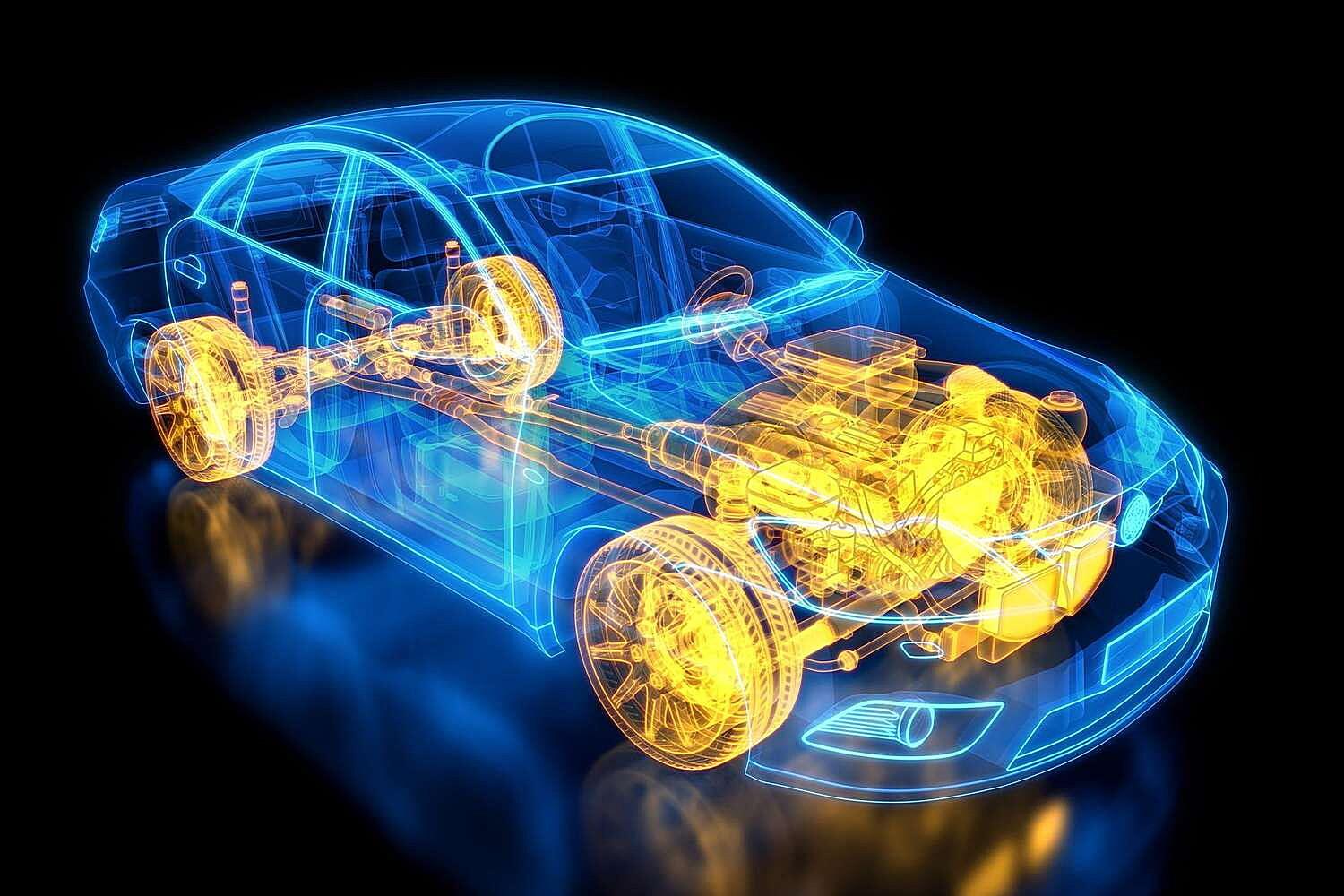
What Exactly Is This “By-Wire” Thing?
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever heard someone say their car has “drive-by-wire” and wondered what they were on about? It’s not quite as futuristic as piloting a spaceship (though that’s where our brains might jump!), but it’s a pretty significant shift in how machines — especially cars — operate. Think of it as replacing physical cables and linkages with electronic signals. Instead of your steering wheel directly tugging on a mechanical arm that turns the wheels, your actions are translated into digital instructions. Those instructions then tell actuators (fancy motors) how to move things.
