The Curious Case of Electricity and the Missing Neutral Wire
1. Understanding the Basics of Electrical Circuits
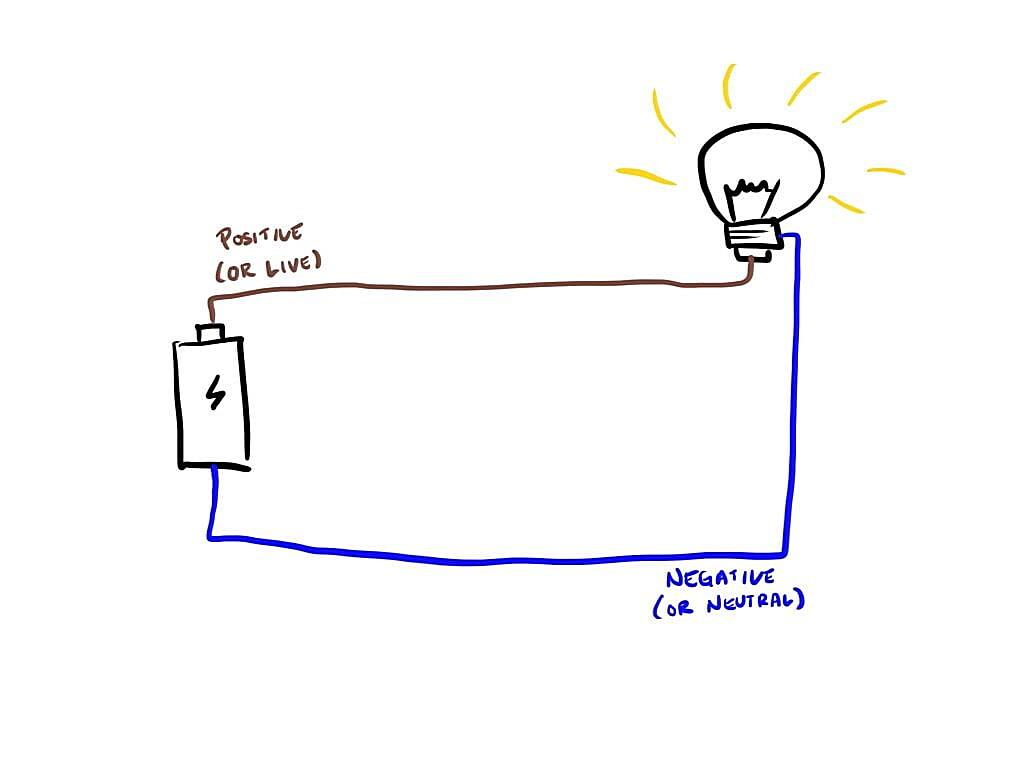
Alright, let’s talk electricity. You flip a switch, the lights come on, the toaster toasts — magic, right? Well, not exactly. It’s more like a well-orchestrated dance of electrons flowing through a circuit. Think of it like a water park. You need a source (the pump, or in our case, the power plant), a path for the water to travel (the wires), and a destination (the slides, or your appliances). But what about the return trip for the water? That’s where the neutral wire comes in, usually.
