Understanding Voltage Differences
1. Why the Voltage Variance Matters
So, you’re staring at a shiny new appliance, itching to plug it in, but a nagging question pops up: “Can you use 208V on 240V?” It’s a valid concern! Electricity, while incredibly useful, is also a bit like a picky eater. It thrives on specific voltages to function correctly, and tossing the wrong voltage into the mix can lead to problems, some minor, some well, let’s just say you might end up with a smoky situation no one wants. Understanding these voltage differences is key to keeping your gadgets happy and your home safe.
Think of it like this: Imagine trying to fuel a car designed for premium gasoline with regular. It might run, but it won’t run efficiently, and over time, you’ll likely damage the engine. The same principle applies to electrical appliances. A device designed for 240V being fed only 208V might work, but it will likely not perform at its peak, and its lifespan could be significantly shortened. Conversely, trying to power a 208V device with 240V is almost certainly going to lead to immediate and possibly catastrophic failure, and that’s not the kind of excitement anyone needs after a long day.
The actual voltage in your home or business can vary slightly depending on the time of day, the load on the power grid, and even your location. However, major discrepancies between what an appliance requires and what it receives can lead to problems like reduced performance, overheating, premature failure, or, in the worst-case scenario, electrical fires. It’s always best to know what voltage you are working with to minimize the risk and maximize the efficiency of your appliances.
In short, voltage isn’t just a number; it’s a critical factor in the safe and efficient operation of all your electrical devices. Taking the time to understand the voltage requirements of your appliances and the voltage supplied by your electrical system can save you time, money, and a whole lot of potential headaches down the road. So, let’s dive deeper into this voltage variance mystery and clear up any confusion!
Delving Deeper
2. The Technicalities of Voltage Compatibility
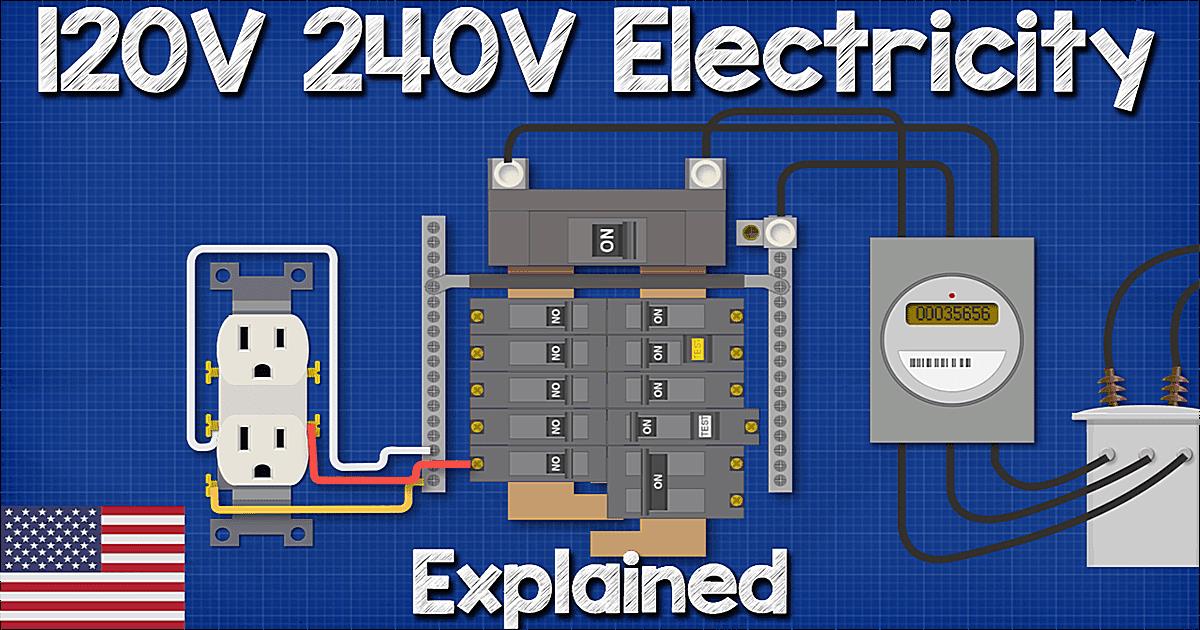
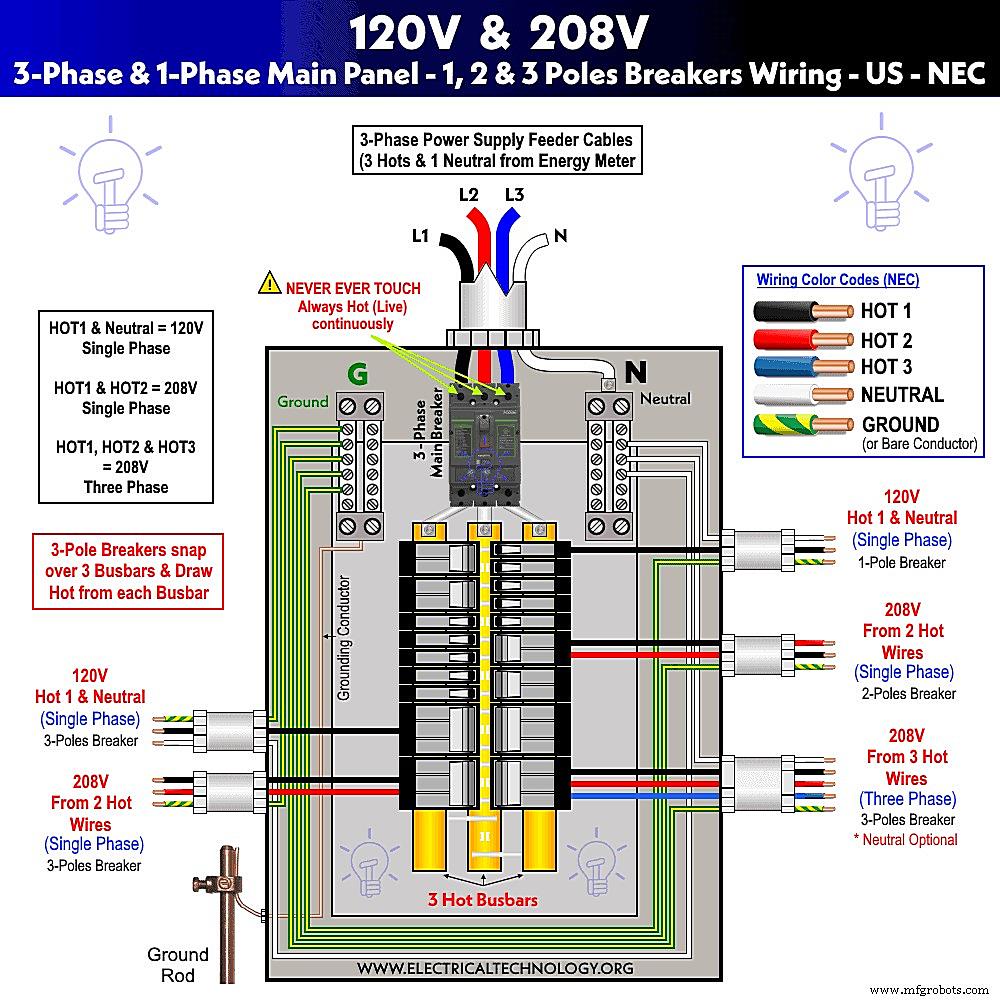
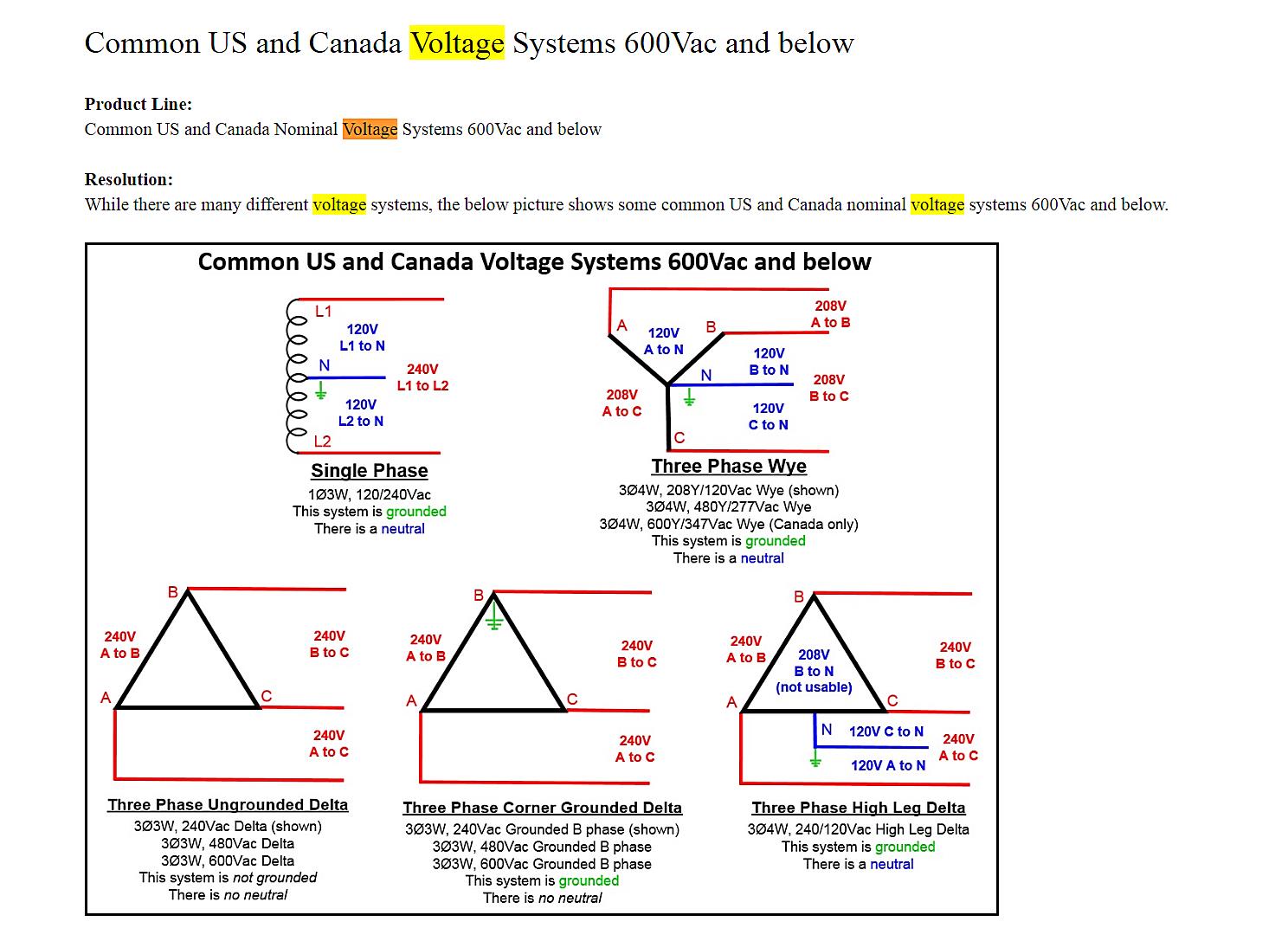
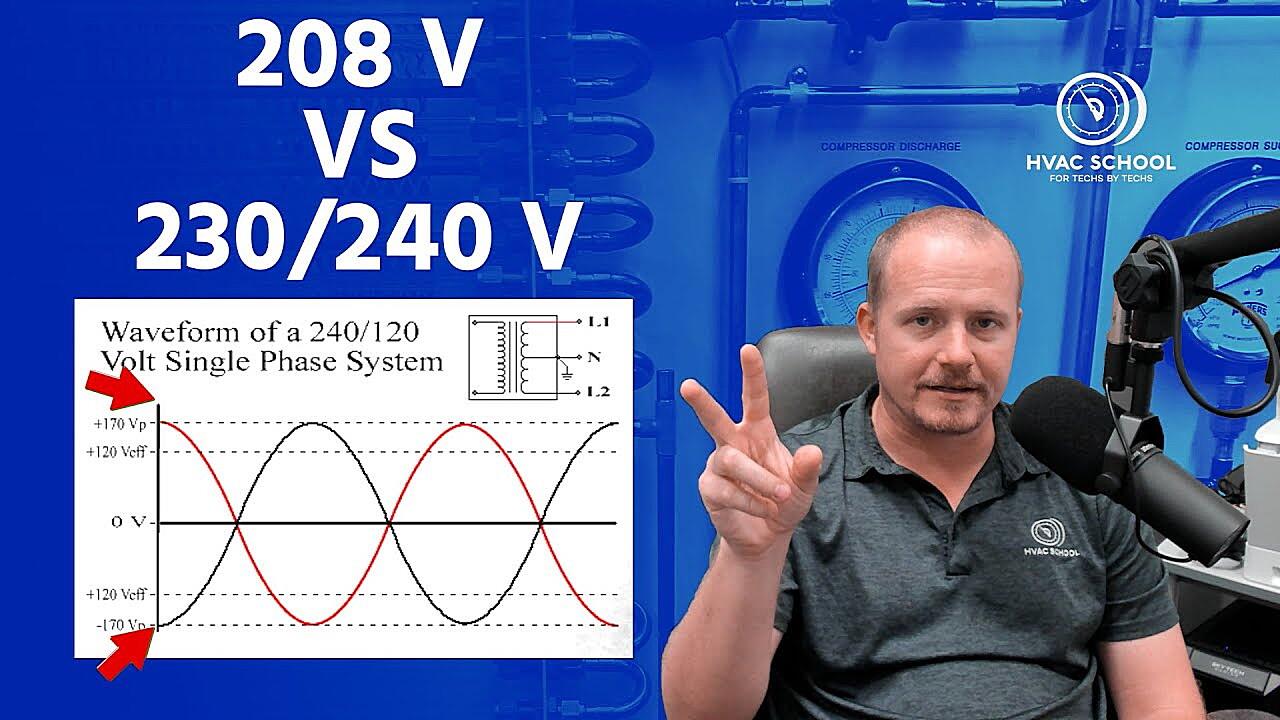
Alright, let’s get a little technical, but I promise to keep it as painless as possible. Electrical systems in North America (and some other parts of the world) commonly use 120V/240V for residential power. The 240V is generally used for larger appliances like stoves, dryers, and air conditioners, while 120V handles everything else your lamps, TVs, and that all-important coffee maker. The 208V, however, is more common in commercial settings, often derived from a three-phase power system. So, what happens when these voltages meet?
