Exploring the Reliability of Star Topology
1. Understanding the Basics of Star Topology
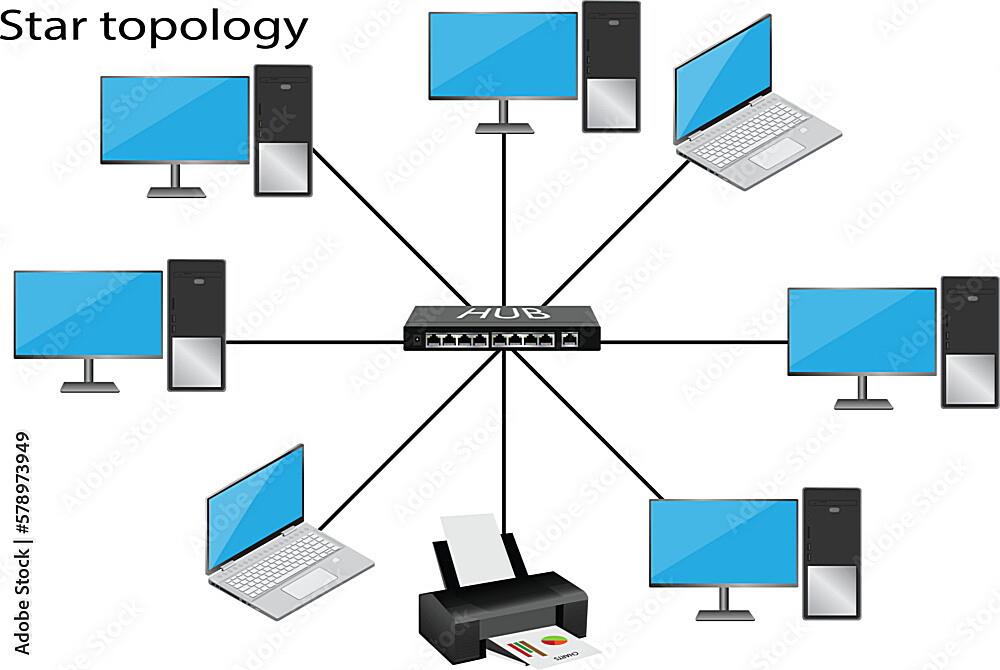
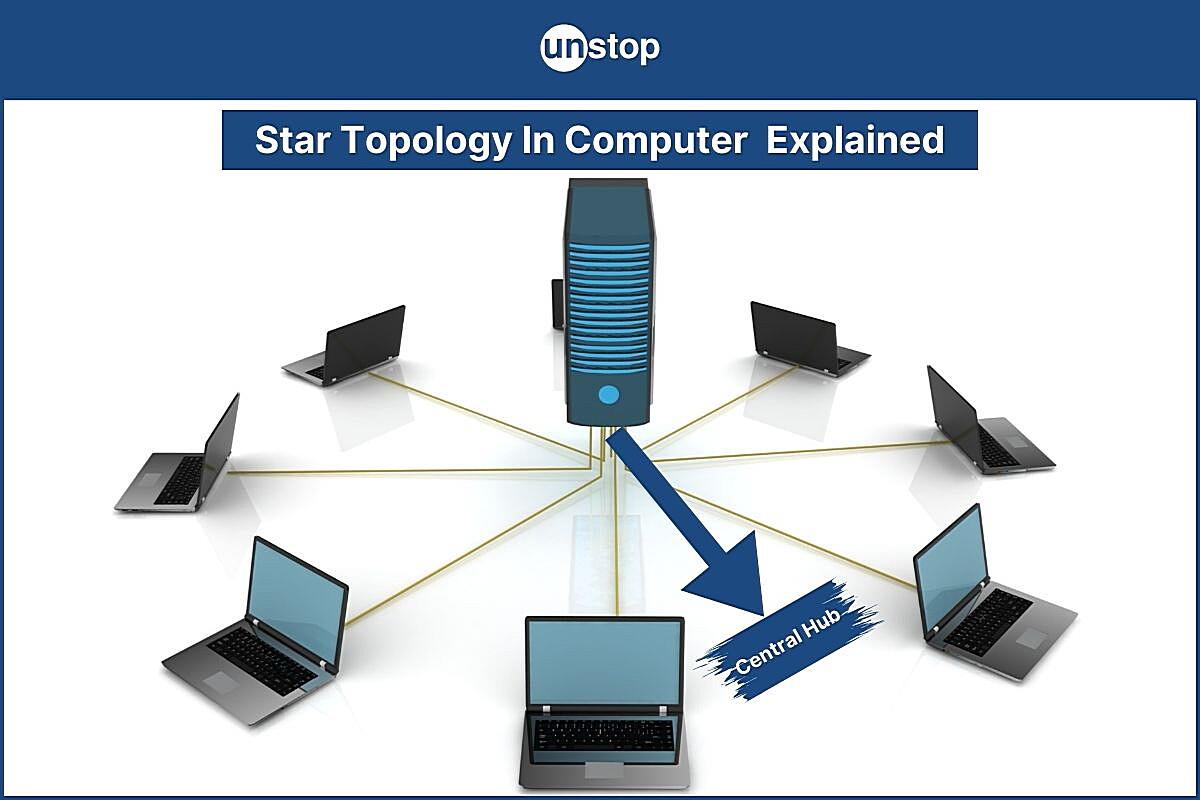
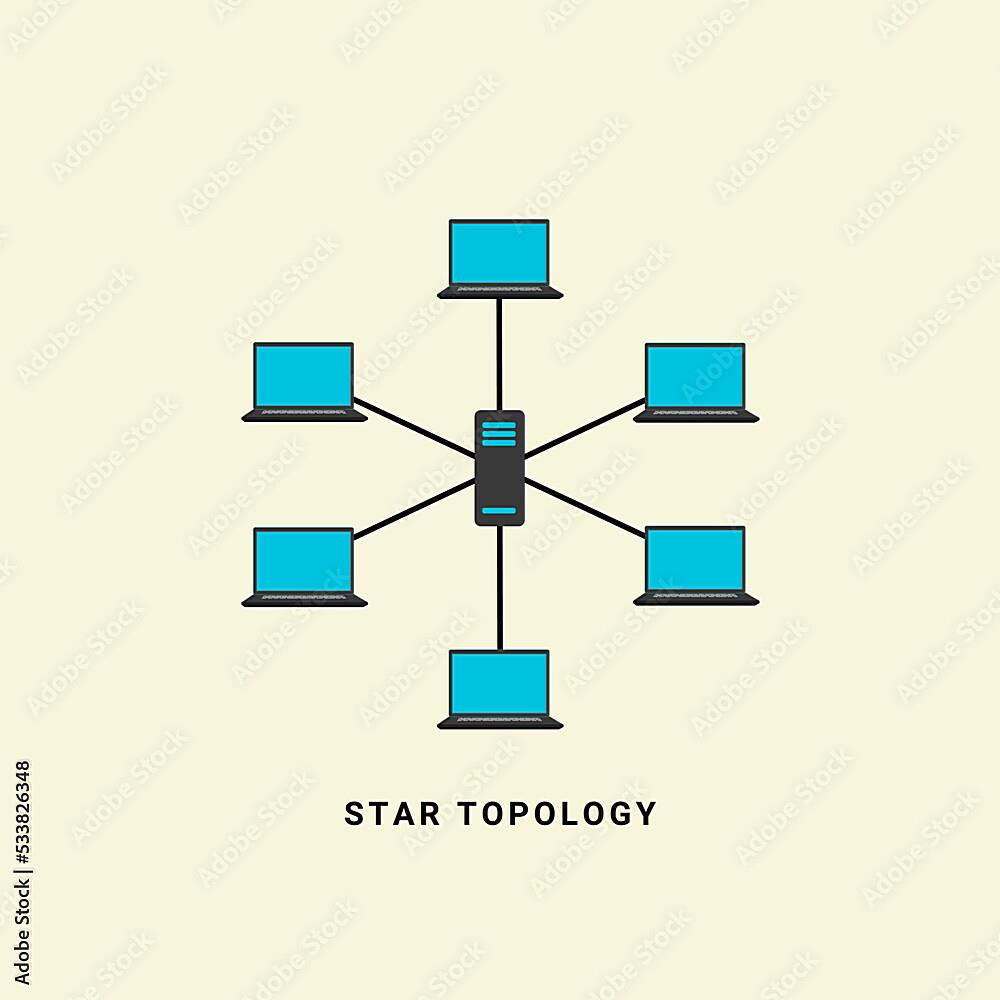
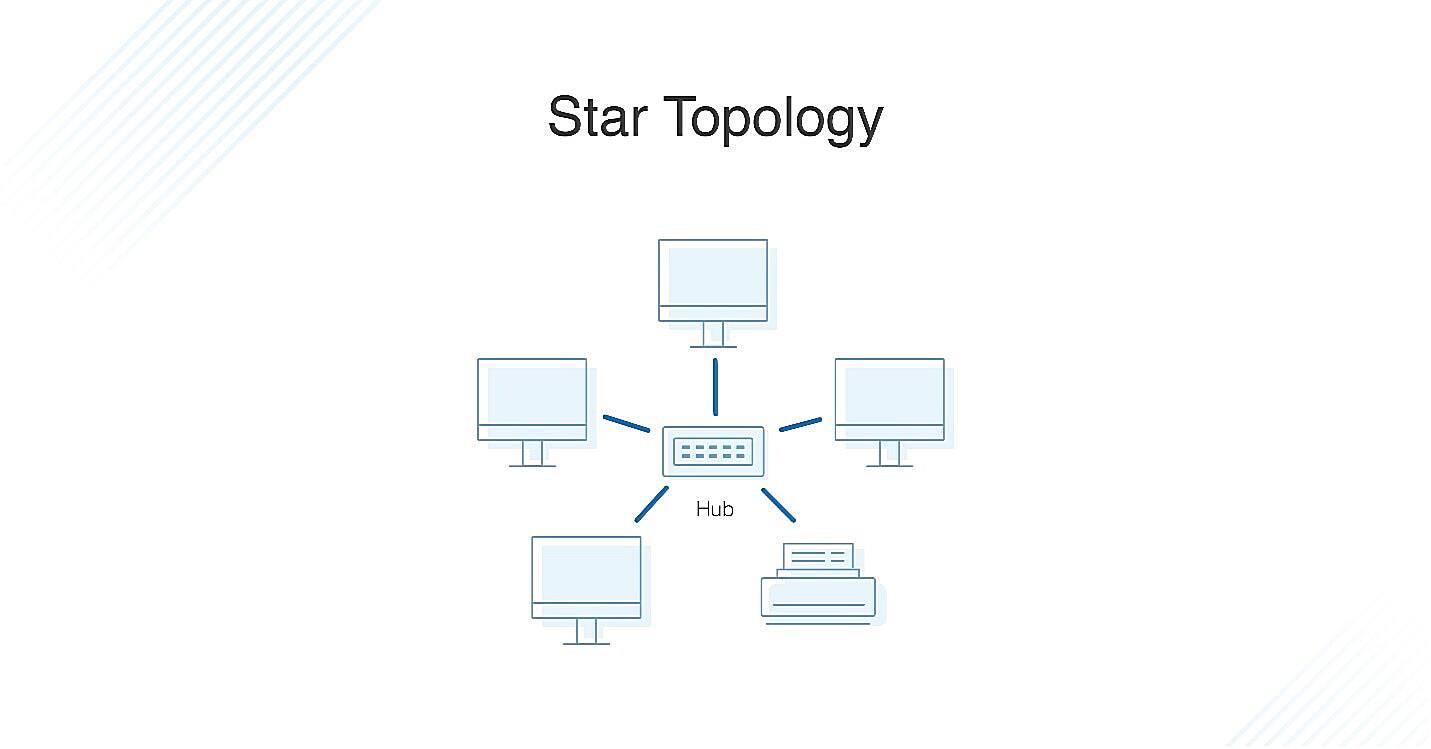
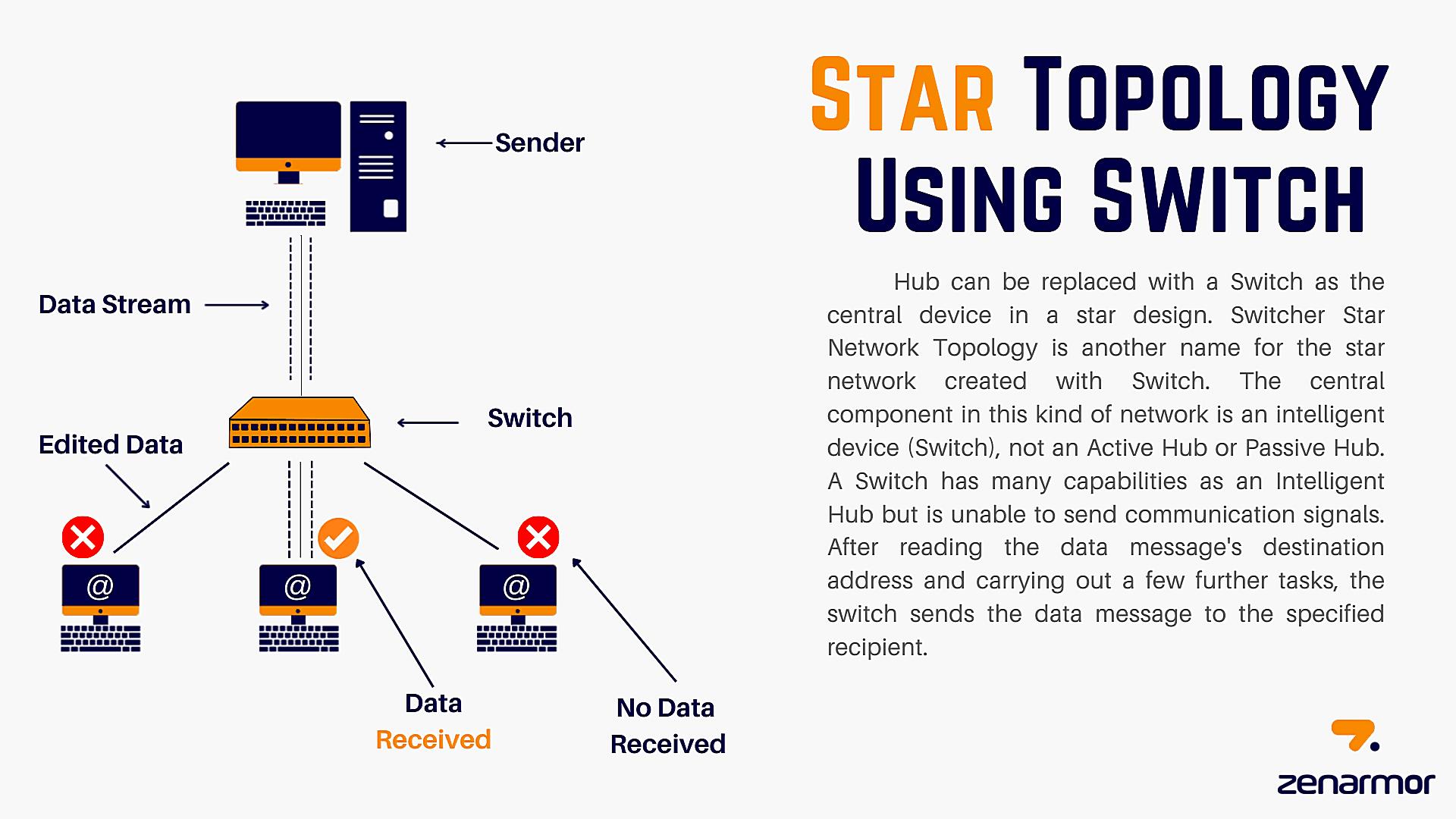
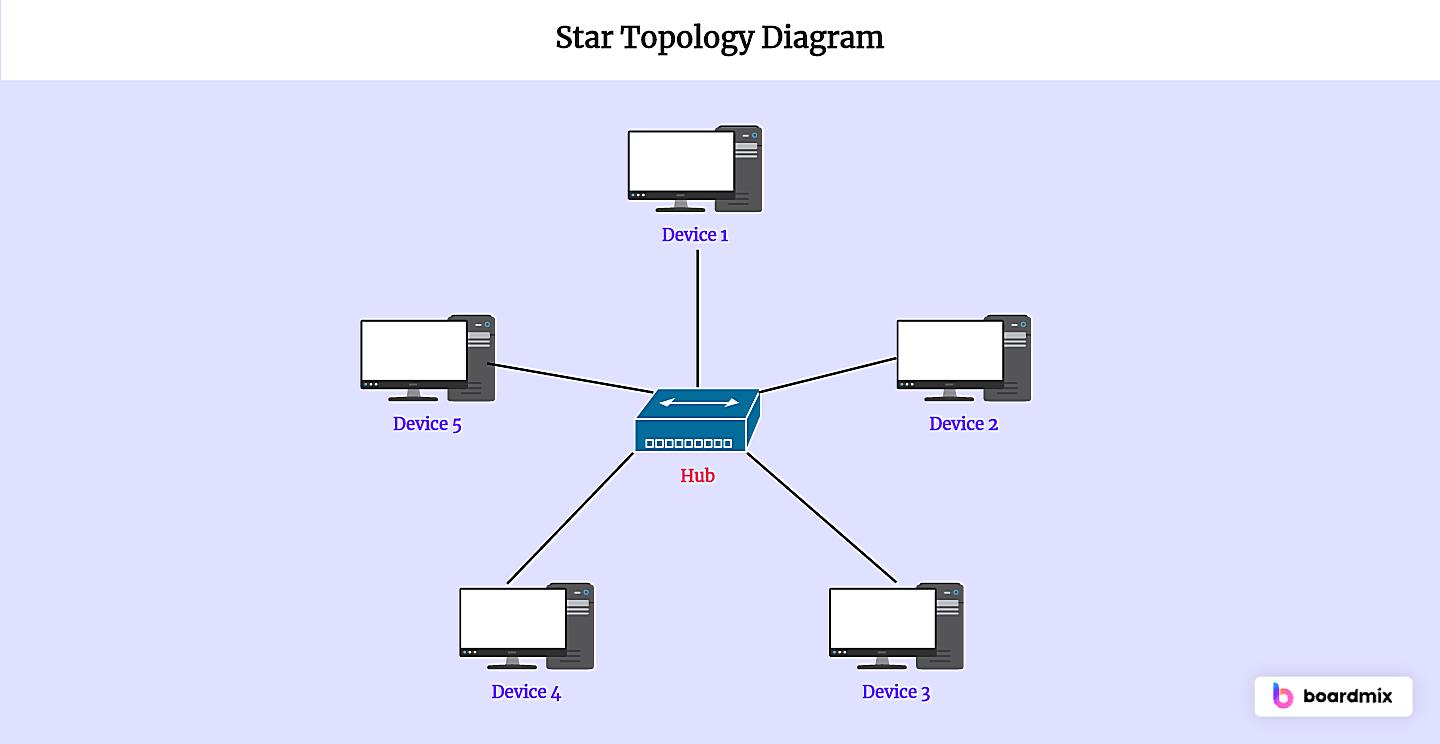
