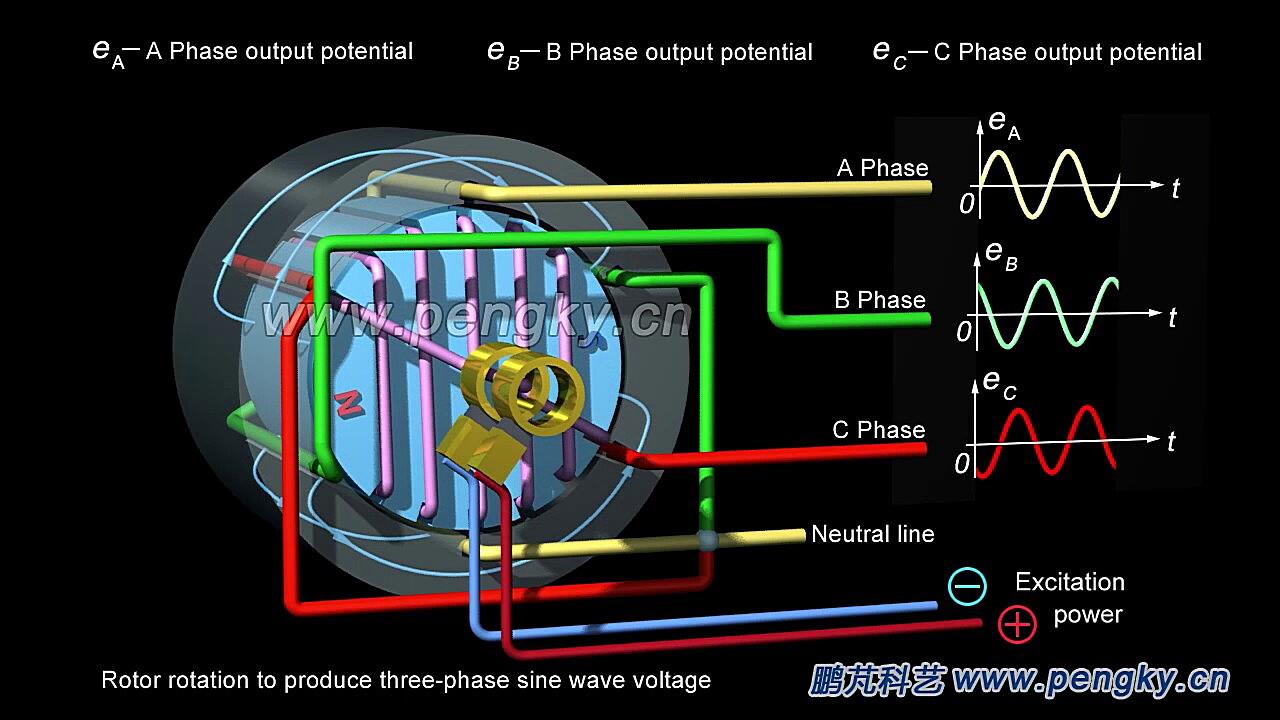
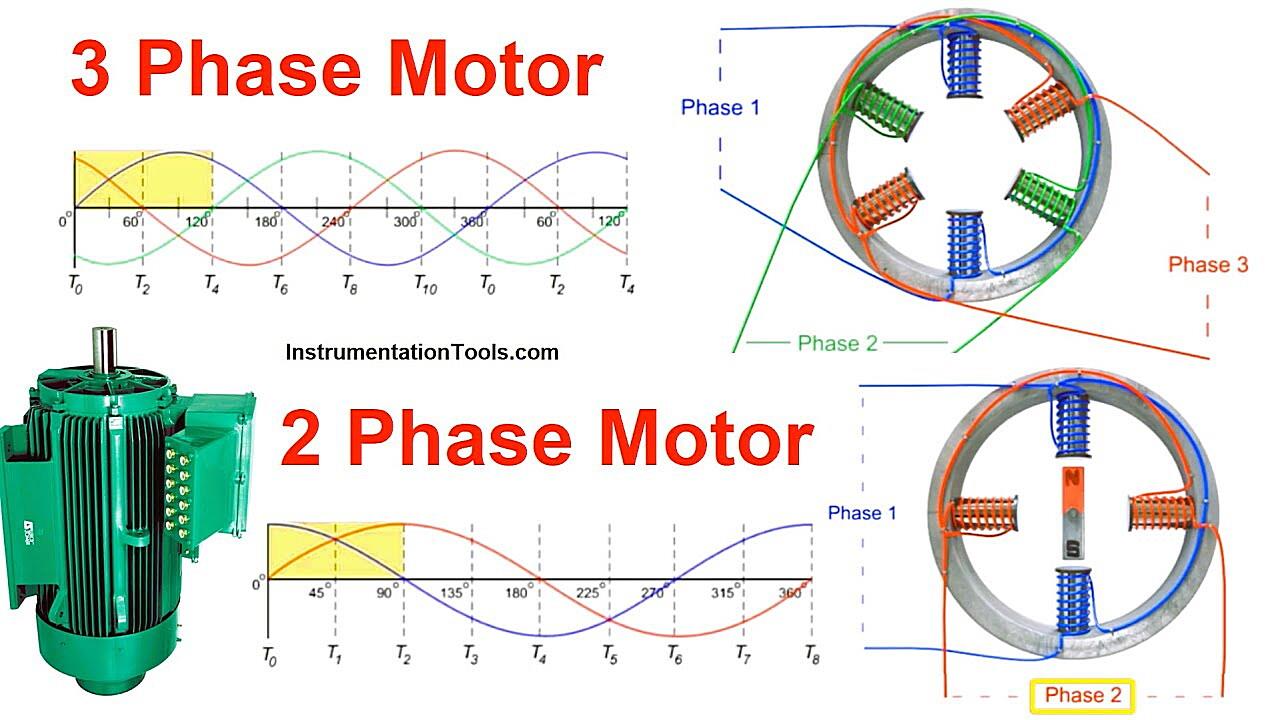
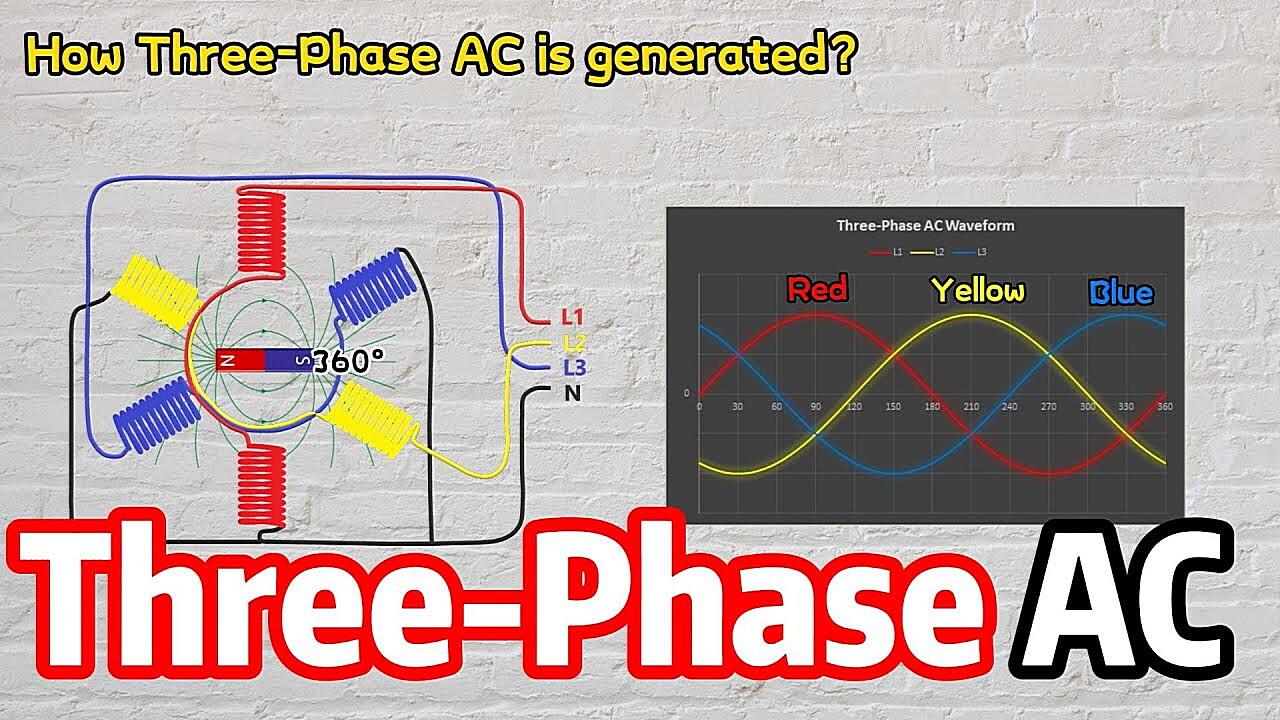
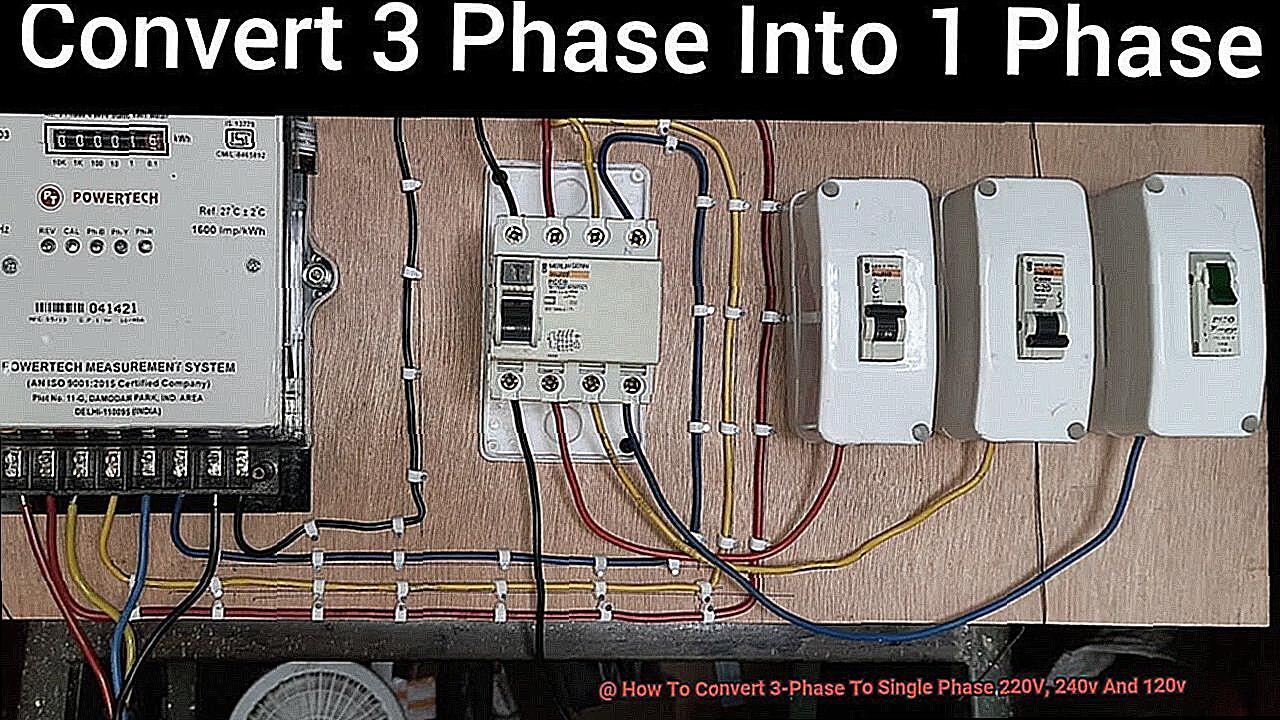
Unlocking the Power of Three
1. Why Bother with 3-Phase? Let’s Keep It Real
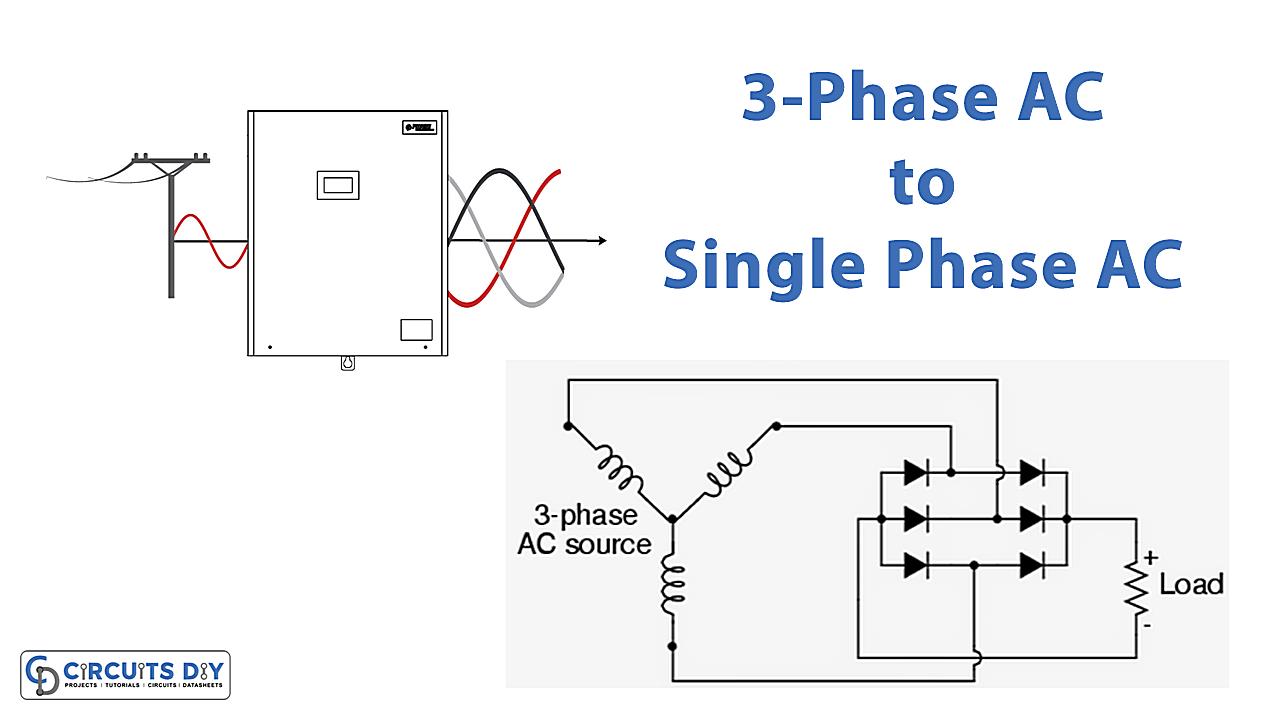
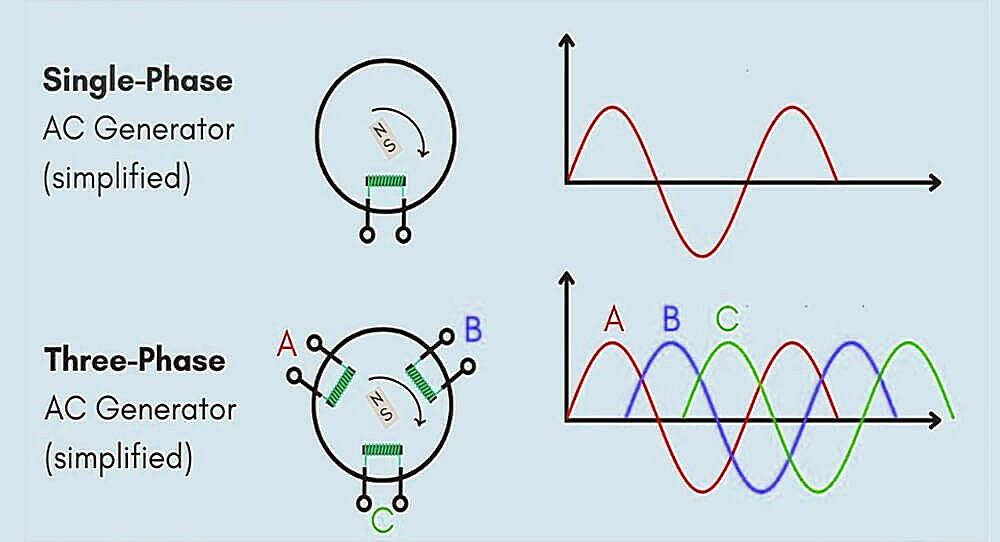
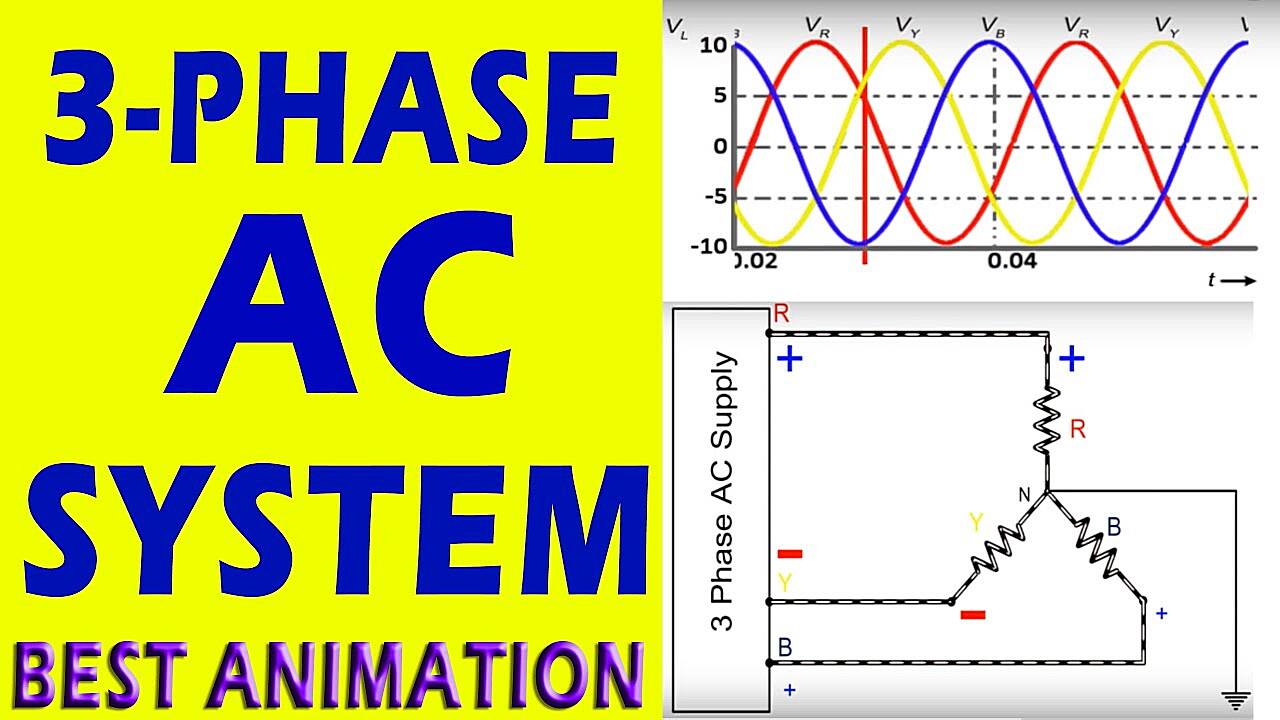
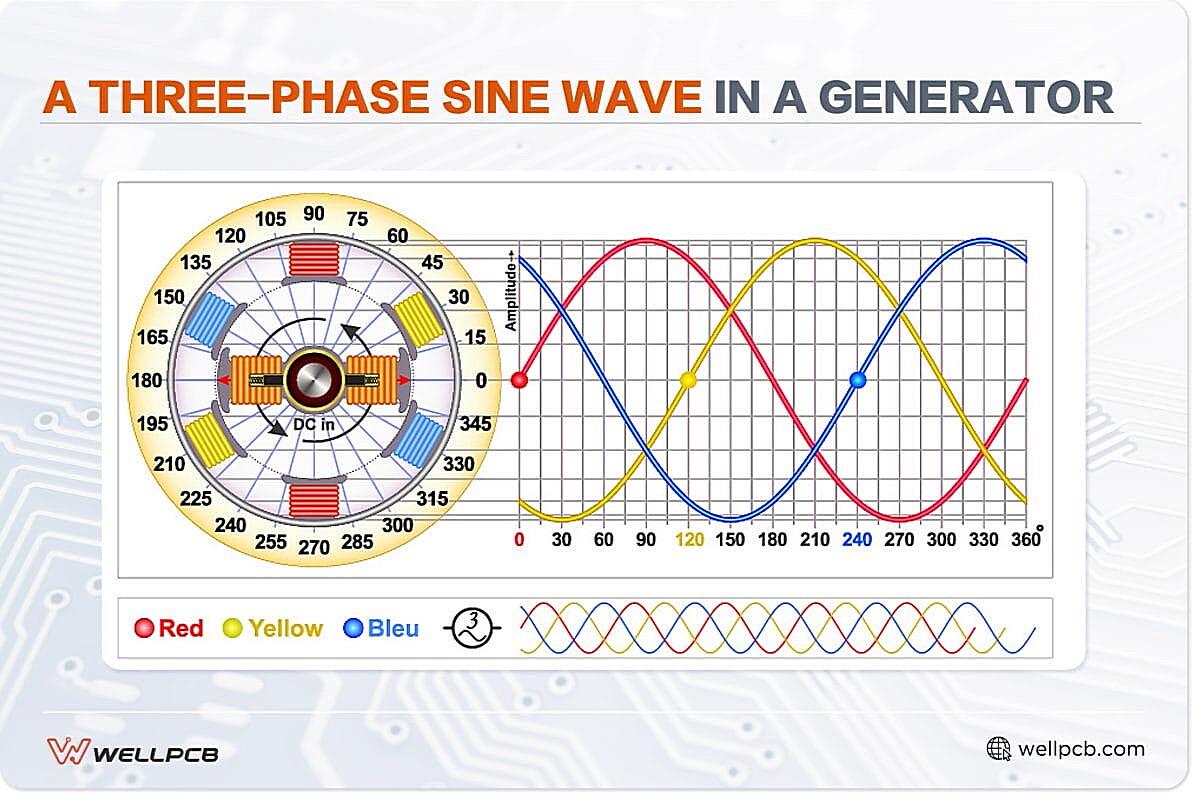
