Unlocking the Mystery
1. Understanding Electrical Configurations
Ever stared at an electrical panel and felt a bit like you were deciphering hieroglyphics? You’re not alone! Electricity, while powering our lives, can seem like a complex beast. One common question that pops up, especially when dealing with higher voltage systems, is whether a 240V setup is “delta” or “wye.” Let’s untangle this electrical enigma, shall we?
Think of “delta” and “wye” as two different ways to wire up a three-phase electrical system. They’re like different recipes for the same dish—both result in power, but they have different characteristics. The key difference lies in how the transformer windings are connected.
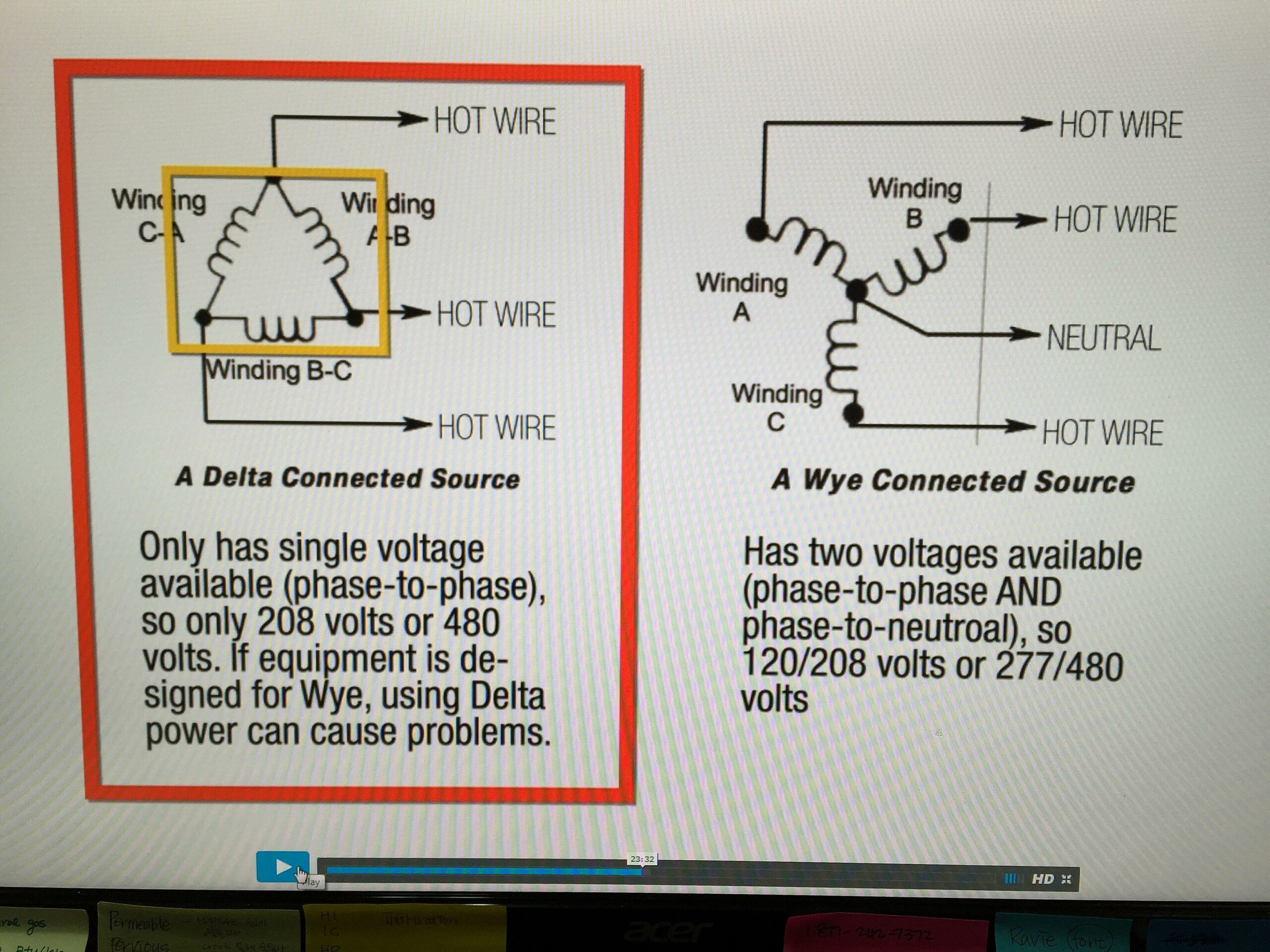
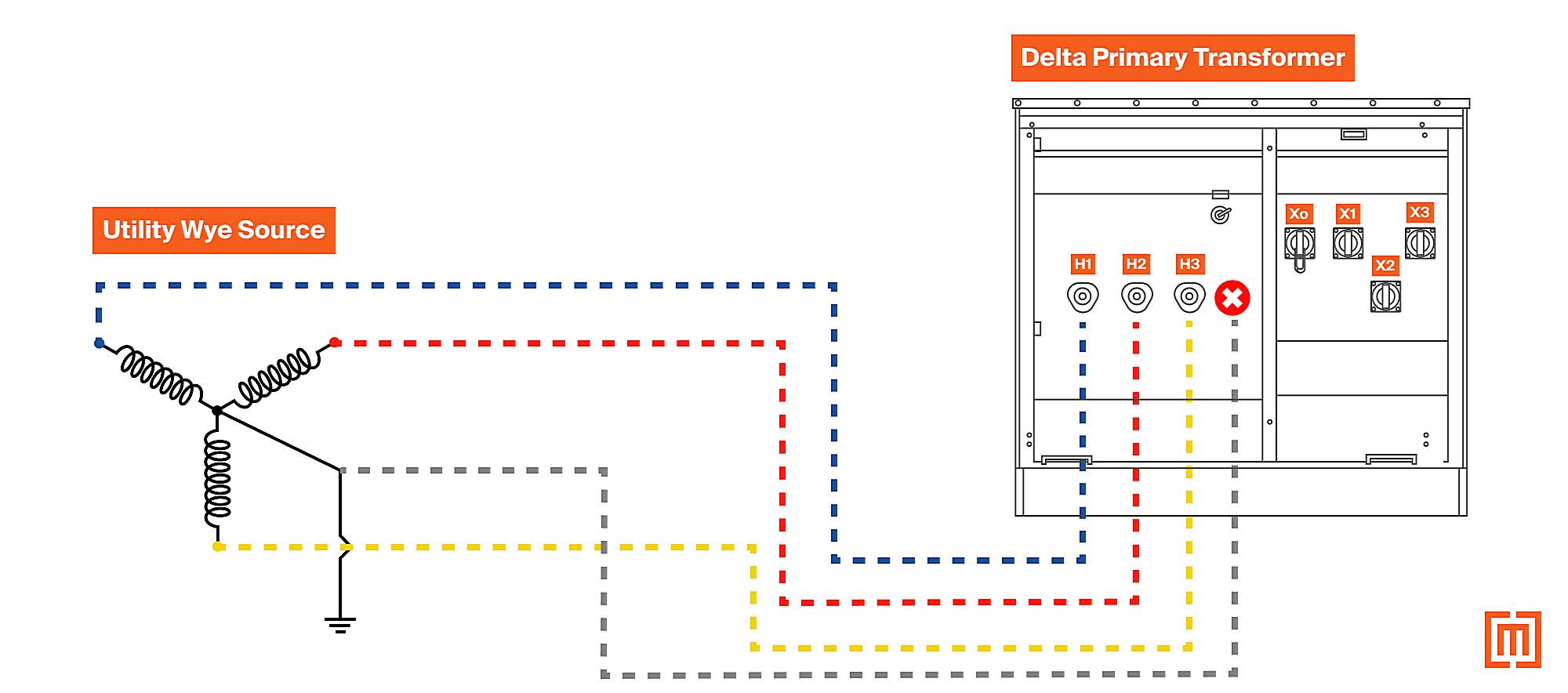
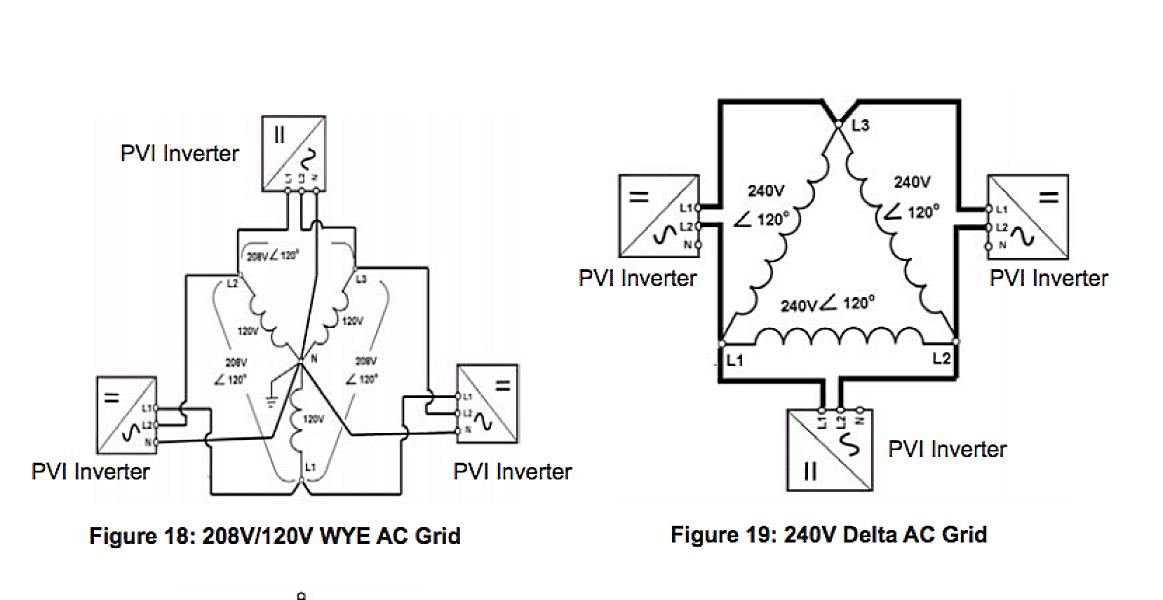
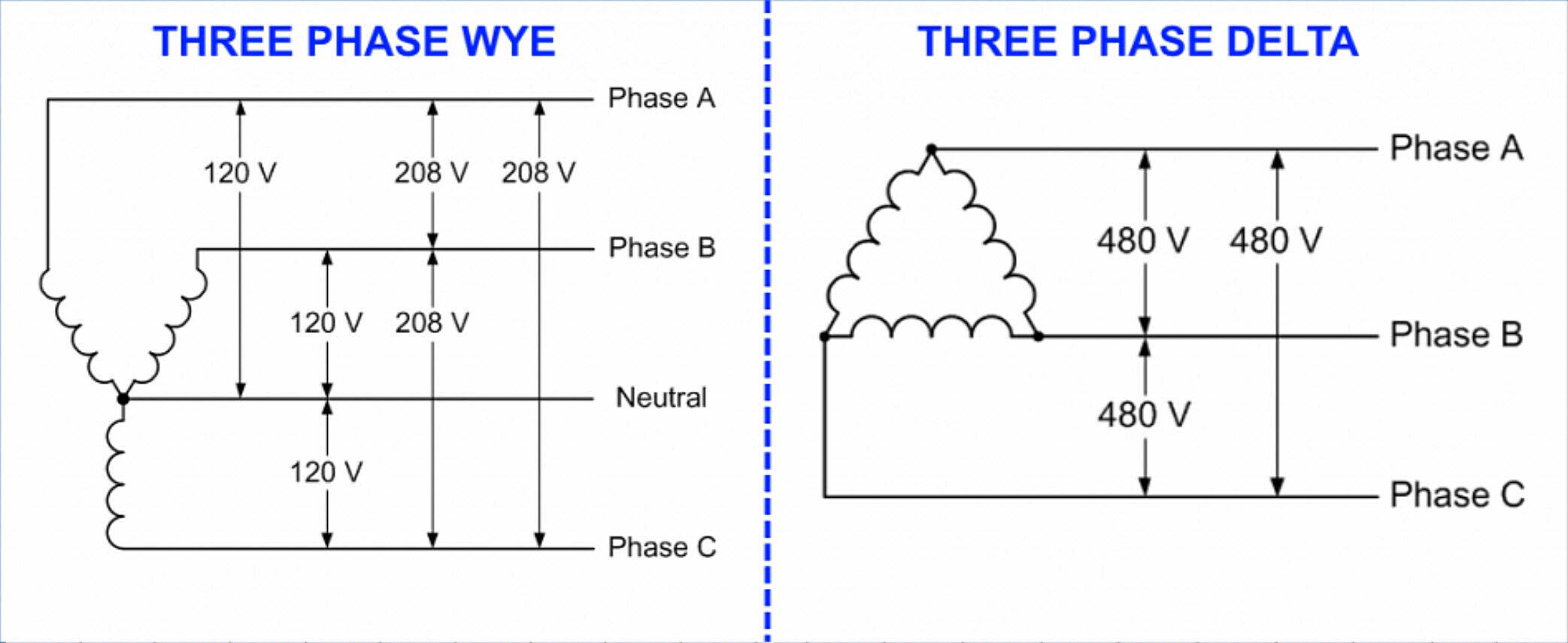
