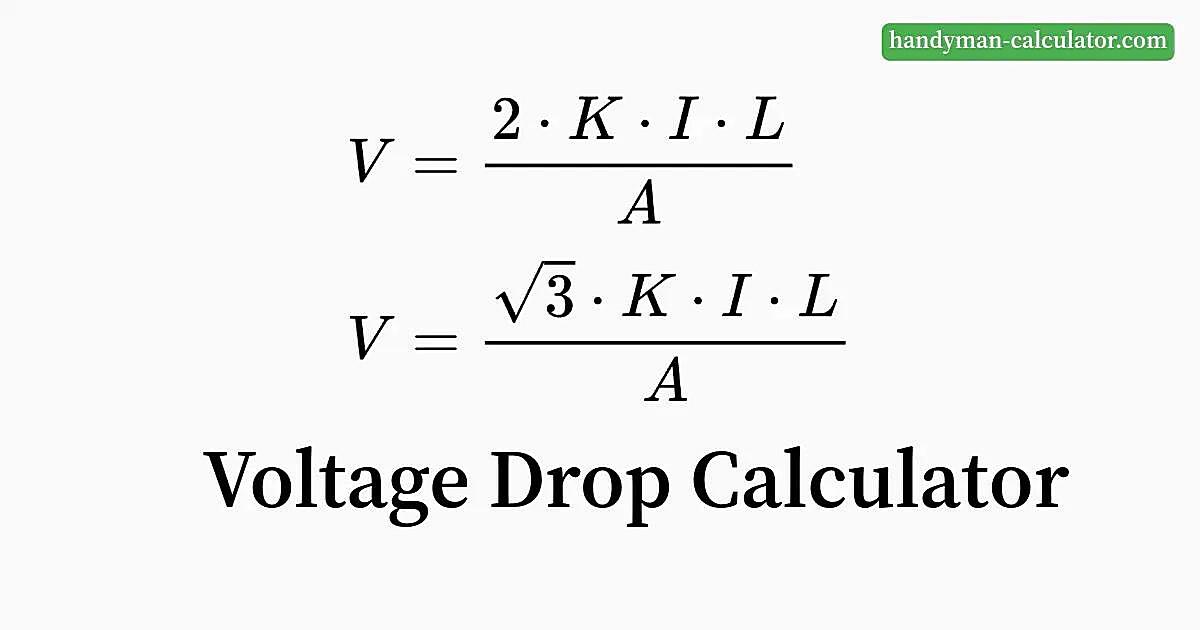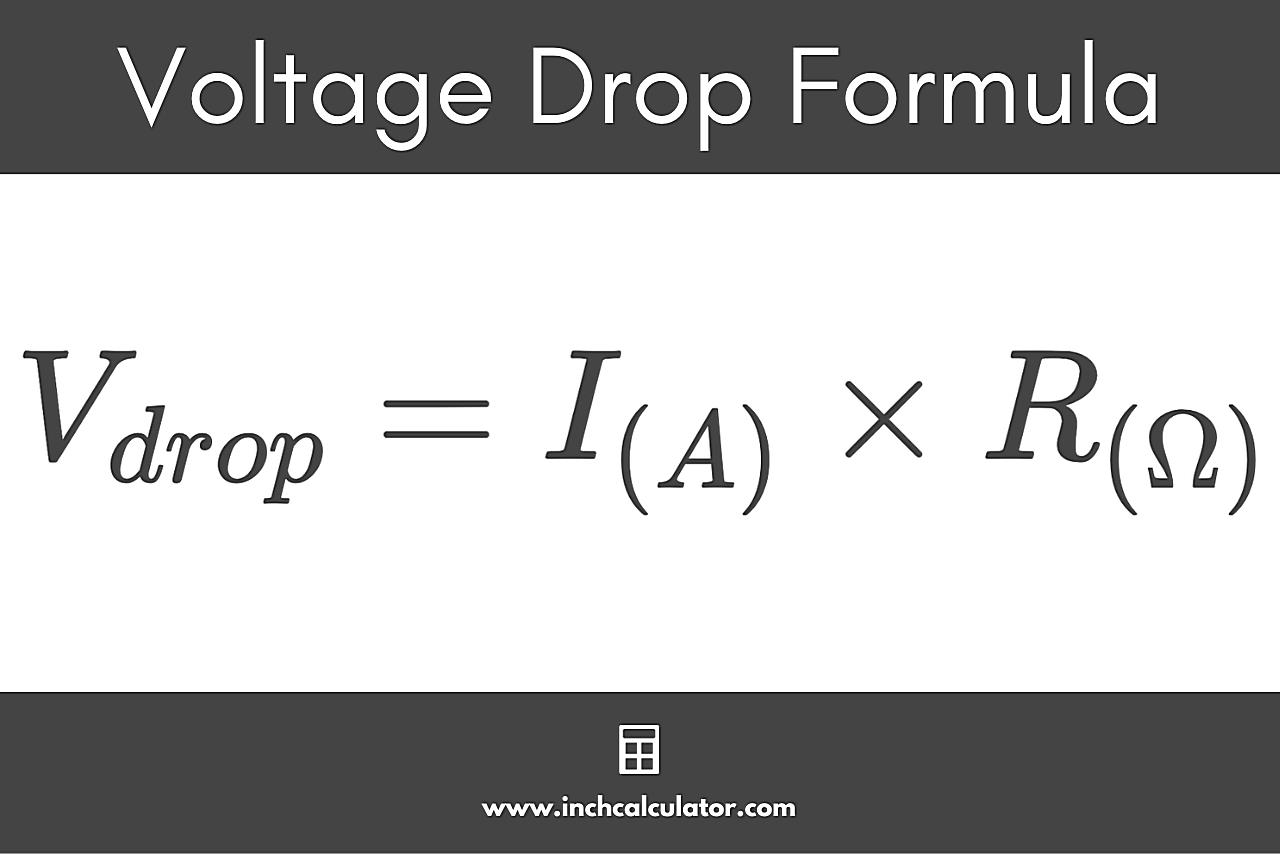Understanding Voltage Drop
1. What’s the Big Deal with Voltage Drop Anyway?
Alright, let’s talk electricity. It’s not exactly the most thrilling subject, but understanding voltage drop is actually pretty crucial if you’re messing with electrical circuits, whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a seasoned electrician. Think of voltage like water pressure in a pipe. If the pressure drops too much, things just don’t work as efficiently, right? Light bulbs dim, motors run