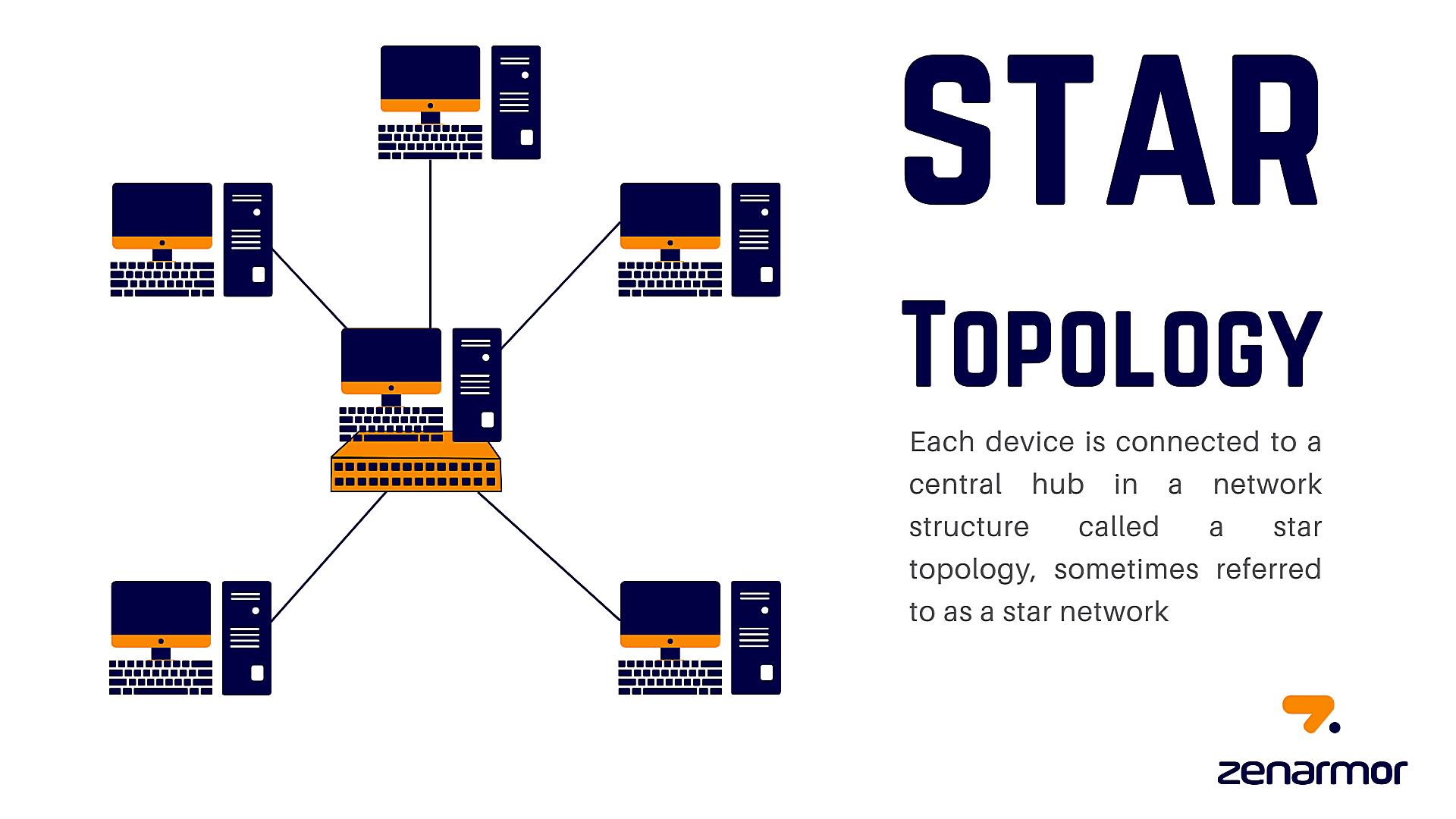
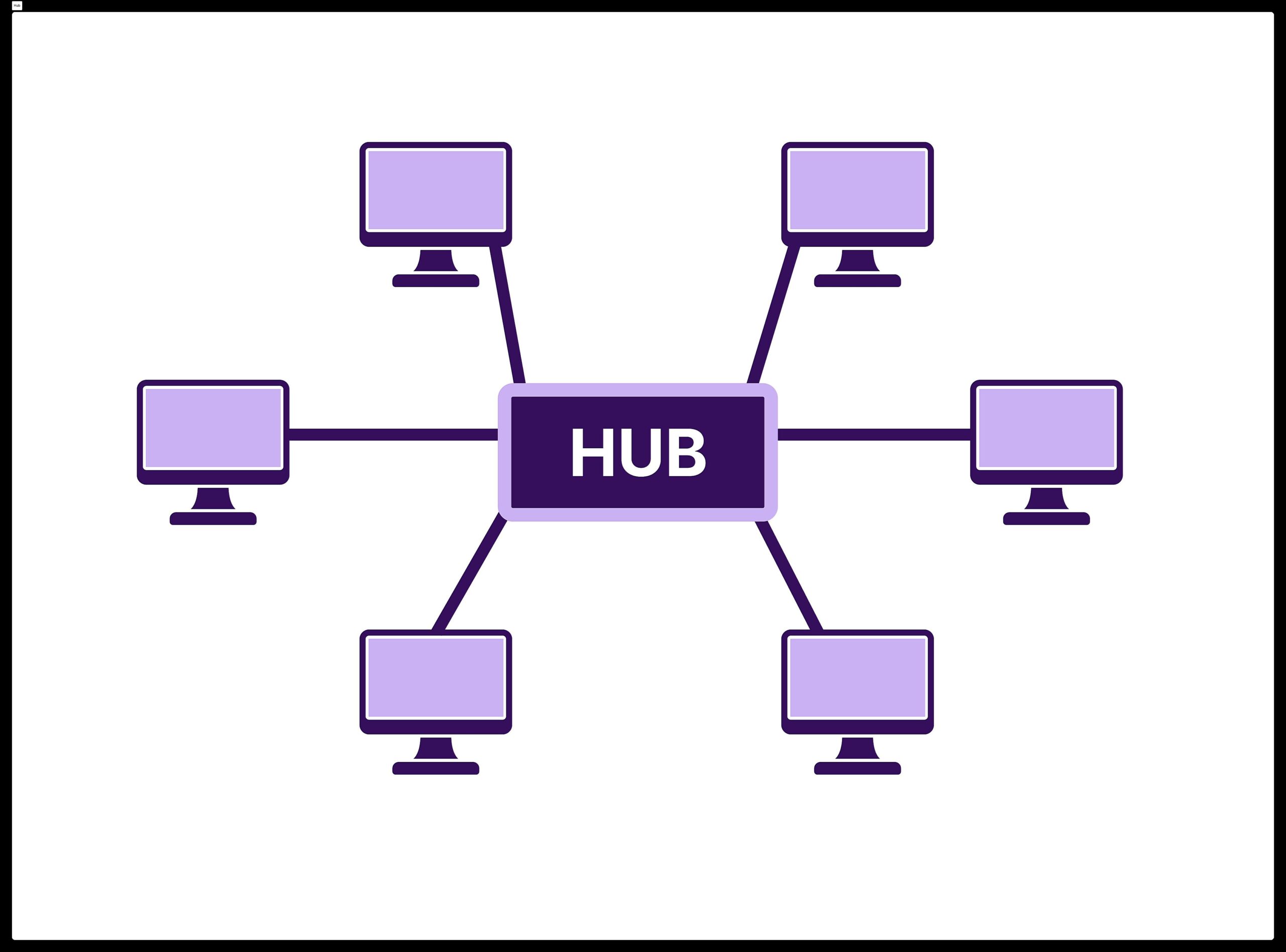
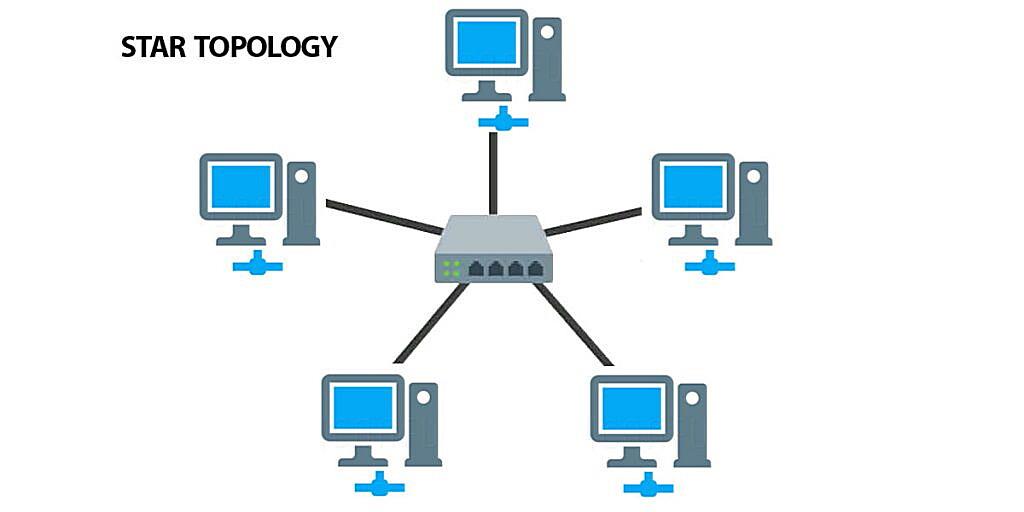
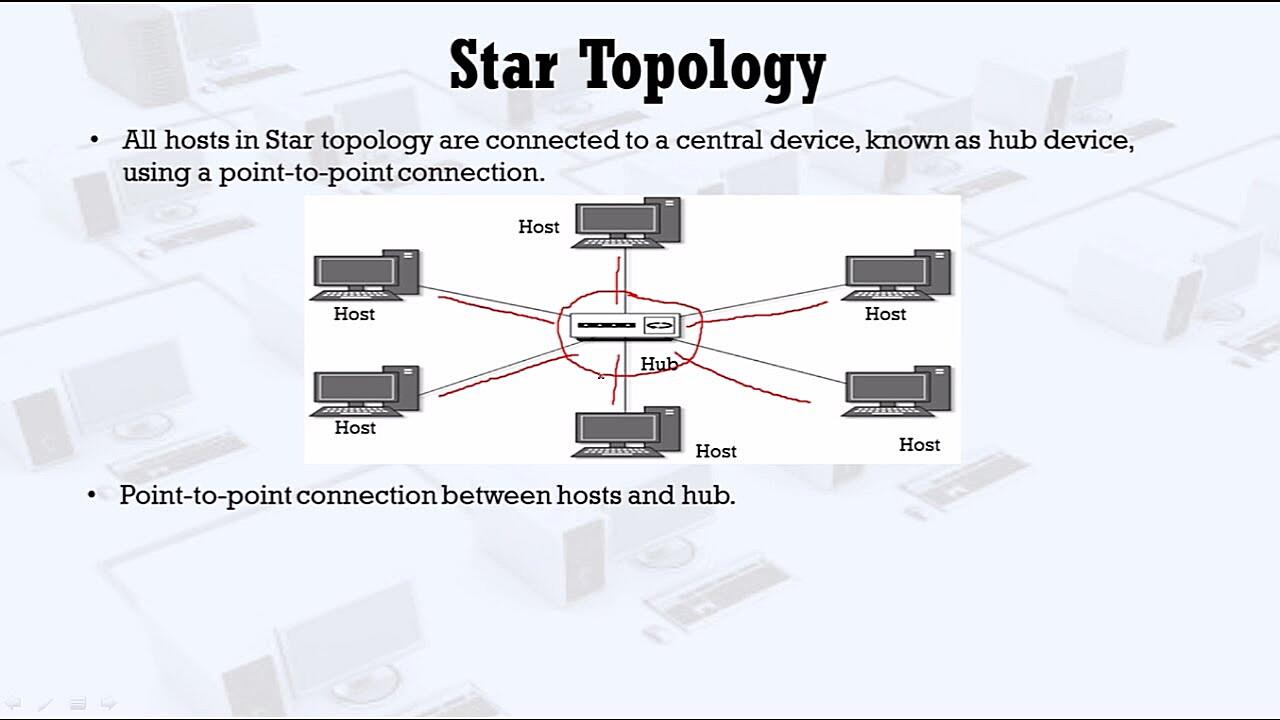
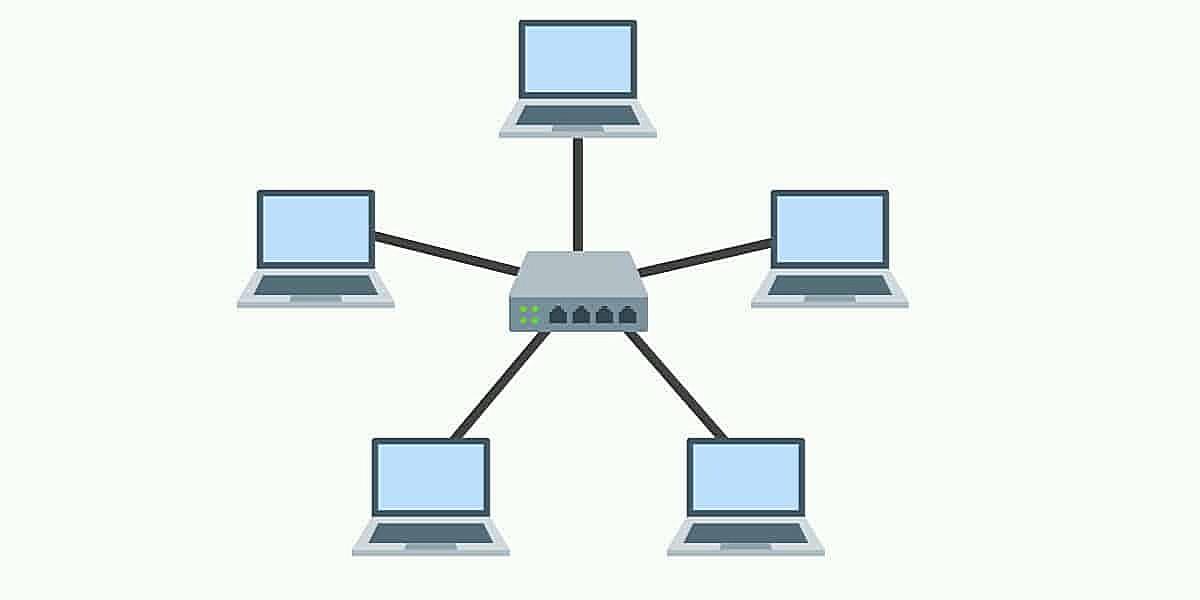
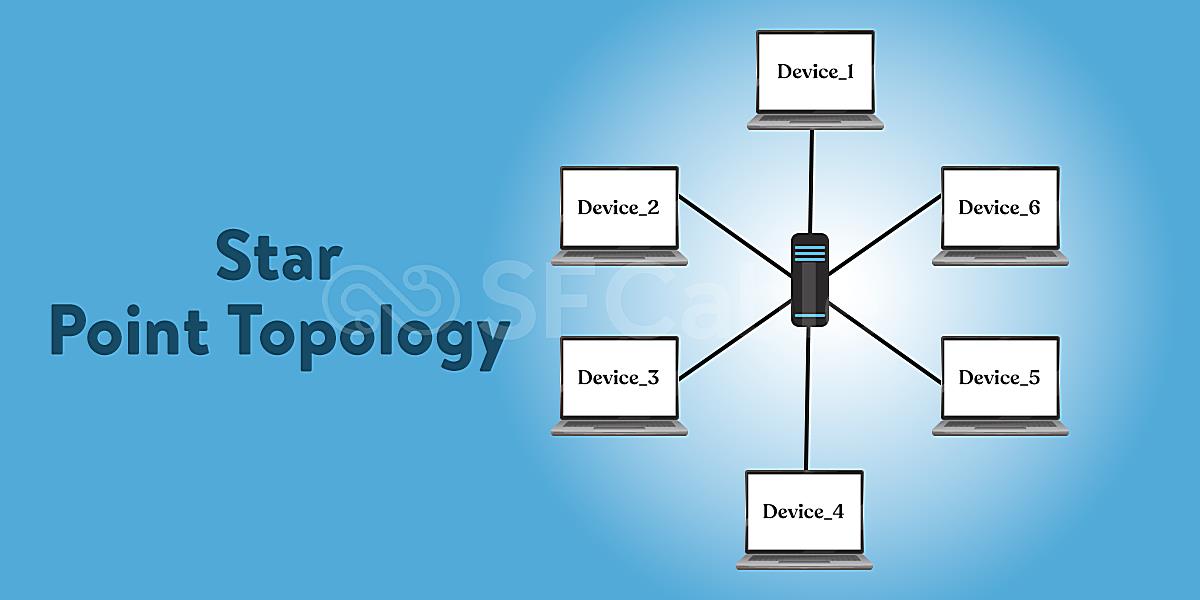
So, you’re curious about star topology and how reliable it is? Let’s break it down. Imagine a network where every device connects to a central hub or switch. That’s a star topology in a nutshell. It’s kind of like having a super-organized party where everyone has to check in with the host (the hub/switch) before talking to anyone else. Simpler than shouting across a crowded room, right?
This design offers some distinct advantages. For instance, it’s pretty easy to add or remove devices without disrupting the entire network. Think of it like adding or removing guests from our party — as long as the host is still there, everything keeps running smoothly. Plus, pinpointing a problem area becomes a lot easier. One device misbehaving? You just check its connection to the central hub, instead of tracing connections across a tangled web.
But what happens if the ‘host’ (central hub or switch) crashes? Well, the party’s over. That’s the main vulnerability of a star topology — its reliance on that central point. However, modern switches are generally pretty robust and reliable, so catastrophic hub failures are less common than you might think. Like having a backup generator for your party, you can also implement redundancy to prevent single point of failure.
The reliability really depends on the quality of the central device and how well it’s managed. A cheap, overloaded hub can become a bottleneck and lead to all sorts of performance issues, making the entire network seem unreliable. A well-maintained, high-quality switch, on the other hand, can provide a rock-solid foundation for your network. Think of it as the difference between a DJ playing music from a potato and a professional sound system.
