Decoding the Mystery
1. What’s the Deal with Single-Phase AC?
Okay, let’s cut to the chase: Yes, single-phase AC (Alternating Current) absolutely exists! It’s not some mythical creature lurking in the electrical shadows. In fact, it’s probably powering a good chunk of the devices you’re using right now. Think of it as the workhorse of residential electricity, diligently keeping your lights on and your coffee brewing.
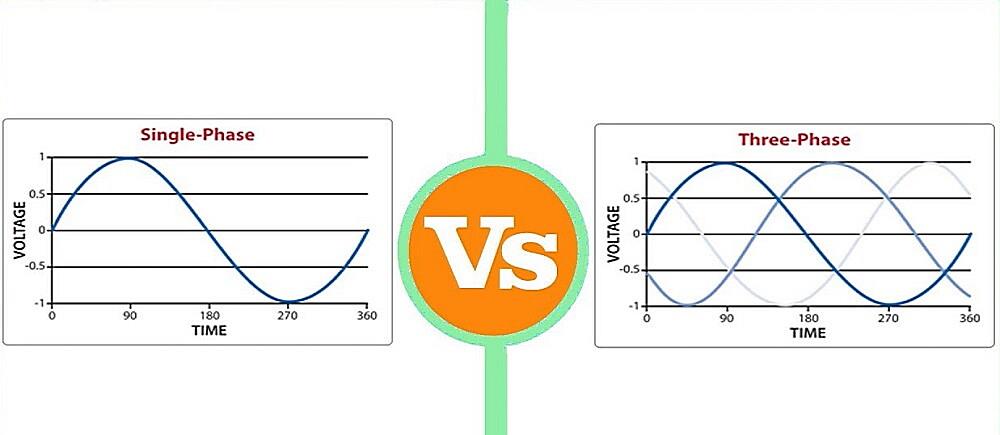
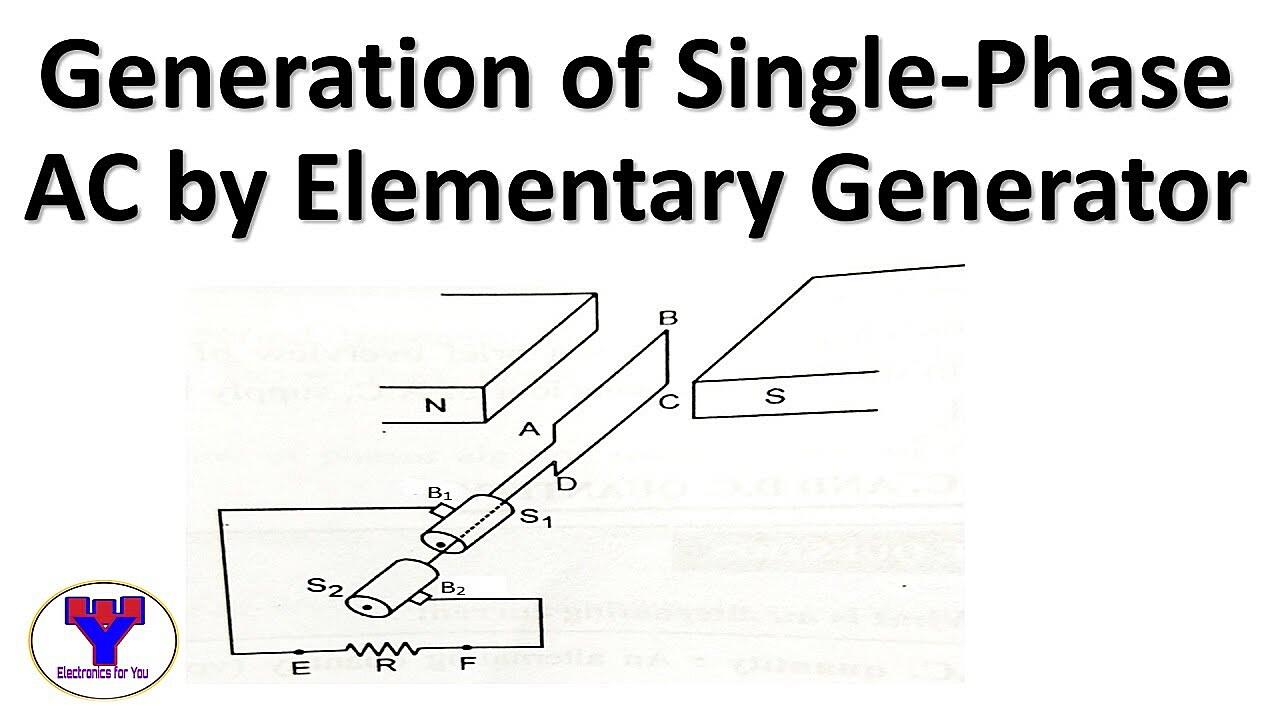
But what is it, really? Imagine electricity flowing like a wave, oscillating back and forth. Single-phase AC is like a lone surfer riding that wave. It has one single voltage wave that fluctuates in magnitude. This simpler setup is perfect for powering homes and small businesses where the power demands aren’t too extreme. Were not talking about running entire factories here, just keeping things humming along nicely.