Imagine a triangle (that’s your delta!). In a delta configuration, the three windings are connected in a closed loop, forming this triangular shape. There’s no neutral point in a pure delta system. Now picture a “Y” shape (that’s your wye!). In a wye configuration, the three windings are connected to a common neutral point, resembling the letter “Y.”
Why does this matter? Well, the configuration affects the voltage relationships and the availability of a neutral connection. This, in turn, influences how the system can be used to power different types of loads.
Spotting the Difference
2. Clues to Look For
Okay, so how can you tell if your 240V system is delta or wye? Unfortunately, it’s not always printed right on the panel. You’ll have to do a little detective work. One of the easiest clues is the presence (or absence) of a neutral wire. Wye systems always have a neutral, while delta systems typically don’t—though there are exceptions like a corner-grounded delta.
Another telltale sign is the voltage you measure between different points. In a 240V delta system, you’ll generally find 240V between any two of the three phases. In a 240V wye system, you’ll usually find 240V between the phases, but you’ll also find 120V from each phase to the neutral. This 120V is what allows you to power standard household appliances.
Carefully examine the wiring. If you see three wires coming in (excluding the ground), it could be a delta system, but don’t jump to conclusions! If you see four wires (three phases and a neutral), it’s almost certainly a wye system. Remember, safety first! Never poke around inside an electrical panel unless you’re a qualified electrician.
When in doubt, the safest and smartest thing to do is consult a licensed electrician. They have the tools and expertise to properly identify the system and avoid any potential hazards. Electricity is not something to mess around with!
Why the Configuration Matters
3. Weighing the Pros and Cons
Each configuration has its strengths and weaknesses. Delta systems, for instance, are often preferred in industrial settings where heavy motor loads are common. They can handle unbalanced loads somewhat better than wye systems in certain scenarios. Plus, a delta system can continue to operate (though at reduced capacity) even if one of the phases fails—a feature known as “open delta” or “V-phase.”
4. Advantage Delta
Delta configured transformers offers a higher level of redundancy. If one transformer in a delta bank fails, the other two can continue to provide power at a reduced capacity. This is known as an open-delta configuration, and it can be a valuable feature for critical loads that cannot tolerate interruptions.
5. Disadvantage Delta
Delta systems do not have a neutral point, which means they cannot supply single-phase loads. This makes them unsuitable for residential applications where single-phase loads are common.