How Robust is It, Really? The Good, The Bad, and The Centralized
2. Advantages That Boost Reliability
Let’s dig a little deeper. One of the significant advantages of star topology that directly impacts reliability is its fault tolerance. If a single device or cable fails, it only affects that specific connection. The rest of the network continues to function without interruption. That’s a huge win compared to older topologies like bus topology, where a single break in the main cable could bring the whole network down. Imagine a single broken string of Christmas lights taking down the entire display — star topology avoids that kind of disaster.
Another reliability booster is the ease of troubleshooting. Because each device has its own dedicated connection, isolating the source of a problem is straightforward. Network administrators can quickly identify and fix issues without having to sift through a complicated mess of cables and connections. This rapid problem resolution translates directly into improved uptime and a more reliable network experience.
Scalability is also a key factor. Adding new devices to a star topology is relatively simple; you just connect them to the central hub or switch. This ease of expansion makes it easier to adapt to changing needs without compromising the overall reliability of the network. You aren’t forced to rewire the entire setup just to add one new computer.
Moreover, the centralized nature of star topology allows for easier monitoring and management. Network administrators can use specialized software to track network performance, identify potential problems, and implement security measures from a single location. This centralized control enhances the reliability and security of the entire network.
The Achilles Heel
3. Addressing the Central Hub’s Vulnerability
Alright, let’s face the music. The biggest potential drawback of star topology is its reliance on the central hub or switch. If that central point fails, the entire network goes down. That’s a critical vulnerability that needs to be addressed. But it isn’t game over! This is where careful planning and smart strategies come into play.
One effective solution is to implement redundancy. This means having a backup switch ready to take over in case the primary switch fails. Redundancy can be achieved through various methods, such as using multiple switches in a failover configuration or employing a redundant power supply for the main switch. Think of it as having a spare tire for your car — you hope you never need it, but you’re sure glad it’s there when you do.
Another key factor is selecting a high-quality, reliable central switch. Don’t skimp on this! Invest in a reputable brand with a proven track record. Choose a switch that’s designed to handle the expected traffic load and has built-in features like error detection and correction. A durable, well-built switch will significantly reduce the risk of failure.
Regular maintenance and monitoring are also crucial. Keep the switch’s firmware up-to-date, monitor its performance metrics, and address any potential issues proactively. This proactive approach can help prevent minor problems from escalating into major outages. It’s like taking your car in for regular checkups — it helps keep everything running smoothly and prevents unexpected breakdowns.
Comparing Star Topology to Other Network Designs
4. Star Topology vs. Bus, Ring, and Mesh
How does star topology stack up against other network designs? Let’s take a quick look. In a bus topology, all devices share a single cable, making it vulnerable to cable breaks. A ring topology connects devices in a closed loop, which can be disrupted if one device fails. Mesh topology offers high redundancy but is complex and expensive to implement. Compared to these alternatives, star topology provides a good balance of reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Bus topology, while simple, suffers from significant reliability issues. A single break in the main cable can bring down the entire network. Ring topology can be more resilient, but complex troubleshooting and the need for specialized hardware can be drawbacks. Mesh topology, with its multiple redundant paths, offers the highest level of reliability but comes at a steep cost.
Star topology stands out for its ease of troubleshooting and its relatively high level of reliability. While it is susceptible to central point failure, this can be mitigated through redundancy and careful selection of hardware. This makes it a practical choice for many small and medium-sized networks.
When choosing a network topology, it’s important to consider your specific needs and budget. If you need the absolute highest level of reliability, regardless of cost, mesh topology might be the way to go. But for most organizations, star topology offers a sweet spot of reliability, scalability, and affordability. It’s a good choice for networks that need to be dependable without breaking the bank.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Star Topology Reliability
5. Ensuring Uptime and Performance
Want to get the most out of your star topology and ensure maximum reliability? Here are some practical tips: Use high-quality cables and connectors to minimize signal loss and interference. Properly ground all network equipment to prevent electrical surges from damaging your devices. Implement a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to protect against power outages. And regularly back up your network configuration to quickly restore settings in case of a failure.
Don’t underestimate the importance of cable management. A messy, tangled network cable infrastructure can be a nightmare to troubleshoot. Use cable ties, labels, and a well-organized patch panel to keep everything neat and tidy. This will make it much easier to identify and fix problems when they arise.
Consider using VLANs (Virtual LANs) to segment your network. VLANs can help isolate traffic and improve network performance. They can also enhance security by preventing unauthorized access to sensitive resources. Think of it as creating separate, secure compartments within your network.
Finally, don’t forget about security. Implement strong passwords, enable firewall protection, and regularly scan for malware. A compromised network can be just as devastating as a hardware failure. A proactive security posture is essential for maintaining the overall reliability of your network.
FAQ
6. Your Questions Answered
Q: What is the biggest disadvantage of star topology?
A: The biggest disadvantage is its reliance on the central hub or switch. If that central point fails, the entire network goes down.
Q: How can I improve the reliability of a star topology?
A: You can improve reliability by using high-quality hardware, implementing redundancy, and performing regular maintenance and monitoring.
Q: Is star topology suitable for large networks?
A: Yes, star topology can be used in large networks, but it’s important to use high-capacity switches and implement proper network segmentation.
Q: Is star topology more reliable than a mesh topology?
A: Generally, mesh topology is inherently more reliable due to its redundancy, but it’s also more complex and costly. Star topology with redundancy measures can achieve a high level of reliability at a more reasonable cost.