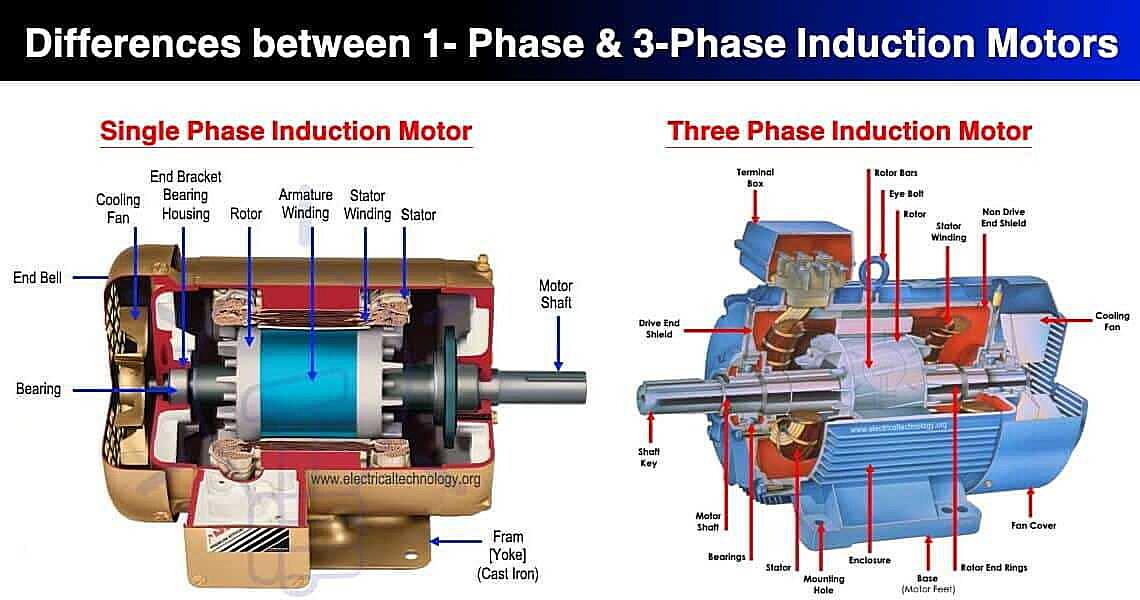
Compared to its beefier cousin, three-phase AC, single-phase is a bit more shall we say polite? Three-phase is like a team of synchronized surfers, delivering a smoother and more consistent power flow. This makes it ideal for industrial applications with high-power machinery. Think giant motors and heavy-duty equipment that need a steady diet of electrical energy. Single-phase AC is more than capable for powering things like lights, computers, refrigerators, and other smaller appliances you’d find at home.
So, next time you flip a light switch, remember the unsung hero that is single-phase AC. It’s the silent partner that keeps your modern life running smoothly. Its efficient, affordable, and perfect for most everyday needs. Who knew electricity could be so relatable?
Peeking Behind the Electrical Curtain
2. The Inner Workings of a Single-Phase System
Alright, let’s dive a little deeper without getting too bogged down in technical jargon. How does this single-phase magic actually happen? It all starts at the power source, typically a transformer that steps down the high-voltage electricity from the power grid to a usable level for homes and businesses (usually around 120V or 240V depending on where you live).
This transformer essentially creates the single alternating current, a sine wave, if you want to get technical. This wave cycles between positive and negative voltage at a certain frequency, commonly 60 Hz in North America and 50 Hz in Europe. This means the current changes direction 60 or 50 times per second! It’s like a tiny electrical dance party happening inside your walls.