Ever wondered why some machines seem to purr with power while others just wheeze and complain? A lot of it comes down to the type of electrical current they’re using. Single-phase, the kind you probably have buzzing through your house, is perfectly fine for lamps, toasters, and charging your phone. But when you need to power serious equipment—think industrial motors, heavy-duty machinery, or even some hefty air conditioning systems—3-phase AC is where it’s at. Its smoother, more efficient, and delivers power more consistently. Basically, it’s the energy drink of the electrical world.
So, what makes 3-phase so special? Imagine a team of three people pushing a merry-go-round, each pushing at slightly different times. That’s 3-phase! It’s like a relay race of power, providing a constant, steady flow. Single-phase, on the other hand, is more like one person pushing really hard, then taking a break. All that starting and stopping can be tough on equipment. Three-phase reduces vibration, noise, and generally makes things run a whole lot smoother. That translates to longer equipment life and fewer headaches.
Now, you might be thinking, “This sounds great, but I only have single-phase! Am I doomed to a life of underpowered appliances?” Fear not! There are ways to conjure 3-phase power from your single-phase setup. It’s a bit like turning water into wine, but with electricity. It might not be exactly the same, but it’ll get the job done, and that’s what counts.
The goal of learning how to generate 3-phase AC from single-phase, will open a lot of possibilities to your existing system or even to new creation. It allows you to optimize the power to heavy duty equipment, and at the same time improving efficiency. So, let’s explore how to accomplish this electrical alchemy, because who doesn’t love a good power upgrade?