sluggishly, and your favorite gadgets might just throw a tantrum and refuse to cooperate. And nobody wants grumpy gadgets.
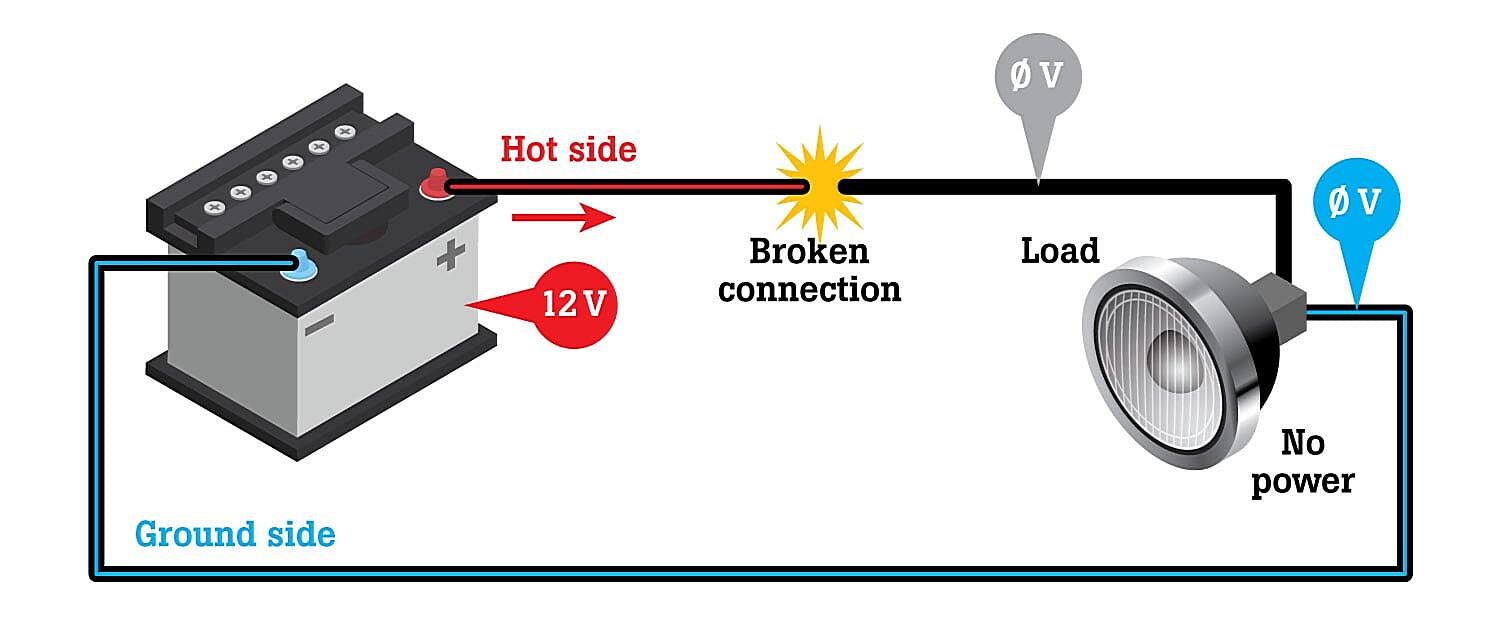
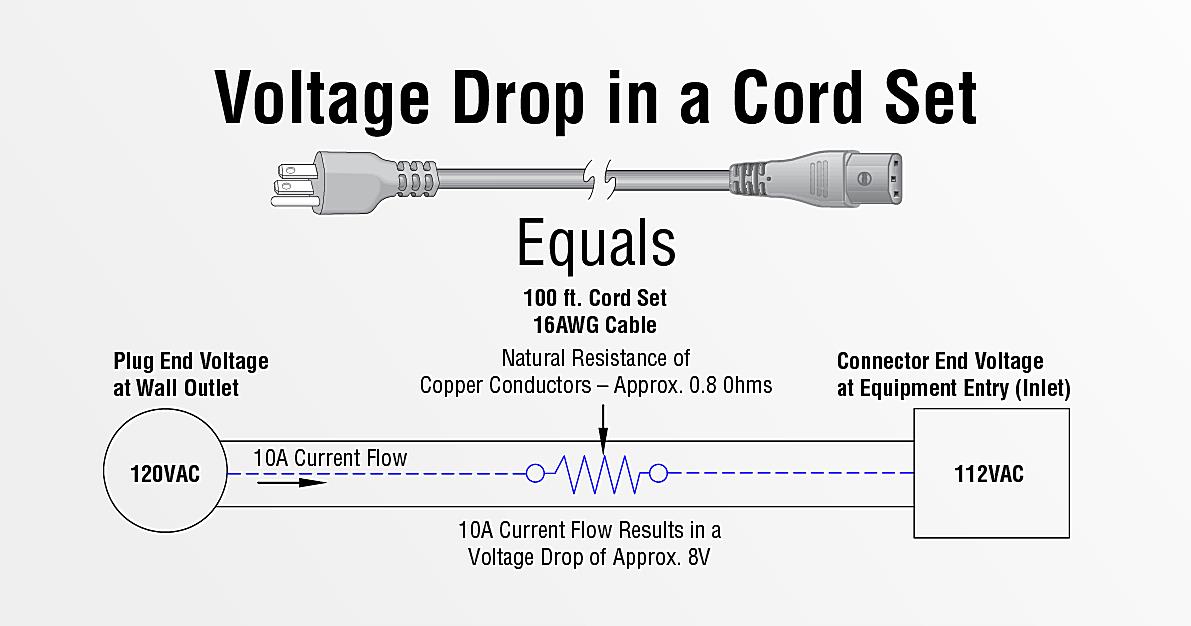
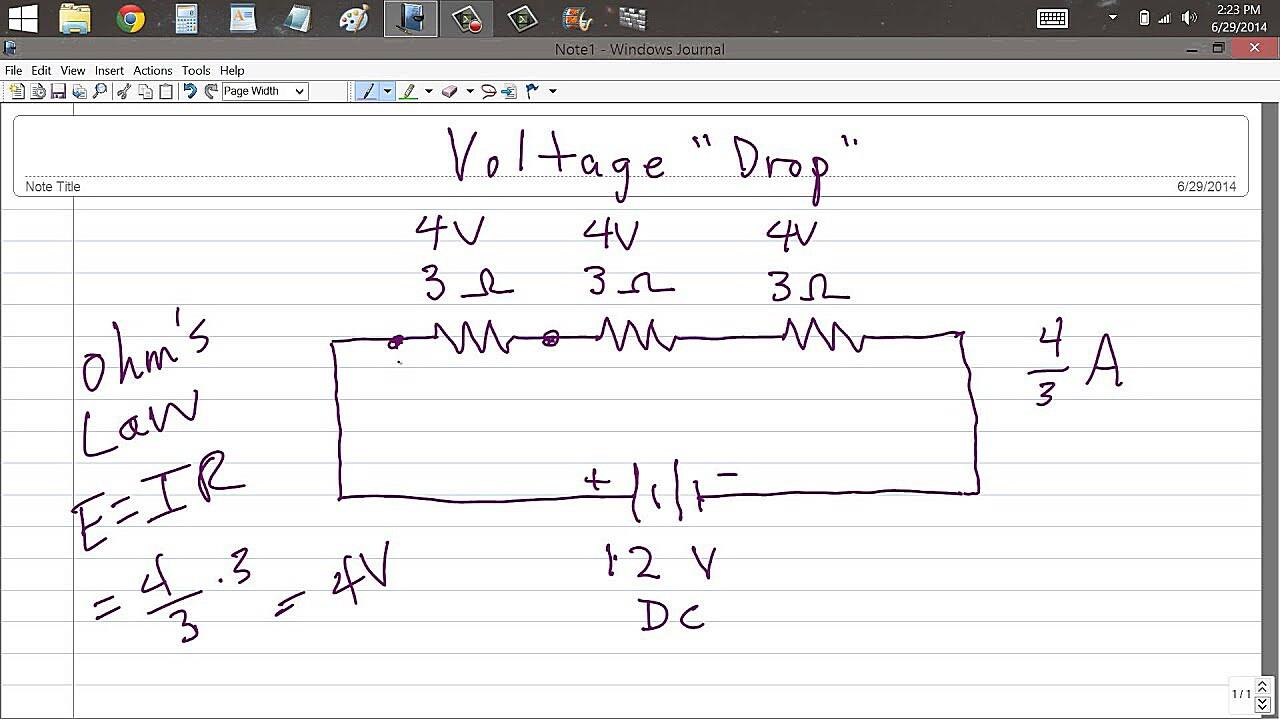
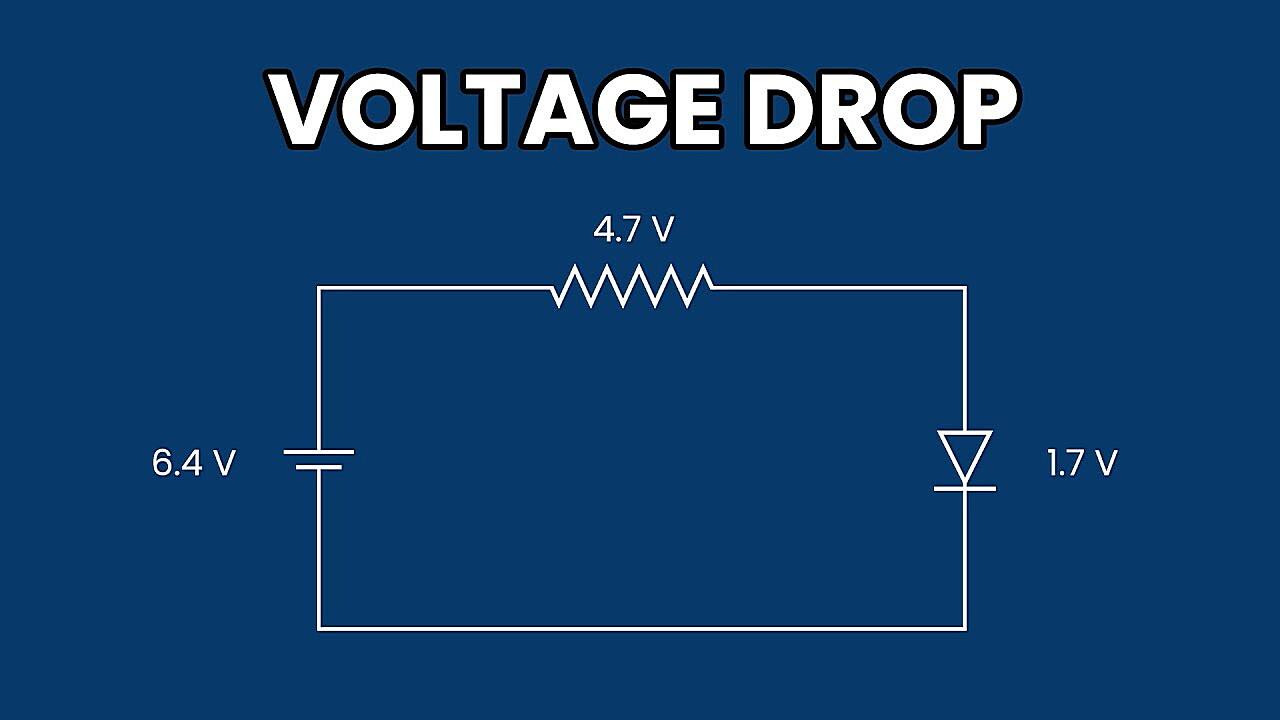
Voltage drop is simply the reduction in voltage that occurs as electrical current flows through a conductor. It’s like when you try to drink through a really long straw — the farther the liquid has to travel, the harder you have to suck. Electrical conductors have resistance, which impedes the flow