Wye systems, on the other hand, are more versatile because they provide both 240V (between phases) and 120V (from phase to neutral). This makes them ideal for residential and commercial buildings where a mix of lighting, appliances, and equipment needs to be powered. They’re also generally more efficient than delta systems when dealing with balanced loads.
6. Advantage Wye
Wye systems offer greater flexibility in terms of voltage options. They can supply both single-phase and three-phase loads, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Additionally, Wye systems typically have lower voltage stress on insulation compared to Delta systems, leading to longer equipment life.
7. Disadvantage Wye
Wye configured transformers are more susceptible to voltage imbalances caused by unbalanced loads. This can lead to overheating and premature failure of the transformer. Additionally, Wye systems do not offer the same level of redundancy as Delta systems. If one transformer in a Wye bank fails, the entire system may be interrupted.
However, wye systems are more susceptible to voltage imbalances caused by uneven loads. So, the “best” configuration really depends on the specific application and the type of loads being powered.
The 240V Misconception
8. Debunking the Myth
A common misconception is that 240V implies a specific configuration. It doesn’t! The voltage rating simply tells you the potential difference between the conductors. A 240V system can be either delta or wye. The voltage is just one piece of the puzzle; the configuration determines how that voltage is delivered and how it can be used.
Think of it like buying a car. You might say, “I want a car that can go 60 miles per hour.” That doesn’t tell you whether you’re buying a sports car, a sedan, or an SUV. Similarly, specifying 240V doesn’t tell you whether you’re dealing with a delta or wye system.
Focus on the presence of a neutral, the voltage measurements between phases and neutral (if present), and the wiring configuration to accurately identify the system. Don’t rely solely on the voltage rating!
In conclusion, understanding whether a 240V system is delta or wye requires a bit of electrical knowledge and careful observation. But with a little practice (and maybe a multimeter!), you can become a voltage-detecting virtuoso! Just remember: safety first, and when in doubt, call a pro.
Real-World Examples
9. Practical Applications
So, where might you actually encounter these different configurations in the real world? Well, delta systems are commonly found in industrial settings powering large motors, welders, and other heavy equipment. They’re often used in manufacturing plants, factories, and workshops.
Wye systems, on the other hand, are ubiquitous in residential and commercial buildings. They provide the 240V for appliances like dryers and water heaters, as well as the 120V for lights, outlets, and smaller devices. Think of your home’s electrical panel—chances are, it’s a wye system.
Farms also frequently use a combination of both systems. They might have a delta system for powering irrigation pumps or grain dryers, and a wye system for the farmhouse and other outbuildings. The specific configuration depends on the electrical needs of the application.
Think of a commercial kitchen, it may have a wye system for the general lighting and small appliances, while a large pizza oven might be on a dedicated delta circuit. This allows for efficient power distribution tailored to the specific demands of each piece of equipment.
FAQ
10. Clearing Up the Confusion
Still scratching your head? Here are a few frequently asked questions to further illuminate the delta vs. wye landscape.
11. Question 1
Q: Can I convert a delta system to a wye system, or vice versa?
A: Technically, yes, but it’s usually a major undertaking involving replacing transformers and rewiring significant portions of the electrical system. It’s rarely a simple “flip a switch” kind of change. It’s usually more cost-effective to just install the appropriate system for the application in the first place.
12. Question 2
Q: What happens if I accidentally connect a 120V device to a 240V circuit?
A: Bad things! You’ll likely fry the device and potentially cause a fire. Always double-check the voltage requirements of your appliances and equipment before plugging them in. Using the wrong voltage can lead to expensive repairs or, worse, a dangerous electrical hazard. So, play it safe and read those labels!
13. Question 3
Q: Are delta and wye systems used in other countries with different voltages?
A: Absolutely! The delta and wye configurations are used worldwide, but the voltage levels may vary. For example, in some European countries, you might find 400V wye systems. The principles remain the same, but the specific voltage values will differ. Always check the local electrical standards when working with electrical systems in different countries.