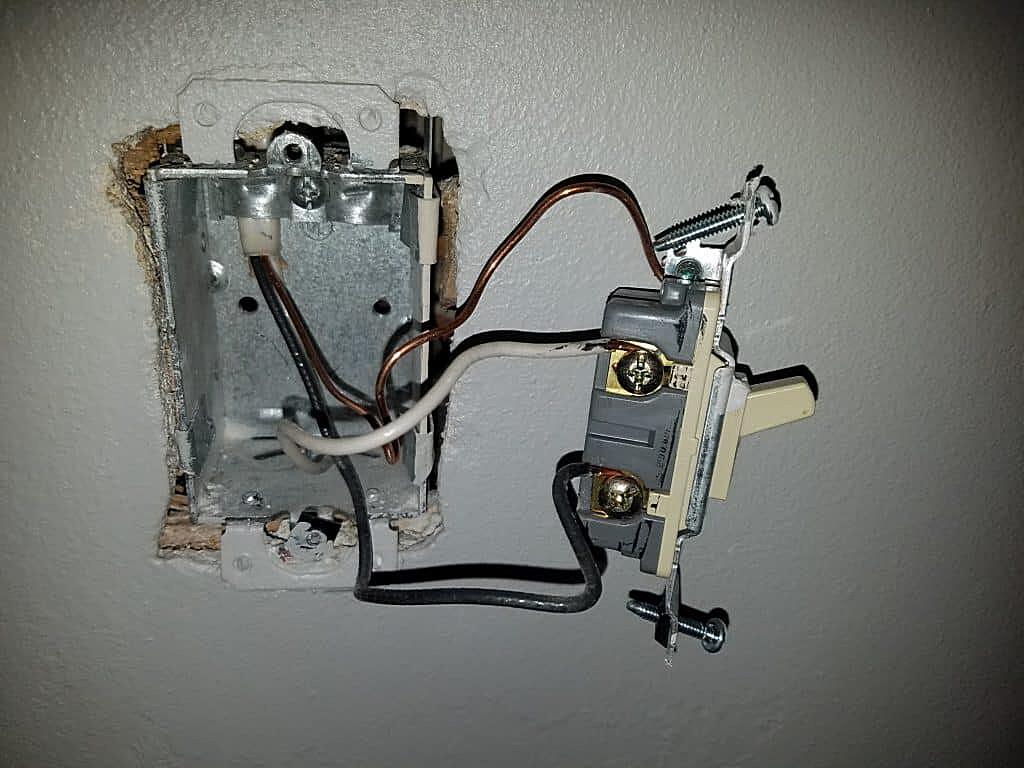
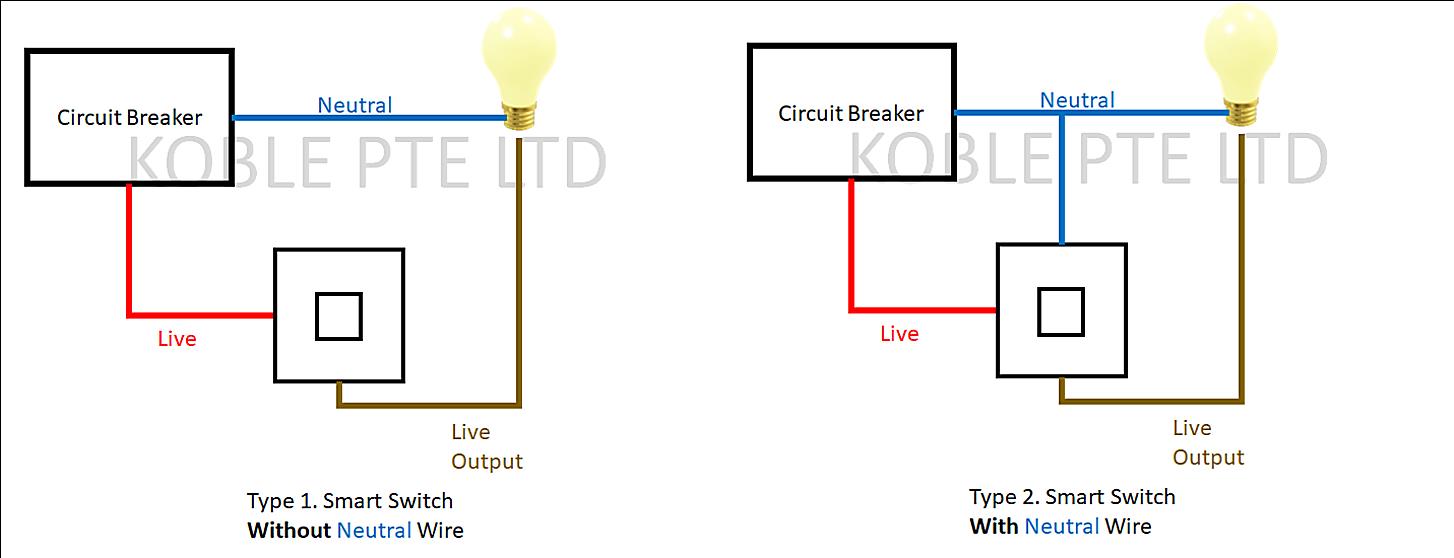
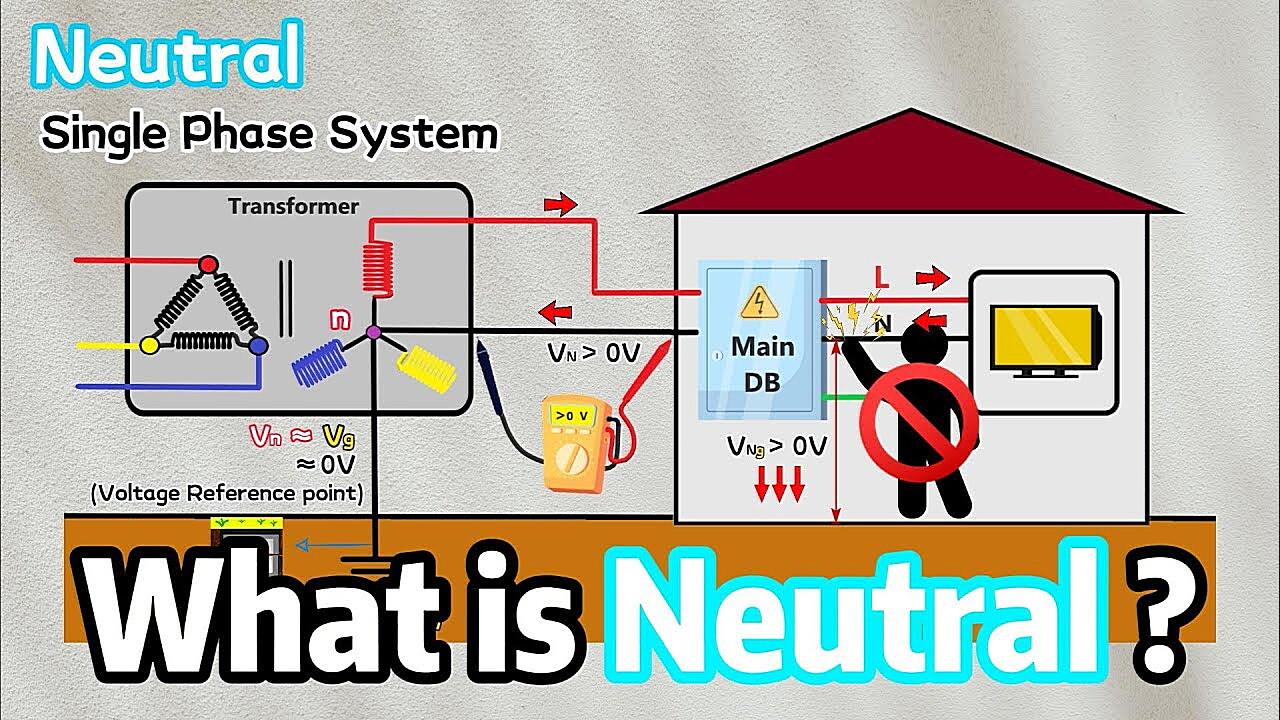
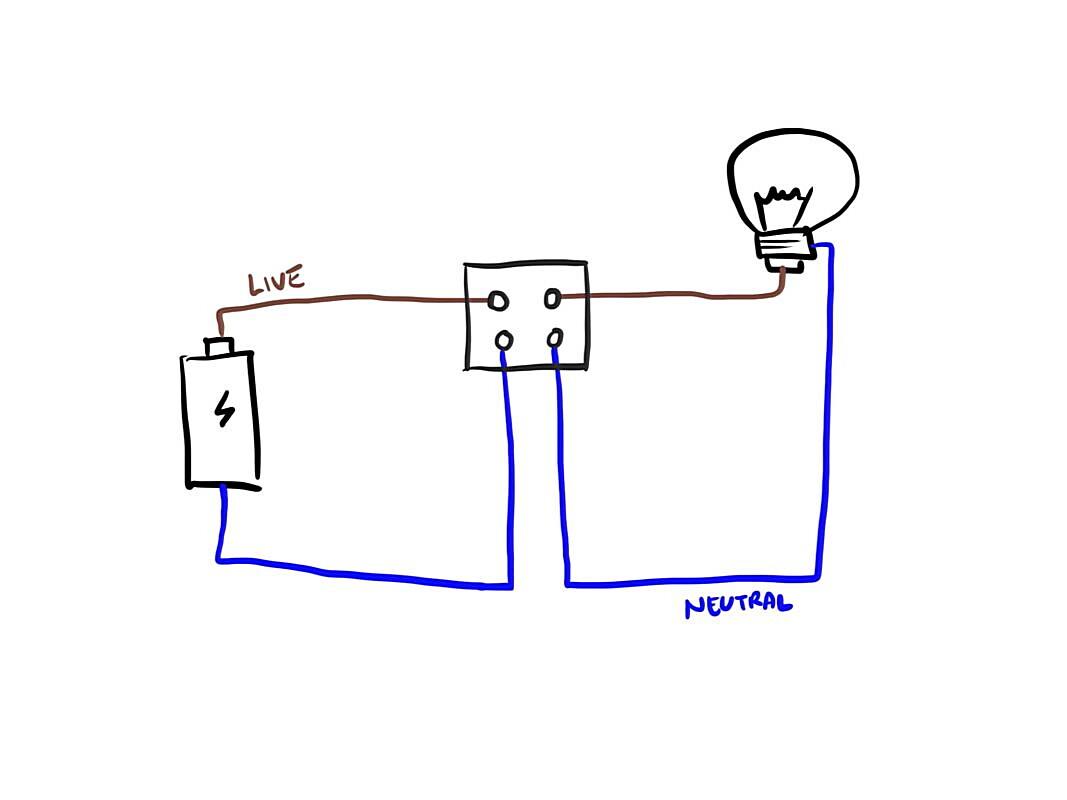
The neutral wire, typically identified by its white color, is a vital part of most electrical circuits. It provides a return path for the current back to the source, completing the loop. Without a complete loop, the electrons get stuck, and your devices don’t work. Imagine trying to fill a bucket that has no bottom, pretty futile, right? That’s electricity without a neutral.
So, the big question: Can electricity actually function without this seemingly crucial neutral wire? Well, its a bit of a yes, but situation. Let’s dive into the ‘but’ part, because that’s where things get interesting.
In a balanced three-phase system, the neutral wire is theoretically not needed. The current returns through the other phases. Imagine a perfectly balanced spinning top, each push (phase) canceling each other out, allowing a stable rotation (electricity flow). However, perfectly balanced systems are rare in the real world. Imbalances can occur as different appliances are turned on and off, which is why a neutral wire is often included to handle these imbalances and ensure safety.
Going Neutral
2. The Importance of a Complete Circuit
Imagine you’re trying to throw a boomerang. You throw it (that’s the hot wire sending the electricity), and you expect it to come back (that’s the neutral returning the electricity). If it doesn’t come back, well, that’s a problem. Maybe it got stuck in a tree. That’s kind of like what happens when electricity doesn’t have a neutral return. It doesn’t necessarily mean it won’t work at all, but it can lead to inefficiencies and, more importantly, safety hazards.