of current and causes some of the voltage to be “lost” along the way. This loss is what we call voltage drop. Factors that influence voltage drop include the length of the wire, the gauge of the wire (its thickness), the amount of current flowing through it, and the material the wire is made of.
Now, why do we even care? Well, excessive voltage drop can lead to all sorts of problems. As mentioned, lights dim, motors underperform, and appliances might not work correctly. In more extreme cases, it can even damage equipment or create a fire hazard. Maintaining the correct voltage at the point of use ensures optimal performance and safety. Plus, if you’re running a business, consistent voltage translates to consistent operation, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Think of it as keeping your electrical arteries clear and flowing smoothly.
So, while it might sound technical and a bit boring, understanding voltage drop is fundamental for anyone working with electrical systems. It’s about ensuring your circuits run efficiently, your appliances work properly, and, most importantly, that everything is safe. Let’s dive deeper into that 6% figure and see where it fits into all of this.
Is 6% Voltage Drop Okay? A Deeper Dive
2. The Permissible Percentage
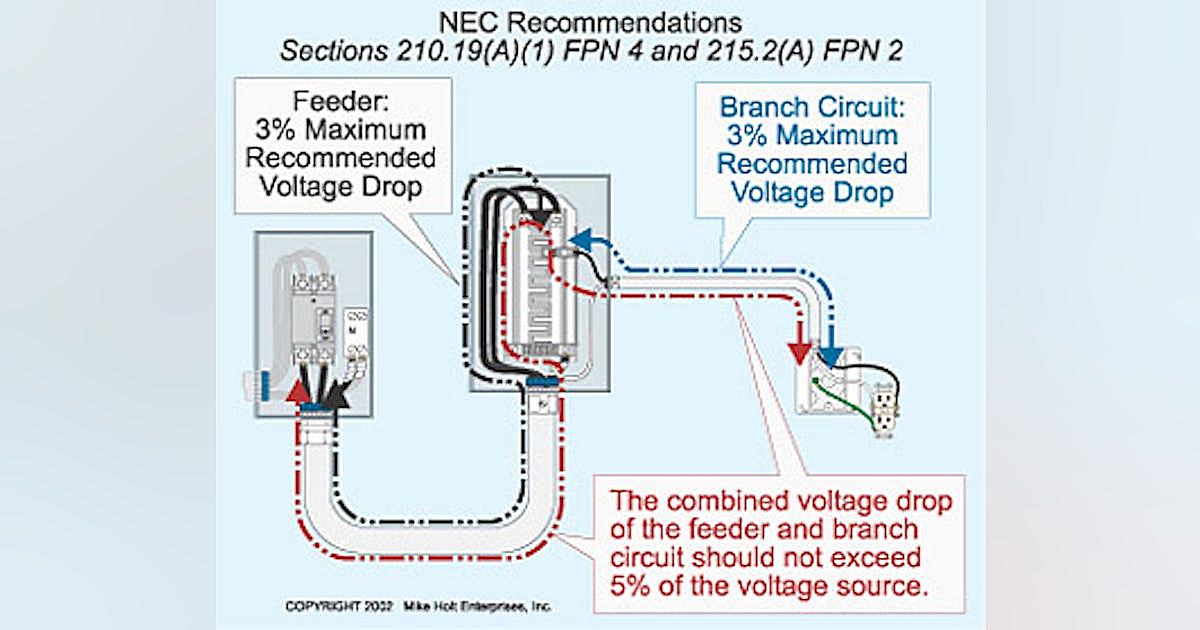
Okay, let’s get to the heart of the matter: “Is 6% voltage drop okay?” The short answer is: it depends. But that’s not a very helpful answer, is it? Generally, the accepted standard for voltage drop in branch circuits (the wires running to outlets, lights, etc.) is 3% for lighting and 5% for power, with a maximum total voltage drop of 5% to the furthest outlet. So, 6% exceeds the common recommended limit.
