You May Also Like :
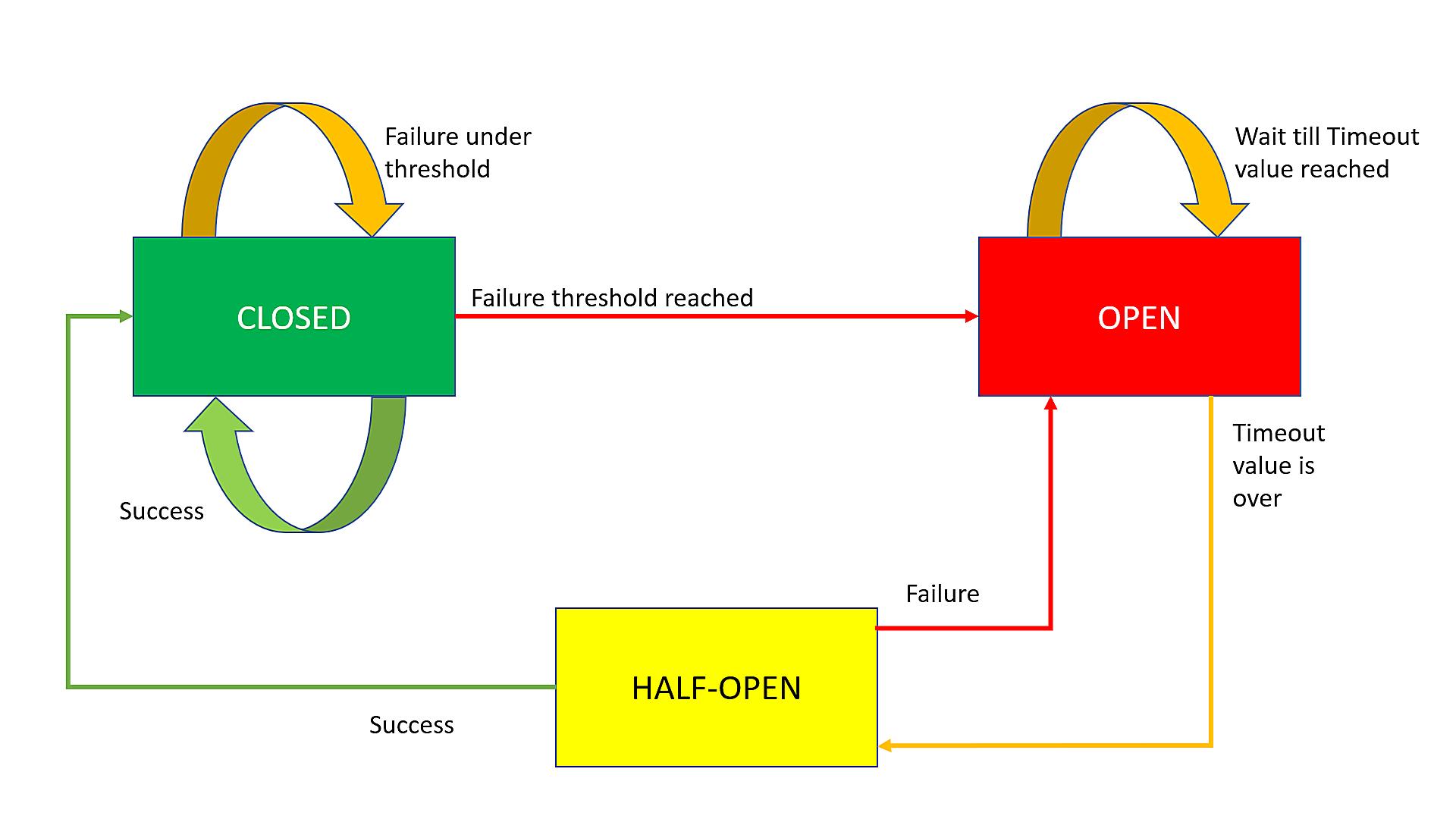
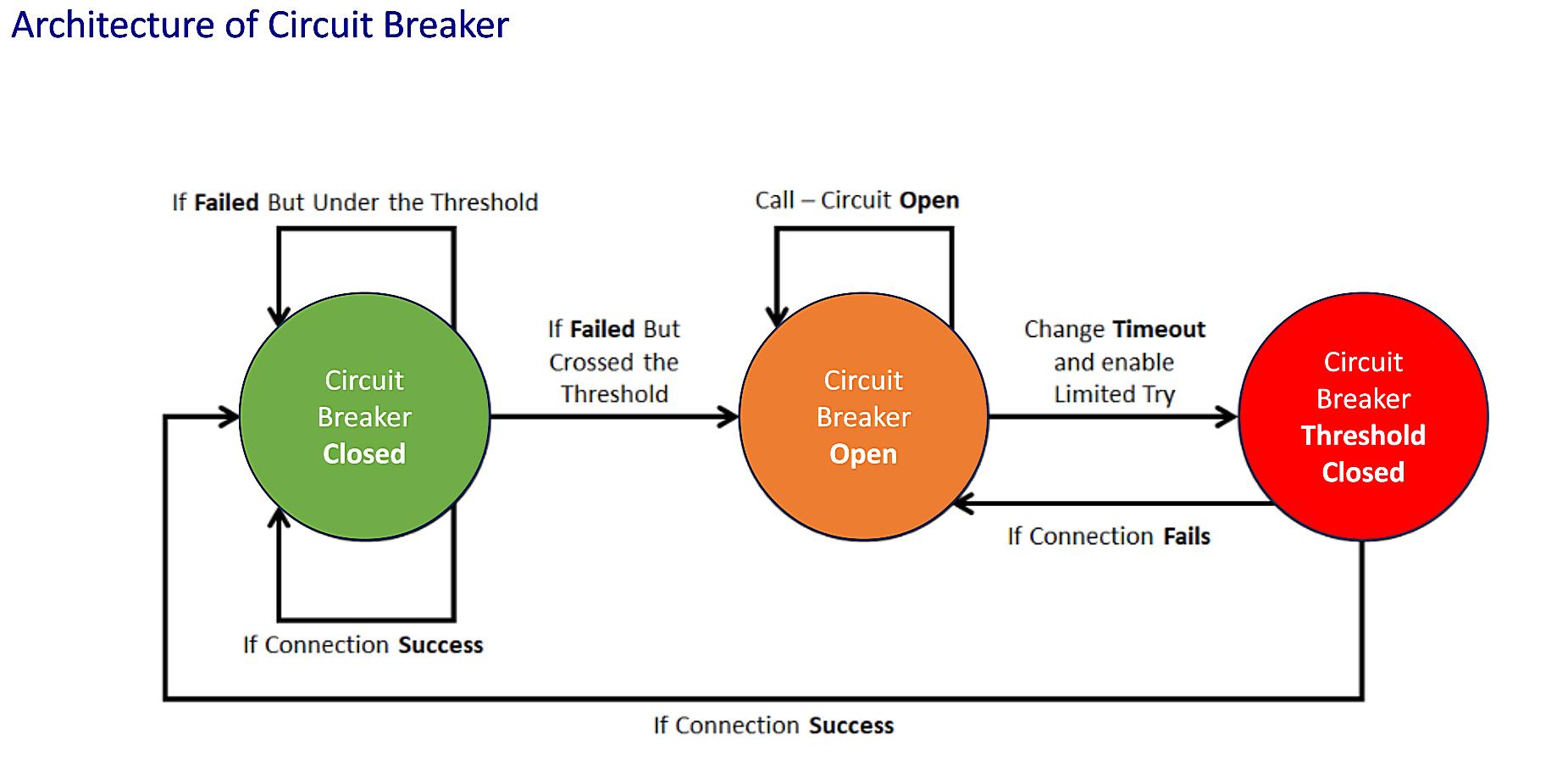
Understanding the Circuit Breaker Threshold
1. What Exactly is a Circuit Breaker Threshold?
Ever wondered what prevents your home’s wiring from turning into a crispy critter situation? That’s where circuit breakers, and more specifically, the “circuit breaker threshold,” come into play. Think of it as your electrical system’s bouncer, guarding against overloads and potential hazards. It’s the level of electrical current that, when exceeded, triggers the breaker to trip, cutting off the power to that circuit. No sparks flying, no singed wires — just darkness and a walk to the breaker box.
So, the circuit breaker threshold is basically the upper limit of amperage (that’s electrical current, measured in amps) that a circuit can safely handle. Each circuit in your home is designed to handle a specific amount of electricity, depending on the wiring and the breaker installed. A typical household circuit might be rated for 15 or 20 amps. Go over that limit, and the breaker says, “Nope, not on my watch!” and flips the switch.