Think of the neutral wire as a safety valve. If something goes wrong in the circuit — say, a short circuit — the neutral wire provides a low-resistance path for the current to flow, tripping the circuit breaker and preventing a potential fire or electric shock. It’s like having a designated escape route in a building; you hope you never need it, but you’re really glad it’s there if something bad happens.
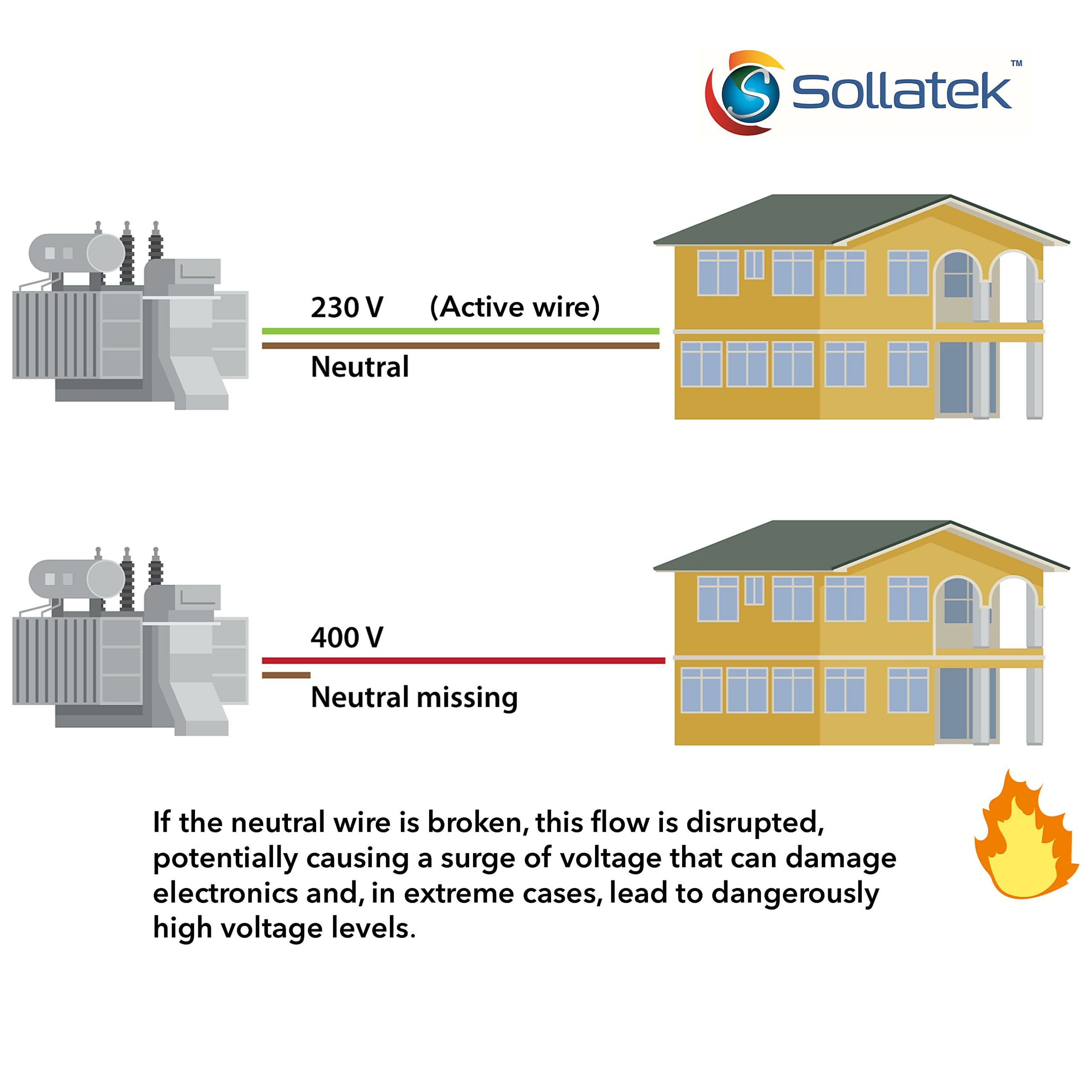
Without a properly functioning neutral, the voltage in the circuit can fluctuate wildly. This can damage sensitive electronic equipment, like your fancy TV or computer. It’s like trying to drive a car with square wheels — it might technically move, but it’s not going to be a smooth ride, and eventually, something’s going to break. In fact, it might just explode.