Why these numbers? These recommendations are based on ensuring that equipment operates within its designed voltage range. Most appliances and devices are designed to work optimally within a certain voltage range. A voltage drop exceeding these limits can cause them to function inefficiently or even damage them over time. Consider it like trying to run a car on low tire pressure — it’ll still move, but it won’t be as efficient, and you risk damaging the tires.
However, there are exceptions. For example, some specific types of equipment might have different voltage tolerance requirements. Also, local electrical codes can vary, so it’s essential to check the specific regulations in your area. This is where consulting a qualified electrician becomes invaluable. They can assess your specific situation and provide tailored recommendations. They are also up-to-date on local codes.
Therefore, while 6% might seem like a small number, it’s generally not considered acceptable based on common standards. While slightly exceeding the limit won’t necessarily cause immediate disaster, it can lead to long-term problems and should be addressed if possible. Lets see what options you might have to fix it.
What Happens When Voltage Drop is Too High?
3. The Consequences of Excessive Voltage Loss
So, what happens when you ignore that pesky voltage drop and let it creep beyond the recommended limits? The consequences can range from mildly annoying to downright dangerous. Let’s break down some of the common issues.
Firstly, you’ll likely notice performance degradation in your electrical equipment. Lights will dim, motors will run slower and hotter, and sensitive electronics might malfunction. Imagine your refrigerator struggling to maintain temperature, leading to spoiled food, or your air conditioner not cooling as effectively on a hot day. That is all due to insufficient voltage causing them to struggle.
Secondly, excessive voltage drop can lead to increased energy consumption and higher electricity bills. When equipment isn’t operating at its optimal voltage, it has to work harder to achieve the same output, which translates to more energy being used. Think of it like a car constantly driving uphill; it’ll burn through more fuel than if it were driving on a flat road.
Thirdly, and perhaps most concerningly, high voltage drop can create a fire hazard. Over time, wires can overheat due to the increased current draw caused by insufficient voltage. This overheating can damage insulation, leading to short circuits and, in the worst-case scenario, electrical fires. Its not worth risking for a bit of savings!
In short, ignoring excessive voltage drop is a recipe for trouble. It can lead to equipment damage, increased energy costs, and potentially dangerous situations. Addressing it promptly is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your electrical system.
How to Fix Excessive Voltage Drop
4. Practical Solutions for Voltage Drop Problems
Alright, so you’ve determined that you have excessive voltage drop. Don’t panic! There are several solutions you can implement to address the issue. Let’s explore some of the most common and effective methods.
First, consider increasing the wire size. Using a thicker wire (lower gauge number) reduces resistance and allows more current to flow with less voltage drop. This is often the simplest and most effective solution, especially if you’re dealing with long runs of wire. Its like using a bigger pipe for better water flow.
Second, shorten the wire run if possible. The longer the wire, the greater the voltage drop. If you can relocate the electrical panel or move the appliance closer to the power source, you can significantly reduce the voltage drop. Sometimes, a simple repositioning can make a big difference.
Third, reduce the load on the circuit. If you’re running multiple high-power appliances on the same circuit, consider distributing the load across different circuits. This will reduce the amount of current flowing through any one wire, minimizing voltage drop. It’s like sharing the workload to avoid overloading a single worker.
Fourth, ensure all connections are clean and tight. Loose or corroded connections can increase resistance and contribute to voltage drop. Regularly inspect and tighten all connections to ensure a good electrical pathway. This is a simple maintenance task that can prevent a multitude of problems. Finally, consulting with a qualified electrician is always a good idea. They can assess your specific situation and recommend the most appropriate solution based on your needs and local electrical codes.