So, what does this actually mean? Imagine trying to explain to your grandpa that you’re not physically connected to the throttle, but instead, you’re sending requests. The computer does the rest. Initially, you get a blank stare. Then, maybe a grudging, “Sounds like more things to go wrong!” And he might have a point…but let’s explore why by-wire systems are actually quite clever.
The core concept is simple: replace mechanical links with electrical signals. This isn’t entirely new — many cars already have some electronic components controlling various functions. But true by-wire systems take it to the next level, impacting everything from steering and braking to throttle control. The result is often improved precision, faster response times, and a whole lot of potential for customization and computer-aided control.
Consider the old saying, “There’s more than one way to skin a cat.” Well, there’s more than one way to build a car, too. By-wire is simply a different approach, one that prioritizes electronic control and communication over purely mechanical connections. It’s a bit like moving from a typewriter to a computer — the end result is the same (words on a page/a moving vehicle), but the underlying technology is vastly different. And, hopefully, much more efficient.
Digging Deeper
2. The Tech Behind the Buzz
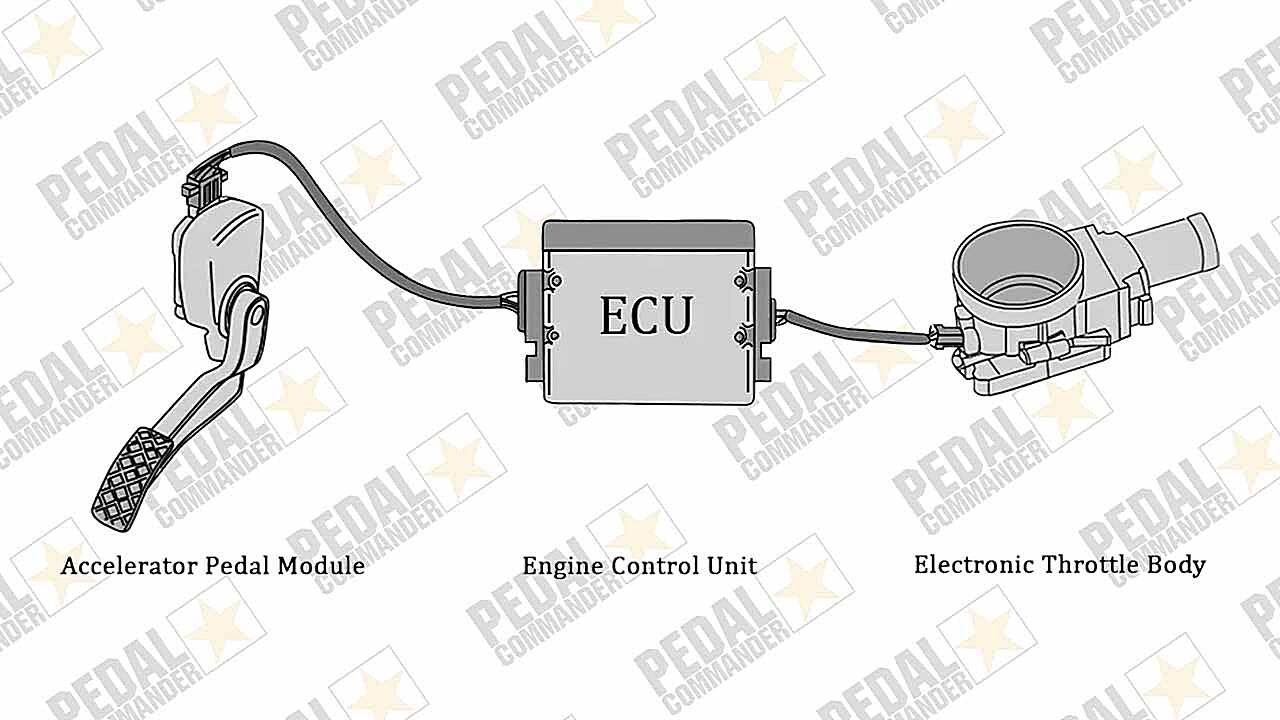
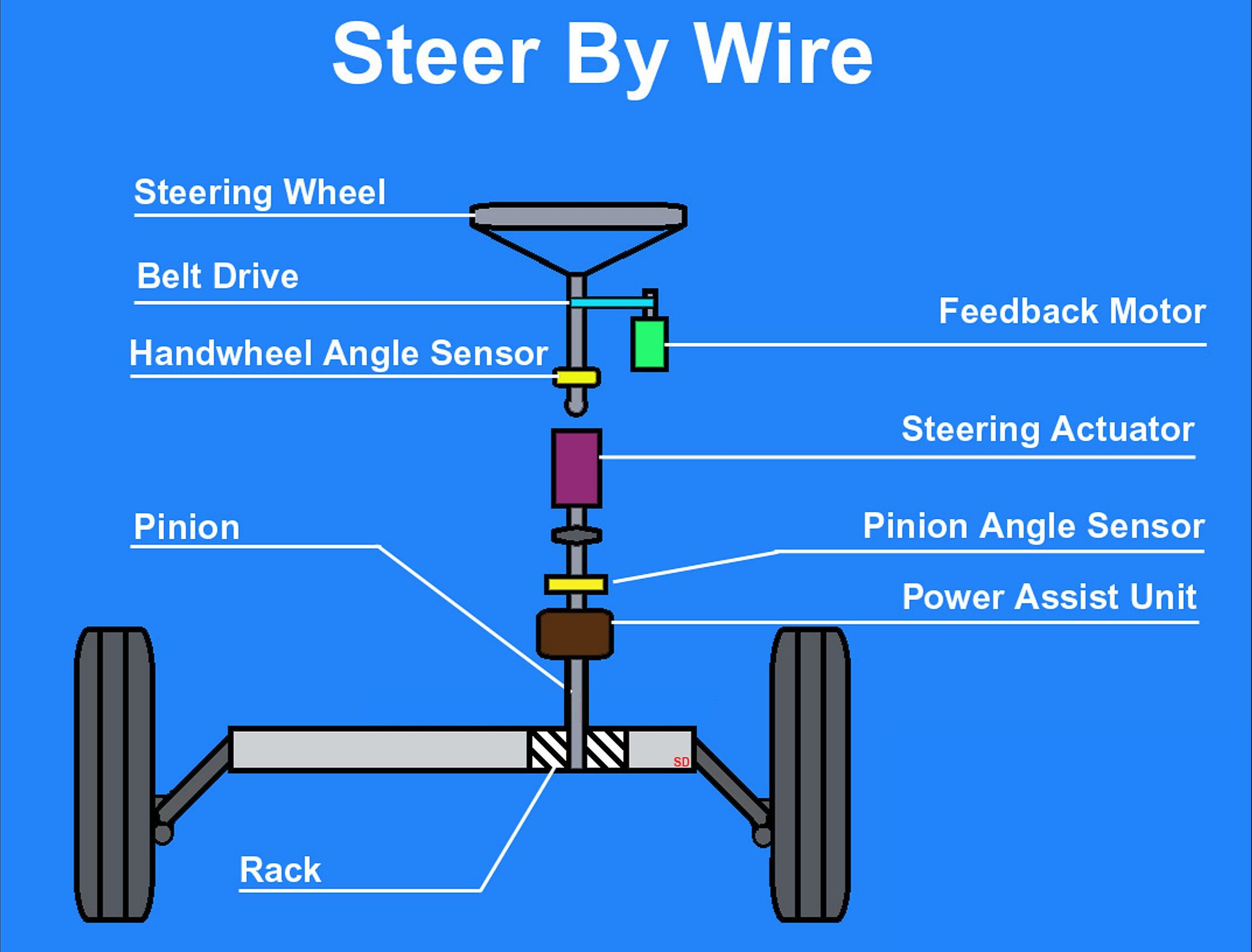
Okay, so we know it involves replacing cables with signals. But how does that actually translate into a functioning system? Let’s break it down. First, sensors monitor your actions. When you press the accelerator, the system records how much and how fast. When you turn the steering wheel, the system knows the angle and how quickly it turns. The computer receives all this data from the sensors.
Next, the car’s computer (or Electronic Control Unit — ECU) analyzes the data it receives. This is where the magic happens. The ECU isn’t just blindly relaying your inputs. It’s taking into account a whole host of factors like speed, road conditions, stability control settings, and even what mode the car is in (e.g., sport, economy, etc.). Based on all this information, it decides exactly how the car should respond.
Finally, the ECU sends commands to actuators. These are basically electric motors or other devices that directly control the car’s components. Actuators might adjust the throttle, apply the brakes, or turn the steering rack. Because everything is electronically controlled, the ECU can make incredibly precise adjustments, far faster than a human driver could. The result? A smoother, more responsive driving experience — at least, in theory!