The Rotary Phase Converter
2. Making the Magic Happen with Rotation
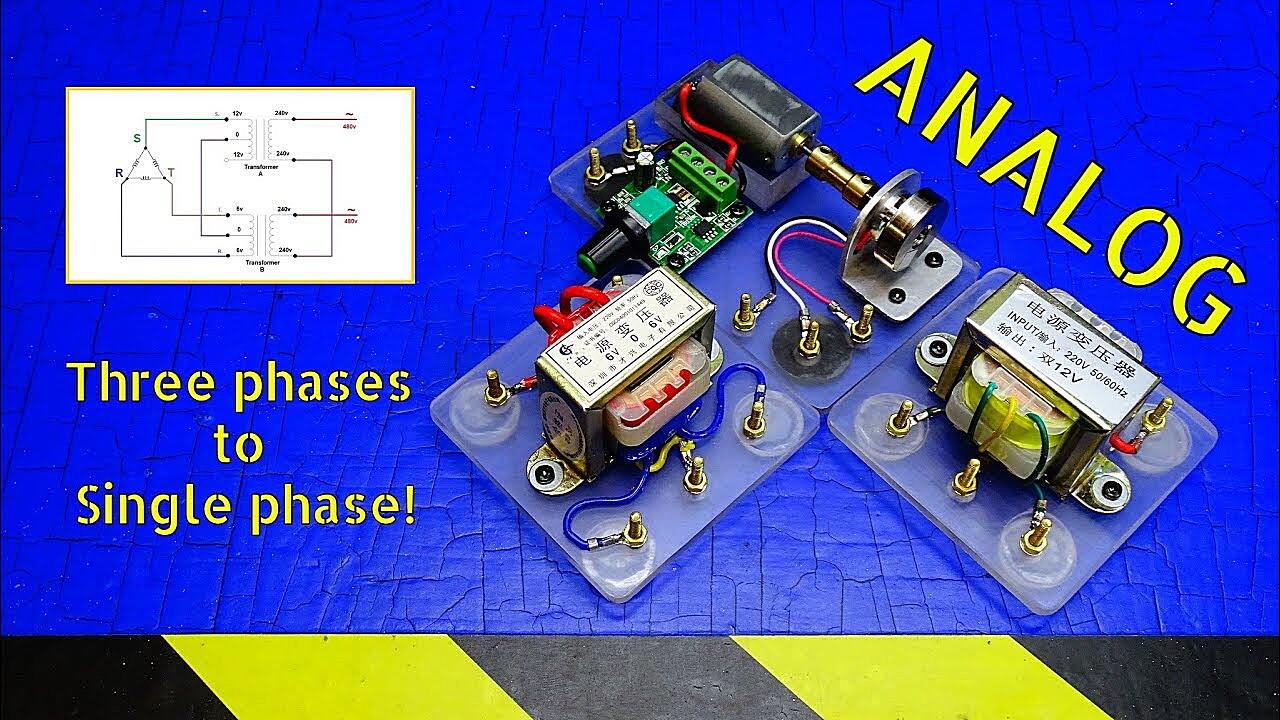
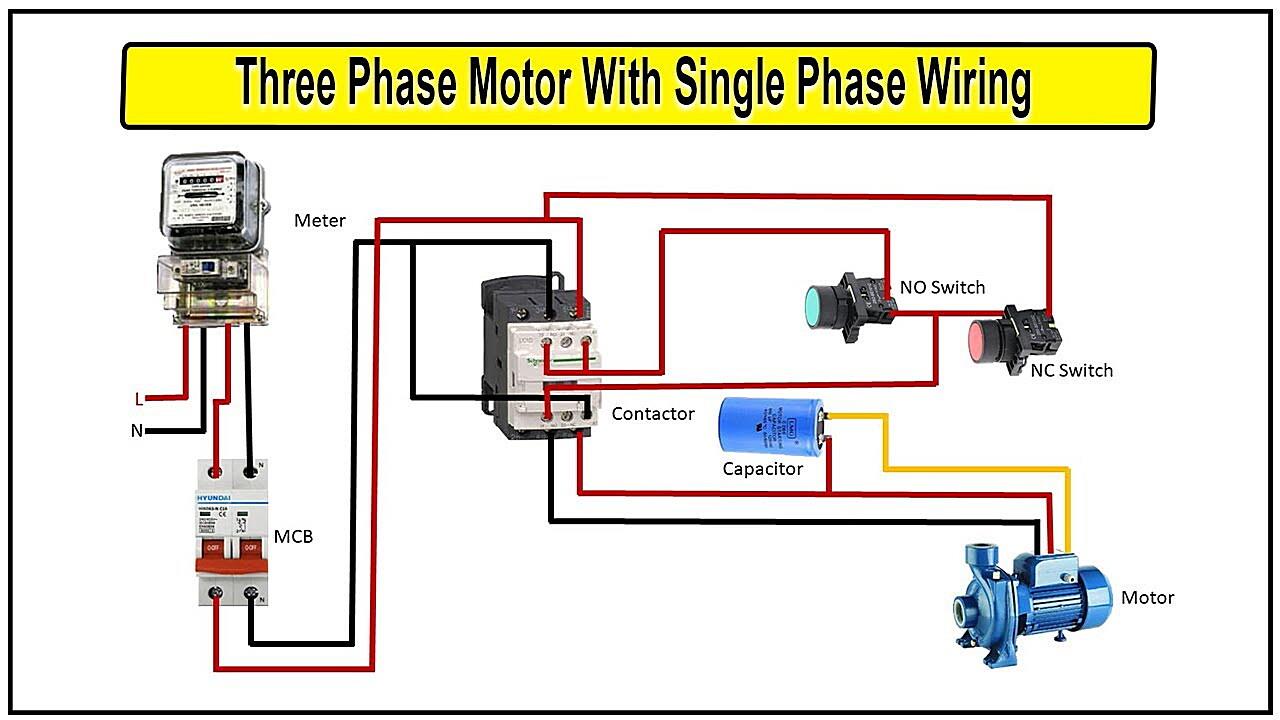
One of the most common ways to get 3-phase power from a single-phase source is by using a rotary phase converter. Think of it as a kind of electrical translator. It takes the single-phase input and uses a rotating motor-generator to create a balanced 3-phase output. It’s a bit more complex than that, of course, but that’s the general idea. Essentially, you’re spinning a motor that acts as a generator, tricking the single-phase power into believing it’s actually part of a three-phase system. It’s like giving your electricity an identity makeover.