Voltage Drop Calculators and Resources
5. Tools and Assistance for Accurate Measurement
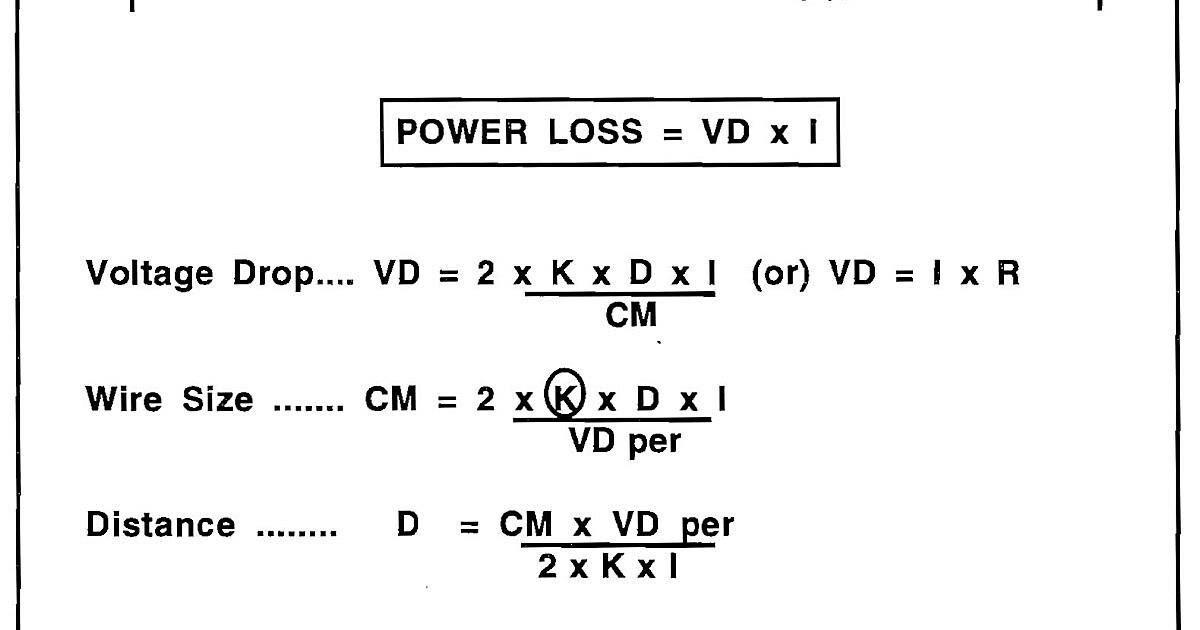
Calculating voltage drop can seem daunting, but thankfully, there are many tools and resources available to make the process easier. Online voltage drop calculators are a great starting point. These calculators typically require you to input information such as wire gauge, wire length, current, and voltage to estimate the voltage drop.
Several websites and apps offer free voltage drop calculators, making it easy to quickly assess your situation. These calculators can provide a good estimate, but it’s essential to remember that they are based on ideal conditions. Real-world factors, such as temperature and wire insulation, can affect the actual voltage drop.