Understanding this threshold is vital because overloading circuits is a common cause of electrical fires. Imagine plugging in a space heater, a hair dryer, and a microwave all into the same outlet. That circuit is probably groaning under the pressure, and exceeding its threshold. The breaker is there to prevent the wires from overheating and potentially starting a fire.
Therefore, knowing the circuit breaker threshold for each circuit in your home is more than just a nerdy detail; it’s a key component of home safety. Check your breaker box labels, and be mindful of how much electricity you’re drawing on each circuit. Your house (and your insurance company) will thank you.
Why is Knowing the Threshold Important?
2. Avoiding Electrical Overloads and Potential Hazards
Beyond simply preventing a power outage, understanding the circuit breaker threshold is essential for safeguarding your home and loved ones. Electrical overloads are a leading cause of house fires, and a tripped breaker is often the only thing standing between you and a potential disaster. Knowing the limit allows you to proactively manage your electrical usage and avoid dangerous situations.
Think of it like this: you wouldn’t load a truck beyond its weight capacity, right? Same principle applies to your electrical circuits. If you consistently overload a circuit, the wires can overheat, insulation can melt, and eventually, a fire can ignite. A tripped breaker is a warning sign that you’re pushing the limits. Ignoring that sign can have serious consequences.
Furthermore, repeated tripping of a circuit breaker can actually damage the breaker itself. Each time it trips, the internal mechanisms experience stress. Over time, this can weaken the breaker, making it less reliable and potentially unable to trip when it needs to. This can lead to a false sense of security, where you think your circuits are protected, but in reality, they’re vulnerable.
So, take the time to map out your circuits, identify their amperage ratings, and be mindful of the appliances you’re plugging in. A little bit of awareness can go a long way in preventing electrical hazards and keeping your home safe and sound.