Think of it as a highly efficient translator. You “speak” to the car through the steering wheel and pedals, and the ECU “translates” those requests into actions that the car can understand and execute. It’s not just about mimicking your movements, but about optimizing them based on a vast array of data. This allows for advanced features like traction control, stability assistance, and even semi-autonomous driving modes. But, like any good translator, it relies on accurate input and flawless execution!
The Good, the Bad, and the “Is This Thing Safe?” of By-Wire
3. Exploring the Pros and Cons
With all this talk of electronic wizardry, you might be wondering: is this actually an improvement? Like most things in life, by-wire systems come with both advantages and disadvantages. One of the biggest upsides is enhanced control and responsiveness. The computer can react much faster than a human, making adjustments to keep the car stable and safe. This can be particularly helpful in emergency situations, like when you need to brake hard or avoid an obstacle.
Another benefit is increased efficiency. By-wire systems can optimize engine performance and reduce fuel consumption. For example, the electronic throttle control can precisely manage the air-fuel mixture, leading to better mileage. Some systems also allow for adjustable steering ratios, meaning the car can be easier to maneuver at low speeds while remaining stable at high speeds.
But there are downsides, too. One of the biggest concerns is reliability. What happens if the electronics fail? Redundancy is key here, with multiple backups and fail-safe mechanisms. Still, the potential for a system failure remains a valid concern. Moreover, some drivers find by-wire systems less engaging than traditional mechanical controls. The direct feedback from the road can be muted, creating a slightly artificial feeling. This is especially true with steering, where some systems lack the tactile feedback that experienced drivers rely on.
And then there’s the learning curve. Drivers accustomed to traditional mechanical controls may need time to adjust to the feel of by-wire systems. The steering can feel lighter, the brakes more sensitive, and the throttle more responsive. It’s not necessarily a bad thing, but it does require some getting used to. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to embrace by-wire technology comes down to individual preferences and priorities. Do you value the increased control and efficiency, or do you prefer the more direct feel of traditional mechanical systems? It’s a question worth pondering.
Where Will You Find By-Wire Systems?
4. Applications Across Industries
By-wire technology isn’t limited to just cars. You’ll find it popping up in various industries, from aviation to robotics. In airplanes, fly-by-wire systems have been around for decades. They allow pilots to control aircraft with greater precision and stability, particularly in challenging conditions. Modern aircraft would be far less safe and efficient without these systems.
The maritime industry is also embracing by-wire. Ships with steer-by-wire systems can navigate more accurately and efficiently, reducing fuel consumption and improving safety. These systems are particularly useful for large vessels that require precise maneuvering in tight spaces.
Even in the world of construction and agriculture, by-wire technology is gaining traction. Heavy machinery like excavators and tractors can benefit from the increased control and precision offered by these systems. This allows operators to perform tasks more efficiently and safely.
And let’s not forget robotics! By-wire systems are essential for controlling robots that perform complex tasks in hazardous environments. Whether it’s disarming bombs or exploring deep-sea trenches, these robots rely on precise electronic control to navigate and manipulate their surroundings. So, the next time you see a robot doing something amazing, remember that it’s likely powered by by-wire technology.
By-Wire’s Future
5. Innovation and Evolution
What does the future hold for by-wire technology? The sky’s the limit! As computers become more powerful and sensors become more sophisticated, we can expect even greater advancements in this field. One area of focus is improving the reliability and safety of these systems. Redundancy will become even more important, with multiple backup systems to ensure that a single failure doesn’t compromise the entire vehicle. Artificial intelligence can also be integrated into this for much safer experience
Another trend is increased customization. By-wire systems allow for a greater degree of personalization than traditional mechanical controls. Drivers will be able to adjust the steering feel, throttle response, and brake sensitivity to suit their individual preferences. This could even extend to creating entirely different driving modes for different situations, like a “track mode” for performance driving or a “comfort mode” for long road trips.
And then there’s the potential for even greater integration with autonomous driving systems. By-wire technology is a key enabler of self-driving cars, allowing the computer to control all aspects of the vehicle. As autonomous driving becomes more prevalent, by-wire systems will become even more ubiquitous.
It’s also worth thinking about how by-wire might impact vehicle design. Without the need for mechanical linkages, engineers will have greater freedom to design more aerodynamic and efficient vehicles. This could lead to radical changes in the shape and layout of cars, trucks, and other machines. So, keep an eye on this space — the future of by-wire is sure to be exciting!