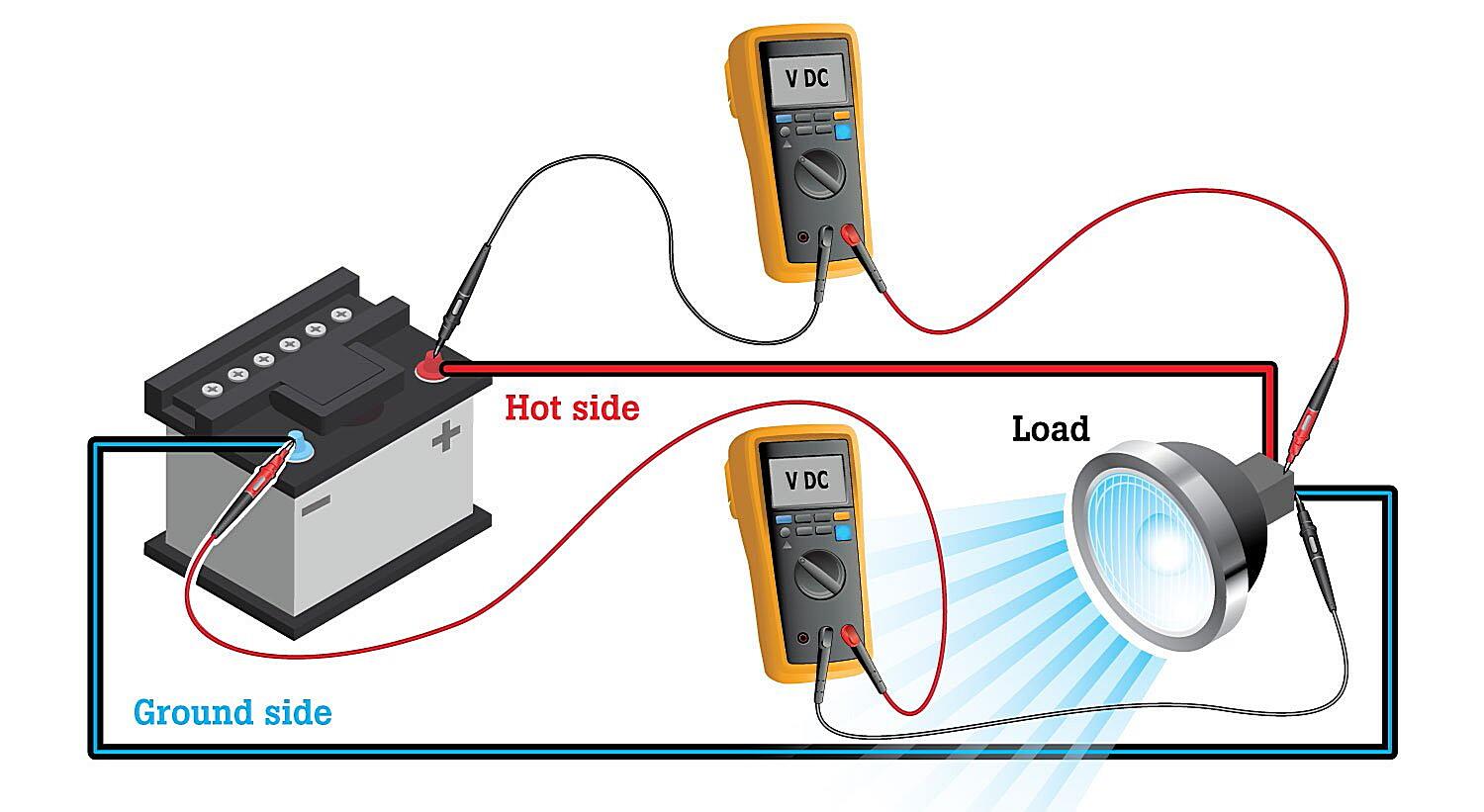
In addition to online calculators, there are also specialized tools, such as multimeters and voltage testers, that can be used to measure voltage drop directly. These tools can provide more accurate readings and are particularly useful for troubleshooting existing circuits. A multimeter allows you to measure voltage at different points in the circuit to determine where the voltage drop is occurring.
Ultimately, while online tools and calculators can be helpful, the best approach is often to consult with a qualified electrician. They have the knowledge and experience to accurately assess your electrical system, identify potential problems, and recommend the most appropriate solutions. They can also ensure that all work is done safely and in compliance with local electrical codes. So, while you can certainly do some research and calculations on your own, don’t hesitate to call in the professionals when needed.
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still have some questions about voltage drop? Here are a few frequently asked questions to help clear things up.
7. Q
A: While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, “voltage drop” generally refers to the expected and calculated reduction in voltage due to wire resistance. “Voltage loss” can refer to other voltage reductions due to factors like faulty connections or damaged components.
8. Q
A: Yes, excessive voltage drop can definitely contribute to appliance failure. When appliances don’t receive the proper voltage, they have to work harder, generating more heat and potentially damaging internal components over time. Think of it as constantly pushing your car to its limit — eventually, something will break.
9. Q
A: While a very small amount of voltage drop might not cause immediate problems, it’s generally best to address even minor voltage drops. Over time, even small reductions in voltage can lead to inefficiencies and potential equipment damage. It’s like ignoring a small leak in your roof — it might not seem like a big deal at first, but it can lead to significant problems down the road.
10. Q
A: Absolutely. Although LEDs are energy-efficient, they still require a specific voltage to operate correctly. Excessive voltage drop can cause LEDs to dim, flicker, or even fail prematurely. Ensuring proper voltage is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of your LED lighting.