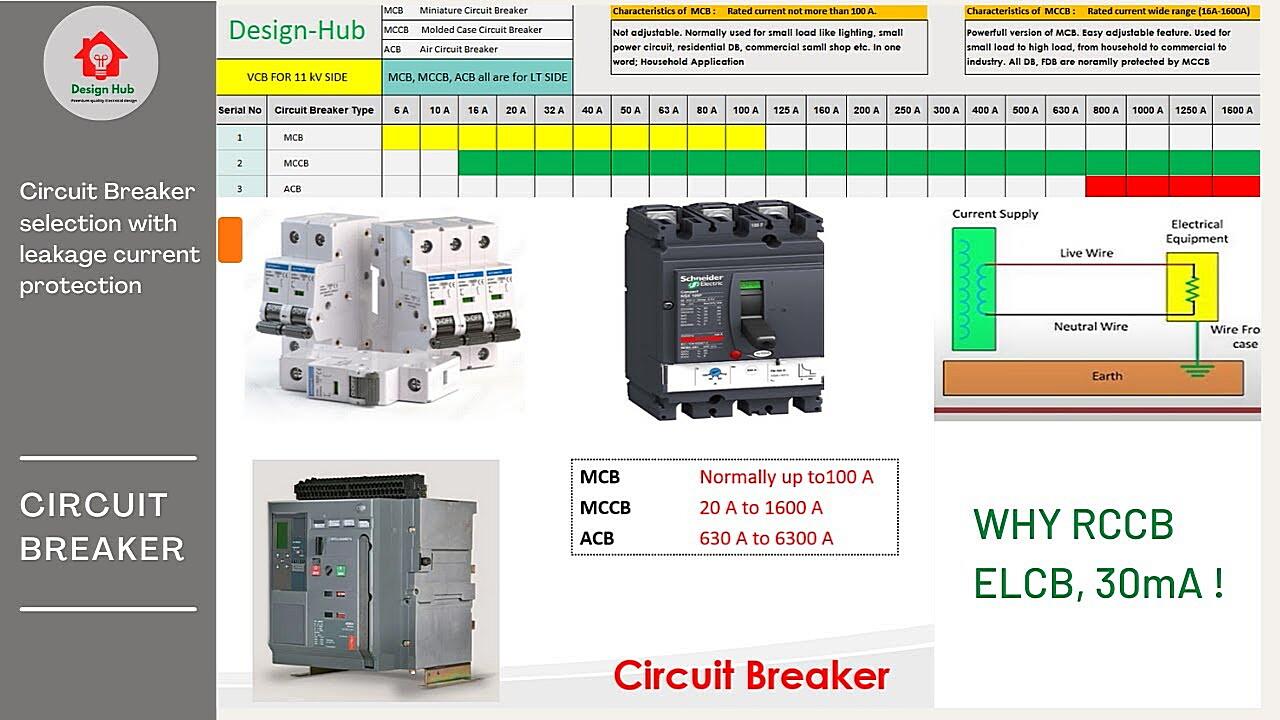
Identifying the Circuit Breaker Threshold in Your Home
3. Finding the Amperage Rating
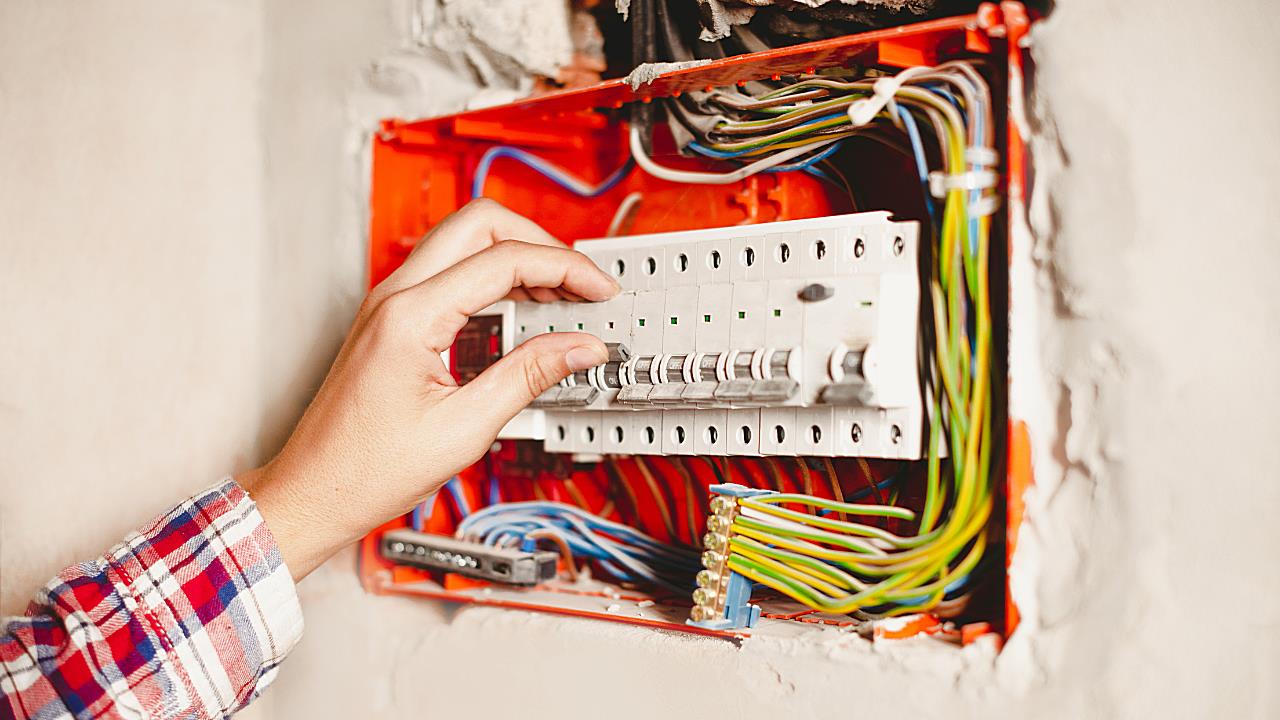
Okay, so you’re convinced that knowing your circuit breaker thresholds is a good idea. But how do you actually find them? The good news is, it’s usually pretty straightforward. The most common place to look is on the circuit breaker itself. Each breaker should have a number printed on it, indicating its amperage rating (e.g., 15, 20, 30). That number represents the threshold.
Another important place to look is at your breaker box’s directory, which is often a little piece of paper (or, in some fancier setups, a label) that lists which breaker controls which circuit. Ideally, this directory will also include the amperage rating for each circuit. However, sometimes these directories are outdated or incomplete, so double-checking the breakers themselves is always a good idea.
If you’re having trouble deciphering the breaker box, or if you’re unsure about the amperage rating of a particular circuit, it’s always best to consult a qualified electrician. They can safely assess your electrical system and provide you with accurate information. Trying to guess or make assumptions about your circuit breaker thresholds can be risky, so when in doubt, call in the pros.
Finally, remember that the amperage rating on the breaker is the maximum amount of current that the circuit can handle. It’s not a suggestion or a target to aim for! It’s the line you don’t want to cross. So, treat it with respect and be mindful of your electrical usage.
What Happens When You Exceed the Threshold?
4. The Tripping Mechanism Explained