In a nutshell, a 240V appliance expects a certain “push” of electricity. If it only gets 208V, it’s like trying to push a car uphill with only half the necessary horsepower. Heating elements, for instance, will take longer to heat up, and motors might run slower or even stall. The appliance may still technically “work,” but it’s struggling, and that strain can lead to problems down the line.
Conversely, sending 240V to a device designed for 208V is like trying to run a marathon at a sprint. The device can’t handle the increased electrical pressure, and components can quickly overheat and fail. This scenario is generally much more dangerous and likely to result in immediate damage. Imagine plugging a phone charger rated for 110V into a 220V outlet — sparks will fly, and your charger is toast. The same principle applies, just on a larger, potentially more dangerous, scale.
Now, there are some appliances that are designed to handle a range of voltages. These are often labeled with something like “120V-240V” or “100V-240V.” These appliances have internal components that can automatically adjust to the incoming voltage. However, always double-check the label on your appliance before plugging it in. When in doubt, err on the side of caution and consult a qualified electrician.
Practical Scenarios
3. Where You Might Encounter This Voltage Issue
Okay, so we’ve talked about the theory, but where might you actually run into this “208V on 240V” dilemma in real life? Well, it’s more common than you might think, especially if you’re dealing with older buildings or commercial properties. Imagine you’re renovating an apartment building and want to install new electric stoves. The building might have a 208V electrical system, common in older multi-unit dwellings, while the stoves you want to install are designed for the standard 240V found in most homes.
Another scenario involves purchasing used appliances. Maybe you found a fantastic deal on a used dryer, but it turns out it was previously used in a commercial laundry with a 208V system. Plugging it into your home’s 240V outlet could lead to problems. It’s crucial to know the origin of the appliance and whether it’s compatible with your electrical system.
Consider a workshop or small business setting. Many workshops utilize three-phase power, which often results in 208V available for certain equipment. If you’re bringing in equipment designed for a standard 240V outlet, you’ll need to address the voltage difference before plugging anything in. Not doing so is just asking for trouble — potentially expensive trouble, at that!
Essentially, anytime you’re dealing with electrical appliances, especially larger ones, it pays to be voltage-aware. Taking a few minutes to verify the voltage requirements can save you a lot of time, money, and potential headaches. It’s a simple step that can make a big difference in the long run.