The heart of a rotary phase converter is an idler motor, which is designed to run even with unbalanced voltages. This motor spins and generates the missing phases. Capacitors and other components help to balance the voltages and currents, ensuring that the resulting 3-phase power is as stable and reliable as possible. It’s a bit like having a team of electrical engineers working behind the scenes to smooth out any rough edges.
Rotary phase converters are often preferred for powering multiple loads or loads that require consistent and reliable power. They can handle inductive loads like motors relatively well, making them a popular choice for workshops, small businesses, and even some home-based operations. However, they can be a bit noisy due to the rotating motor, so you might want to consider soundproofing if you’re sensitive to noise. It’s kind of like having a friendly, but slightly loud, electrical assistant.
Installation generally requires a qualified electrician, because, well, electricity is dangerous! They’ll need to properly wire the converter to your single-phase input and ensure that the 3-phase output is correctly connected to your equipment. Safety first, always. After all, nobody wants an electrical surprise party. Remember to consult your electrical code for proper installation.
Static Phase Converters
3. Sometimes, Simpler Isn’t Always Superior
If the rotary phase converter sounds a bit too complicated or noisy for your taste, you might be tempted to consider a static phase converter. These devices are simpler and cheaper than their rotary counterparts. They use capacitors to create an artificial third phase, essentially faking a 3-phase signal from the single-phase input. Think of it as a slightly less convincing impersonation of a 3-phase system.
The main advantage of a static phase converter is its simplicity and lower cost. There are no moving parts, so they’re quieter and require less maintenance than rotary converters. They’re also smaller and lighter, making them easier to install and transport. However, there’s a catch (isn’t there always?). Static phase converters typically only provide about 30-50% of the rated horsepower of the motor they’re powering. That means you might not be able to run your equipment at full capacity. It’s like having a sports car that’s limited to driving in second gear.
Static phase converters are generally suitable for light-duty applications where you don’t need full power. They’re often used to start motors, but then the motor runs primarily on single-phase power. This can lead to reduced efficiency and increased heat buildup in the motor. So, while they’re cheaper upfront, they might cost you more in the long run due to higher energy consumption and potential equipment damage. It’s like saving money on a cheap pair of shoes, only to have them fall apart after a few weeks.
Because of the limitations, it’s vital to carefully assess if a static phase converter is the right choice for your application. If you’re only running a small motor intermittently, it might be a reasonable option. But if you need reliable, full-power 3-phase operation, a rotary phase converter is usually the better bet. Choosing the correct converter can prevent costly damage, so don’t risk it.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
4. Adding Some Brains to Your Power Conversion
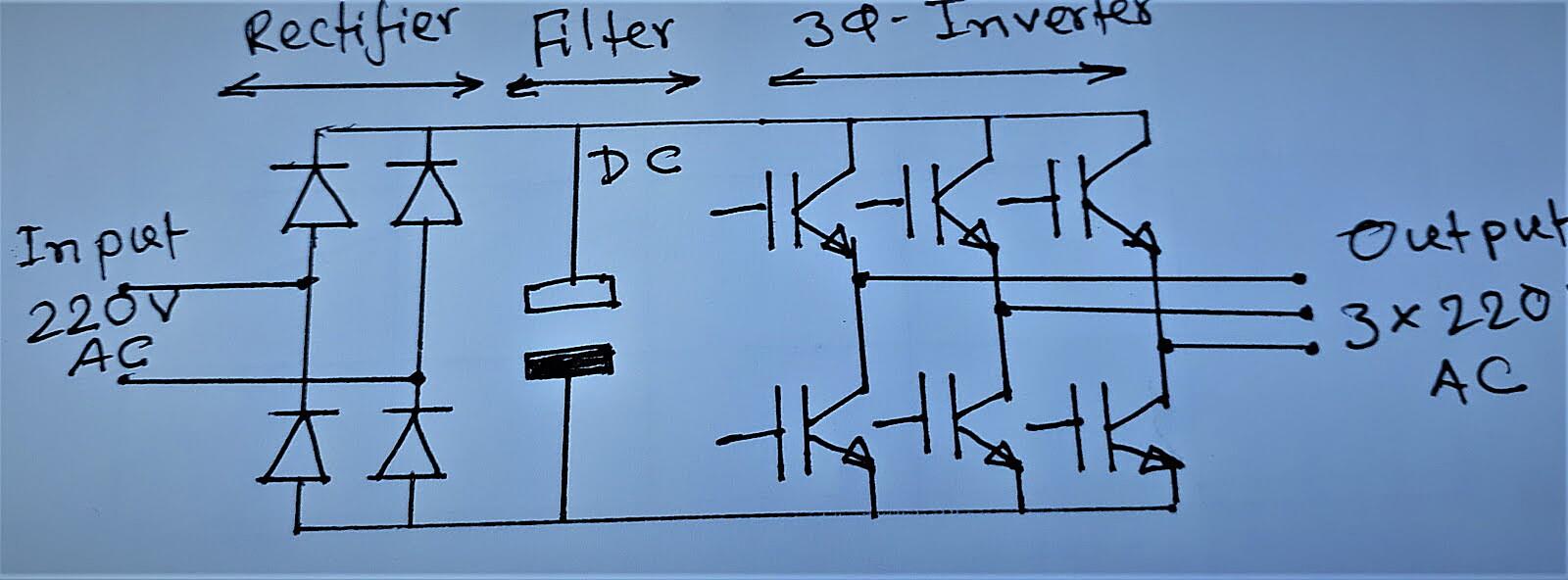
For a more sophisticated approach to generating 3-phase AC from single-phase, consider using a Variable Frequency Drive, or VFD. These devices are electronic power controllers that can take single-phase AC, convert it to DC, and then recreate it as 3-phase AC with adjustable frequency and voltage. Think of it as a smart transformer that not only converts phases but also allows you to control the speed and torque of your motors. It’s like giving your equipment a remote control with fine-tuning capabilities.