From the transformer, the electricity flows through two wires: the “hot” wire, which carries the current, and the “neutral” wire, which provides the return path. When you plug in an appliance, the electricity flows from the hot wire, through the appliance to power it, and then back to the neutral wire, completing the circuit. The size of the wire and circuit breaker will determine what will affect the voltage, this is also called voltage drop.
It’s a fairly simple system, elegant in its efficiency. While it might not be able to power the biggest, baddest industrial machines, its more than capable of handling most household and small business needs. Plus, it’s relatively inexpensive to install and maintain, which is always a bonus, right?
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase
3. Choosing the Right Phase for the Job
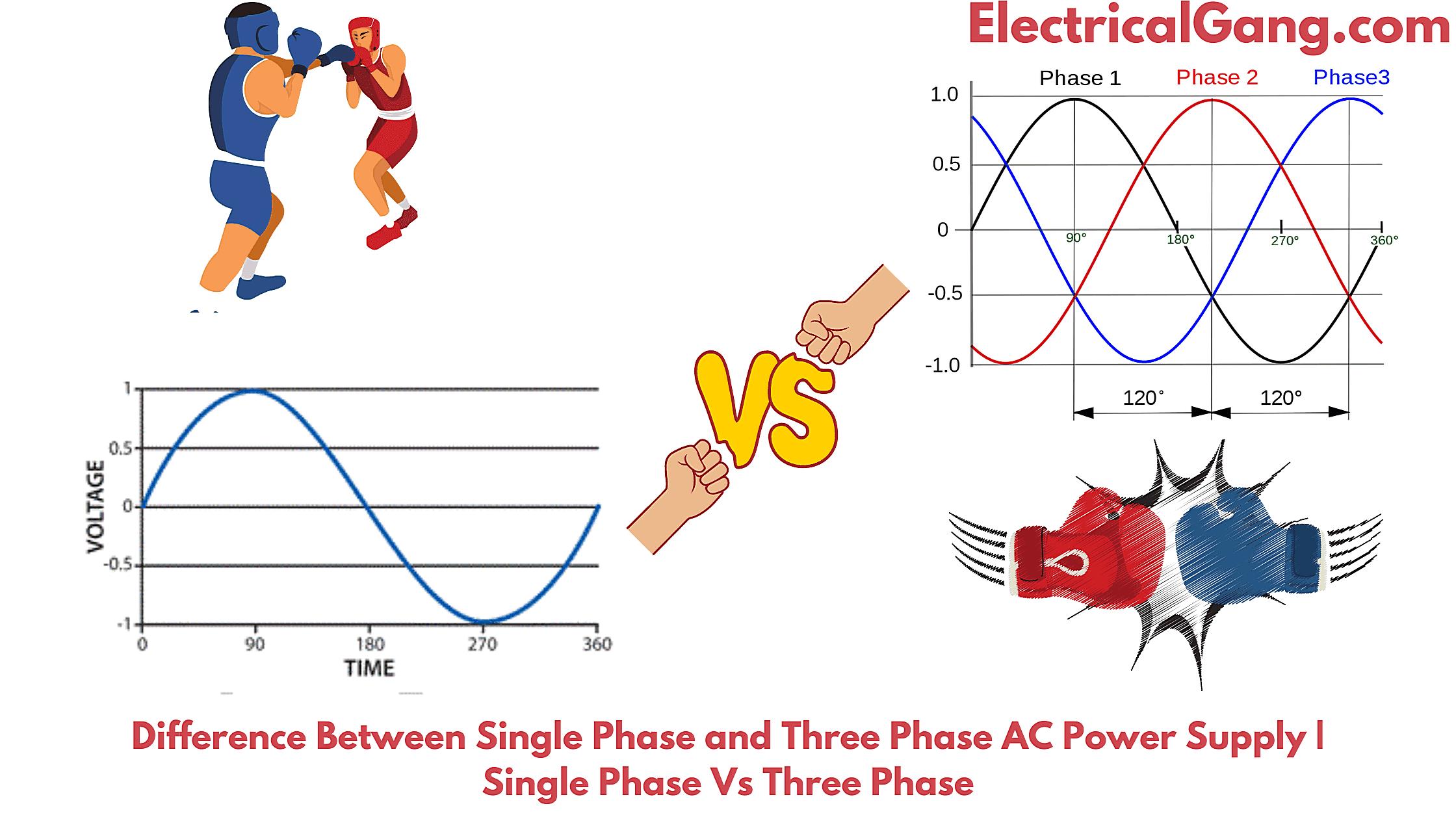
Now that we know single-phase AC exists and how it works, let’s pit it against its more powerful sibling, three-phase AC. It’s not exactly a rivalry, more like choosing the right tool for the right job. Single-phase is the trusty screwdriver in your toolbox, while three-phase is the power drill that can bore through anything.