Solutions and Workarounds
4. How to Make It Work (Safely!)
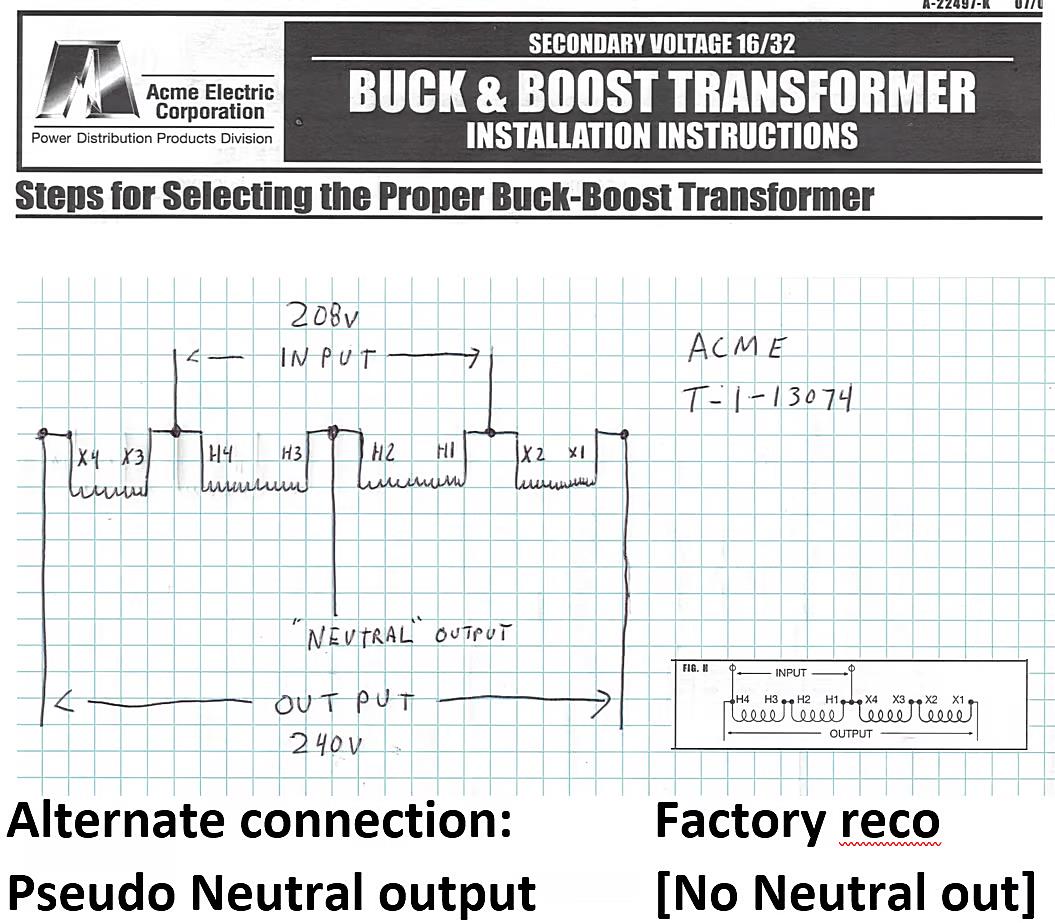
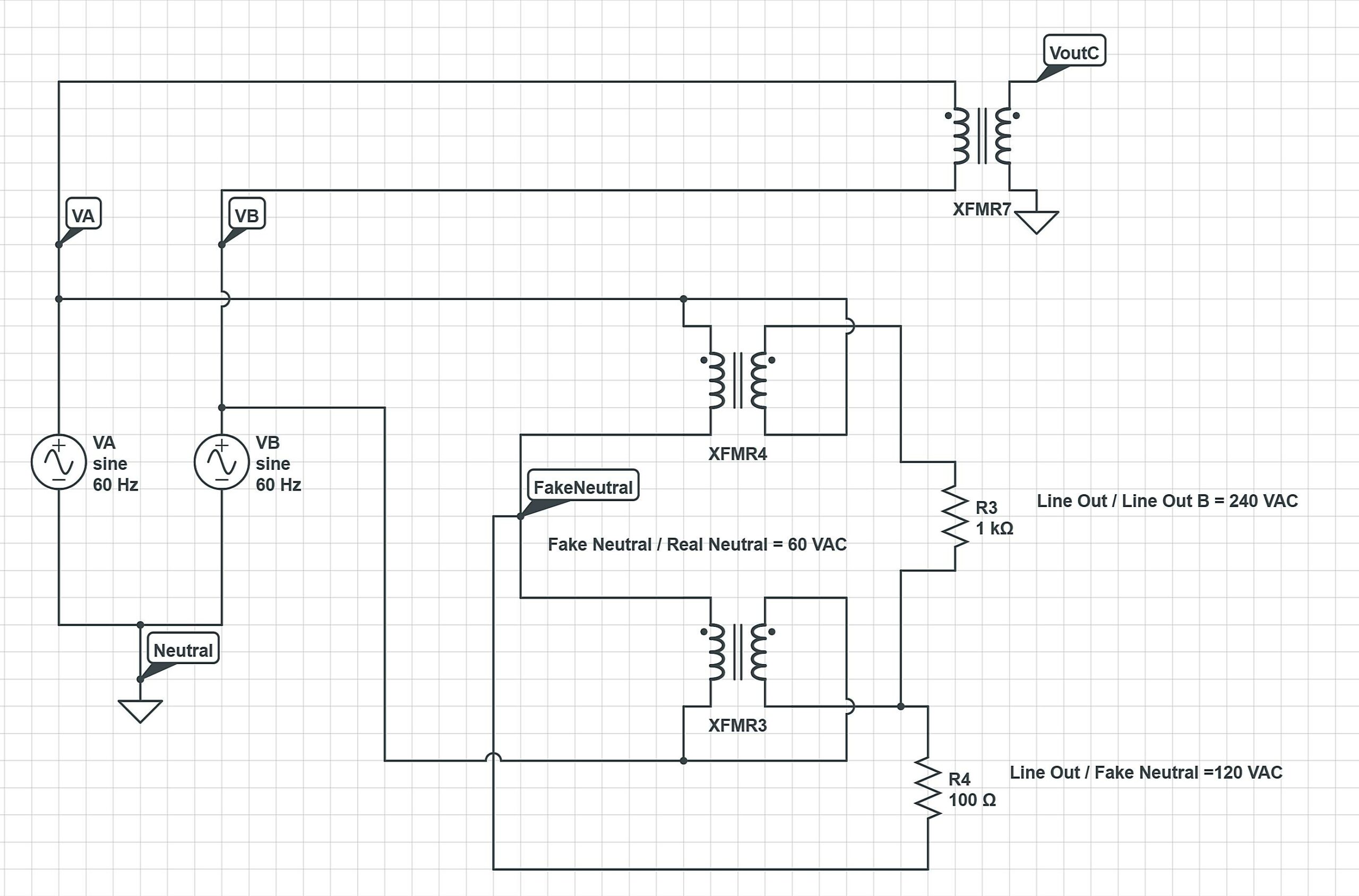
So, you’ve discovered that your appliance and your electrical system are speaking different voltage languages. Don’t despair! There are ways to bridge that gap and get everything working together harmoniously. One of the most common solutions is to use a buck-boost transformer. This device can either step down the voltage from 240V to 208V or step up the voltage from 208V to 240V, depending on your needs. It’s like a voltage translator, ensuring that your appliance gets the power it needs.
However, it’s important to choose the right size transformer for your appliance. You’ll need to know the appliance’s wattage or amperage to ensure that the transformer can handle the load. Overloading a transformer can lead to overheating and failure, so it’s always better to err on the side of caution and choose a slightly larger model. Consulting with a qualified electrician is highly recommended in this scenario.
Another option, in some cases, might be to rewire the appliance itself. Some appliances have internal wiring that can be configured for different voltages. However, this is generally a task best left to experienced professionals. Tampering with the internal wiring of an appliance without proper knowledge and training can be extremely dangerous and could void any warranties.
Finally, it’s worth considering whether it’s simply more cost-effective to replace the appliance with one that’s compatible with your existing electrical system. While the initial cost might be higher, it could save you money in the long run by avoiding the expense of a transformer or the potential risks of rewiring. Plus, a new appliance is always a nice upgrade, right?
Safety First! Key Considerations and Precautions
5. When in Doubt, Call a Pro
Electricity is a powerful force, and messing with it without proper knowledge and precautions can be dangerous. If you’re at all unsure about how to handle voltage differences, always consult a qualified electrician. They have the expertise and equipment to safely assess your electrical system and recommend the best course of action. Remember, your safety and the safety of your home should always be the top priority.
Before working on any electrical circuits, always turn off the power at the breaker box. This will help prevent accidental shocks. Double-check that the power is off by using a voltage tester. It’s a simple step that can save you from a potentially life-threatening situation. Electrical work can be tempting to DIY, but the risk of injury or fire makes the cost of hiring a professional well worth it.