Furthermore, a missing or faulty neutral can cause a phenomenon called “phantom voltage.” This is where you measure a voltage on a circuit that’s supposed to be off. This can be misleading and dangerous, as it can give you a false sense of security and potentially lead to electric shock. Always double check with a professional!
Three-Phase Systems
3. Delving into Alternative Electrical Setups
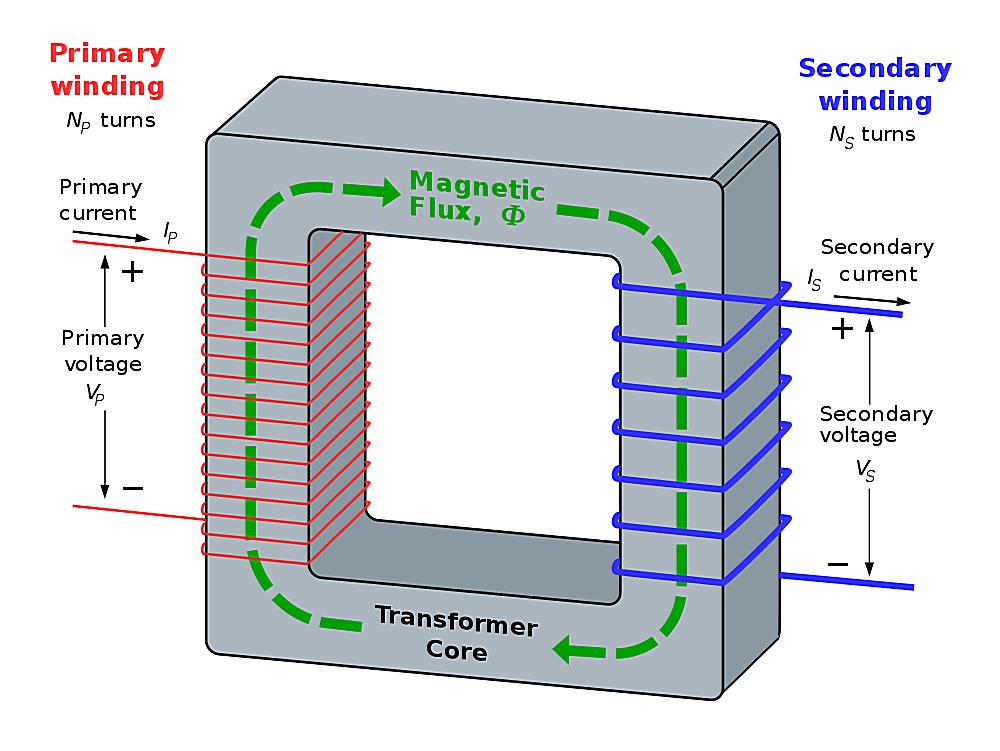
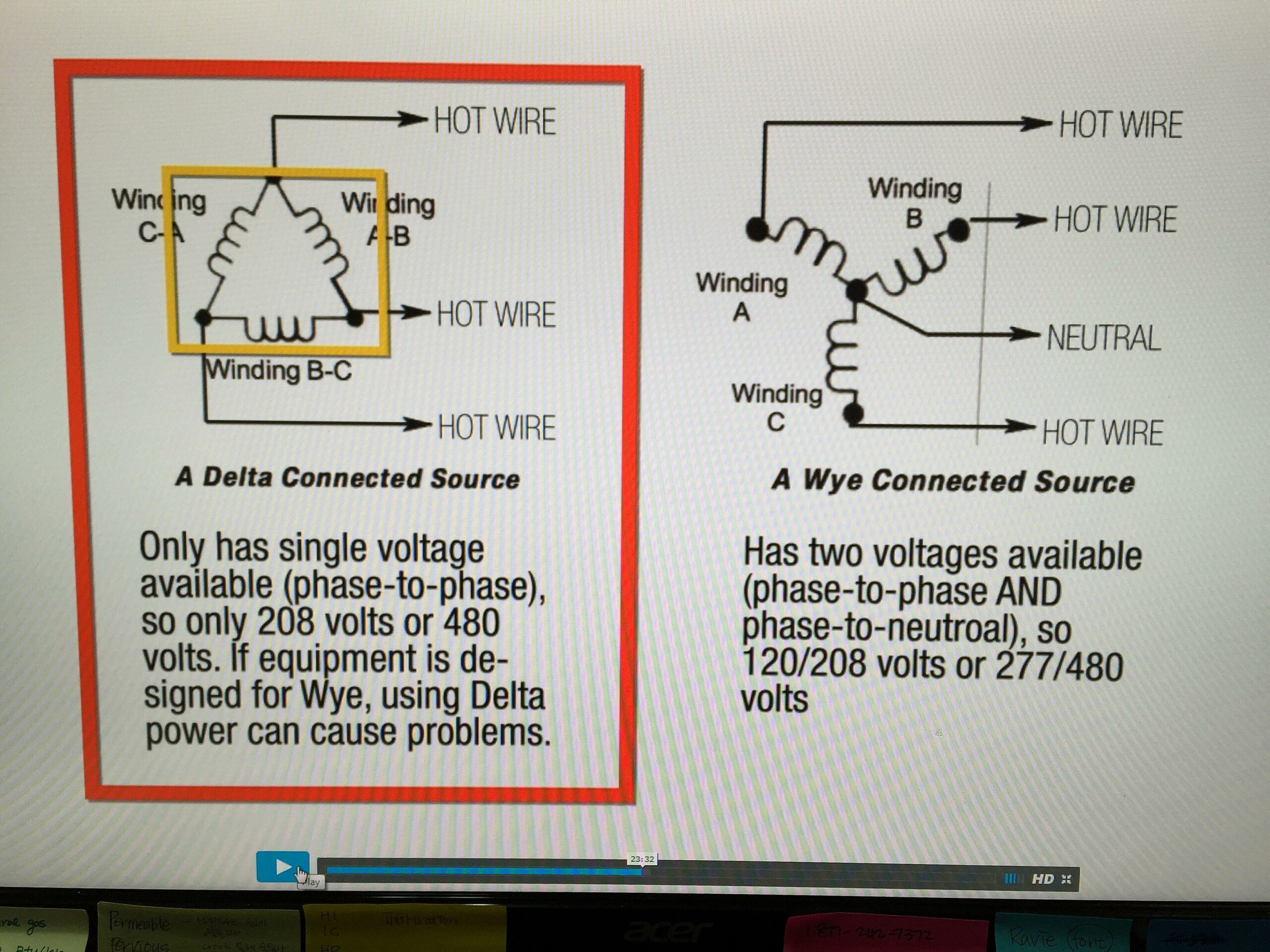
Now, let’s muddy the waters a bit. In some industrial settings, you’ll find three-phase electrical systems. These systems are designed to deliver power more efficiently, and in certain situations, they can operate without a neutral wire. However, this is generally in perfectly balanced loads, which, in reality, are difficult to achieve. Even in balanced loads, it’s standard and safer to use a neutral wire, especially for residential usage.