VFDs offer several advantages over traditional phase converters. They provide precise control over motor speed, allowing you to optimize performance and energy efficiency. They also offer built-in protection against overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults, helping to prolong the life of your equipment. Plus, they can often reduce starting current, which can be a significant advantage for older electrical systems. It’s like having a built-in bodyguard for your machinery.
However, VFDs are generally more expensive than rotary or static phase converters, and they can be more complex to install and configure. They also require careful consideration of motor compatibility and proper grounding to prevent electrical noise and interference. So, while they offer advanced features, they also require a bit more expertise to use effectively. It’s like upgrading from a bicycle to a motorcycle—more power, but also more responsibility.
If you need precise motor control, energy savings, and built-in protection, a VFD might be the best option for your needs. They’re commonly used in industrial applications, HVAC systems, and other applications where variable speed control is beneficial. Just be sure to do your homework and consult with a qualified electrician to ensure proper installation and configuration. It’s always a good idea to have a professional opinion, just in case.
Choosing the Right Converter
5. Considerations for an Informed Choice
So, you’ve learned about rotary phase converters, static phase converters, and variable frequency drives. Now comes the million-dollar question: which one is right for you? The answer, as always, depends on your specific needs and budget. Think of it as ordering off a menu—each option has its own pros and cons, and you need to choose the one that best satisfies your appetite (or, in this case, your power requirements).
Consider factors such as the horsepower requirements of your equipment, the type of load (inductive, resistive, etc.), the duty cycle (how often you’ll be using the equipment), and your budget. Rotary phase converters are a good all-around choice for powering multiple loads or loads that require consistent power. Static phase converters are a cheaper option for light-duty applications, but they might not provide enough power for larger motors. VFDs offer precise motor control and energy savings, but they’re more expensive and complex to install. It’s like weighing the pros and cons of different vehicles—a truck, a sedan, or a sports car.
Don’t forget to consider the long-term costs of each option. Static phase converters might be cheaper upfront, but they could lead to higher energy consumption and potential equipment damage down the road. Rotary phase converters might be noisier, but they’re more reliable and can handle heavier loads. VFDs might be more expensive, but they offer energy savings and built-in protection that can save you money in the long run. It’s like thinking about the fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and reliability of each vehicle.
Ultimately, the best way to choose the right converter is to do your research, consult with a qualified electrician, and carefully evaluate your specific needs. It’s like getting a second opinion from a doctor before making a major medical decision. Electrical systems can be complex, and it’s always better to be safe than sorry. After all, you want your equipment to purr like a kitten, not explode like a firecracker.
FAQ
6. Common Queries About 3-Phase Conversion
Still scratching your head? Let’s tackle some common questions about generating 3-phase AC from single-phase. It’s like having a friendly Q&A session to clear up any lingering doubts.
7. Is it safe to generate 3-phase power from single-phase?
Yes, but only if done correctly and by a qualified electrician. Improper installation or use of incompatible equipment can lead to electrical hazards, equipment damage, and even fires. Always follow safety precautions and consult with a professional. Think of it like cooking with fire—it’s safe as long as you know what you’re doing, but it can be dangerous if you’re careless.
8. Can I run my whole house on 3-phase power generated from a single-phase source?
Technically, yes, but it’s generally not practical or cost-effective for residential applications. Generating 3-phase power from single-phase is usually reserved for specific equipment or machinery that requires it. Most household appliances are designed to run on single-phase power, and upgrading your entire electrical system to 3-phase would be a major undertaking. It’s like installing a commercial kitchen in your home—it’s possible, but probably not necessary.
9. What happens if my phase converter fails?
If your phase converter fails, your 3-phase equipment will likely stop working or experience reduced performance. In some cases, it could also damage your equipment. It’s important to regularly inspect and maintain your phase converter to prevent failures. Consider having a backup plan in place, such as a spare converter or an alternative power source. It’s like having a spare tire for your car—you hope you never need it, but it’s good to have just in case.