The main difference lies in the number of voltage waves. Single-phase has, well, one. Three-phase, as the name suggests, has three. These three waves are offset from each other, creating a more consistent and powerful flow of electricity. This makes three-phase ideal for applications that require high power and torque, like large motors in factories, industrial equipment, and even some commercial HVAC systems.
Imagine trying to start a heavy engine. Single-phase might struggle, but three-phase can crank it right up with its extra oomph. However, for most homes and small businesses, the extra power of three-phase is simply overkill. It’s more expensive to install and requires more complex wiring and equipment. Plus, you probably don’t need to power a giant metal-stamping machine in your living room.
The decision boils down to power requirements and cost. If you’re running a factory, three-phase is the clear winner. But for everyday needs, single-phase is the more practical and affordable choice. It’s like choosing between a pickup truck and a sedan — both get you where you need to go, but one is better suited for hauling heavy loads, while the other is more efficient for daily commutes.
Spotting Single-Phase AC in the Wild
4. Everyday Applications of Single-Phase AC
So, where exactly do you encounter single-phase AC in your everyday life? The answer is pretty much everywhere! It’s the invisible force powering a vast array of appliances and devices in homes, offices, and small businesses.
Think about your kitchen. Your refrigerator, microwave, coffee maker, toaster, and blender all run on single-phase AC. Same goes for your living room TV, computer, and gaming console. Even your lighting system is powered by the same source.
Beyond the home, single-phase AC is also used in many small businesses to power computers, cash registers, lighting, and other essential equipment. It’s the backbone of their electrical infrastructure, ensuring everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
In essence, single-phase AC is the unsung hero of modern life. It’s so ubiquitous that we often take it for granted, but without it, our lives would be a lot darker, quieter, and less connected. So, next time you plug in your phone, take a moment to appreciate the humble yet mighty single-phase AC at work.
Troubleshooting Single-Phase AC Problems
5. When Single-Phase Systems Go Wrong
Even the most reliable electrical systems can sometimes experience problems, and single-phase AC is no exception. But don’t panic! Most common issues are relatively easy to diagnose and fix, although safety should always be your top priority. If you’re not comfortable working with electricity, always call a qualified electrician.
One common problem is tripped circuit breakers. This usually happens when you overload a circuit by plugging too many appliances into the same outlet or running high-power devices simultaneously. The solution is simple: unplug some devices and reset the breaker. If the breaker keeps tripping, you may need to redistribute the load or have an electrician check the circuit.
Another potential issue is voltage drops, which can cause lights to dim or appliances to malfunction. This can be caused by long wire runs, undersized wiring, or a heavy electrical load on the circuit. An electrician can help diagnose the cause and recommend solutions, such as upgrading the wiring or adding a dedicated circuit.
Finally, faulty wiring or connections can also cause problems. Look for signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or burnt outlets. Again, if you’re not comfortable working with electricity, call a professional. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more serious problems, such as electrical fires.
FAQ About Single-Phase AC
6. Q
A: Like any electrical system, single-phase AC can be dangerous if not handled properly. Always follow safety precautions and consult a qualified electrician for any electrical work. Avoid overloading circuits and make sure all wiring and connections are in good condition.
7. Q
A: Yes, it’s possible to convert single-phase to three-phase AC using a device called a rotary phase converter or a static phase converter. However, these converters can be expensive and may not be suitable for all applications. It’s best to consult an electrician to determine the best solution for your specific needs.
8. Q
A: In North America, the standard voltage for single-phase AC in homes is typically 120V for lighting and small appliances, and 240V for larger appliances like stoves, dryers, and air conditioners. In Europe and other parts of the world, 230V is a common voltage.