When using a buck-boost transformer, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Improper installation or use can lead to overheating, fire, or electrical shock. Always ensure that the transformer is properly grounded and that all connections are secure.
And finally, a friendly reminder: Never attempt to bypass safety devices or tamper with electrical equipment. These devices are designed to protect you from harm, and disabling them can have serious consequences. Always respect the power of electricity and treat it with the caution it deserves.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Q: What happens if I plug a 208V appliance into a 240V outlet?
A: Most likely, the appliance will be damaged or destroyed. The increased voltage can cause components to overheat and fail, potentially leading to a fire hazard.
Q: Can I use a standard extension cord with a buck-boost transformer?
A: It’s generally not recommended to use a standard extension cord with a transformer, especially for high-power appliances. Use a heavy-duty extension cord rated for the appropriate amperage to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
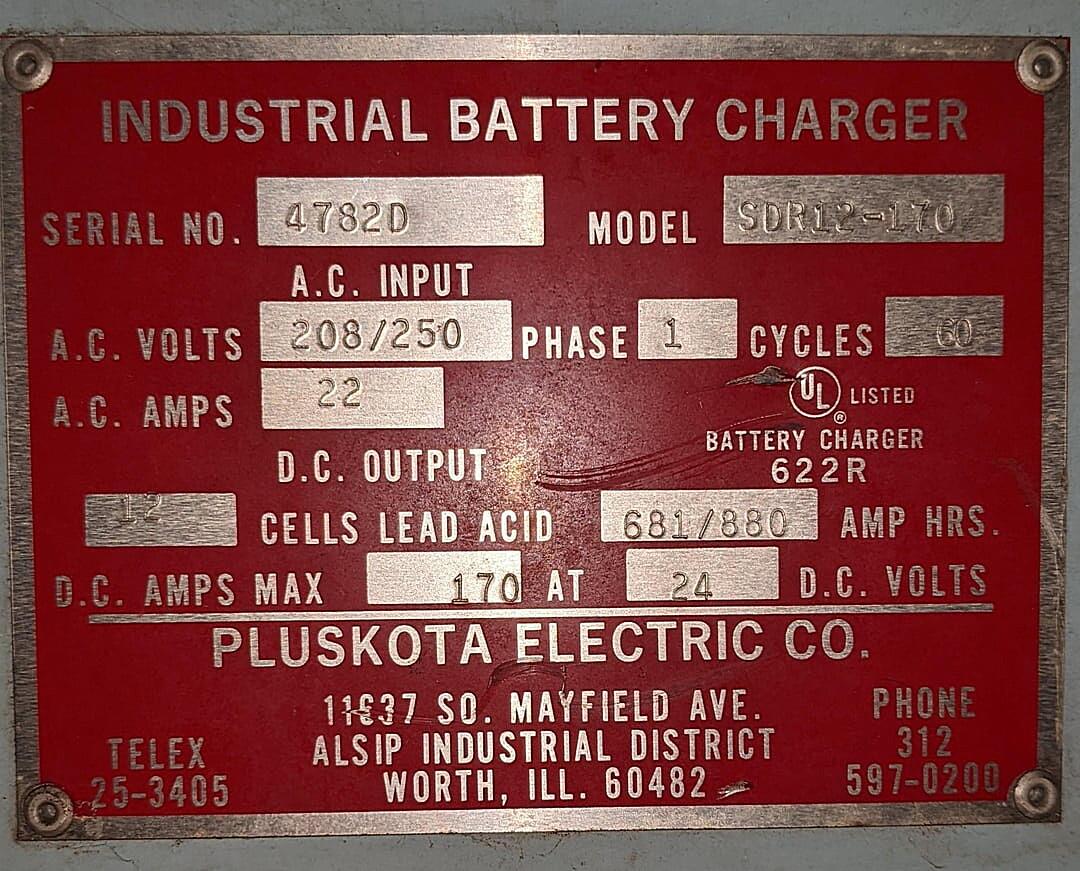
Q: How can I tell if my appliance is designed for 208V or 240V?
A: The voltage requirements are usually printed on a label located on the appliance itself. Look for a sticker near the power cord or on the back of the appliance. If you can’t find a label, consult the appliance’s manual.
Q: Is it safe to convert 208V to 240V myself?
A: While it is possible to convert 208V to 240V yourself using a buck-boost transformer, it is highly recommended to hire a qualified electrician for the installation. Electrical work can be dangerous if not done correctly.