Three-phase power is like having three separate single-phase circuits all working together, offset by 120 degrees. This allows for a more constant and smooth delivery of power, which is ideal for large motors and other heavy-duty equipment. It’s kind of like having three engines working together instead of just one, providing more power and stability. They are more common in big machines like MRI, CT Scan, and Industrial motors.
However, the absence of a neutral wire in a three-phase system is only safe and efficient when the load is perfectly balanced across all three phases. This means that each phase is drawing the same amount of current. Any imbalance can lead to voltage fluctuations and potential damage to equipment. Achieving that is very tricky.
Even in three-phase systems, it’s common practice to include a neutral wire for safety and to handle any potential imbalances. The neutral wire acts as a safety net, ensuring that the voltage remains stable and preventing any dangerous voltage spikes. So, while it might be possible to run a three-phase system without a neutral in theory, it’s generally not recommended in practice.
DIY Dangers
4. Safety First
Messing with electricity is not like changing a light bulb (though even that can be dangerous if you’re not careful). If you’re not a qualified electrician, it’s best to leave electrical work to the pros. We all want to save money, but dealing with electricity is just not it. Trust me on this one.
Trying to bypass the neutral wire or modify your electrical system without proper knowledge and training is extremely dangerous. It can lead to electric shock, fire, and even death. It’s just not worth the risk. Think of it like trying to perform surgery on yourself after watching a YouTube video — you’re probably not going to end up with a good result.
Signs that you might have a problem with your neutral wire include flickering lights, appliances that don’t work properly, and circuit breakers that trip frequently. If you notice any of these issues, it’s important to call a qualified electrician right away. They have the tools and expertise to diagnose the problem and fix it safely and effectively.
In addition, DIY electrical work can also void your home insurance policy. If something goes wrong as a result of your amateur electrical work, your insurance company may not cover the damages. It’s always better to play it safe and hire a professional.
So, Can Electricity Work Without Neutral? The Verdict.
5. Recapping the Complex Relationship
Alright, let’s summarize. Can electricity work without a neutral wire? In some very specific and carefully controlled situations, yes, it technically can. But for the vast majority of residential and commercial applications, the answer is a resounding NO. The neutral wire is a crucial safety component that ensures the stable and safe operation of your electrical system.
Think of the neutral wire as the unsung hero of your electrical system. It’s always there, quietly working behind the scenes to keep your lights on, your appliances running, and you safe from electric shock. It’s the reliability your system needs to function the way it should. It’s the glue that holds everything together.
So, the next time you flip a switch, take a moment to appreciate the humble neutral wire and the important role it plays in bringing power to your life. And remember, when it comes to electricity, always err on the side of caution and leave the work to the professionals.
Ultimately, electricity, like any complex system, demands respect and understanding. While theoretical possibilities exist, practical application almost always necessitates a neutral wire for safety, efficiency, and reliability. So, before you start tinkering with your home’s electrical system, remember the golden rule: when in doubt, call an electrician!
Frequently Asked Questions
6. Your Burning Electrical Questions Answered
Here are some common questions people have about electricity and neutral wires:
7. Question 1
Answer: If the neutral wire is disconnected, it can lead to voltage fluctuations in the circuit. This can damage sensitive electronic equipment and potentially cause electric shock. It’s like removing the stabilizer from a bicycle — things can get wobbly and unpredictable very quickly.
8. Question 2
Answer: While the neutral wire is usually at or near ground potential, it’s never a good idea to touch any wires unless you’re a qualified electrician and have taken appropriate safety precautions. Under fault conditions, the neutral wire can become energized and pose a significant electrocution hazard.
9. Question 3
Answer: No! The ground wire is a safety wire that’s designed to provide a path for fault current to flow back to the source in the event of a short circuit. Using the ground wire as a neutral can create a dangerous situation, as it can energize metal objects in your home and increase the risk of electric shock. This is a serious code violation and should never be attempted.