So, what actually happens inside that little circuit breaker when you exceed the threshold? It’s a fascinating bit of engineering, involving a combination of heat and electromagnetism. Most circuit breakers use a bimetallic strip, which is made of two different metals that expand at different rates when heated. When the current flowing through the circuit is normal, the strip stays cool and everything’s fine.
However, when you overload the circuit, the bimetallic strip starts to heat up. Because the two metals expand at different rates, the strip bends. As it bends, it eventually reaches a point where it triggers a mechanical switch, causing the breaker to trip and cut off the power. It’s like a tiny, heat-activated robot arm that’s programmed to say, “Enough is enough!”
In addition to the bimetallic strip, some circuit breakers also use an electromagnetic mechanism to detect sudden, large surges in current, such as those caused by a short circuit. In this case, a strong magnetic field is created that pulls on a lever, causing the breaker to trip almost instantaneously. This is crucial for protecting against potentially dangerous events like lightning strikes or faulty appliances.
The combination of these two mechanisms — thermal and electromagnetic — provides a reliable and effective way to protect your electrical system from overloads and short circuits. When a breaker trips, it’s not just an inconvenience; it’s a sign that your electrical system is working as intended and preventing a potentially hazardous situation.
Troubleshooting Tripped Circuit Breakers
5. What to Do (and Not Do) When the Lights Go Out
Okay, so your circuit breaker tripped. Don’t panic! It happens to the best of us. The first thing you should do is identify which breaker tripped. Open your breaker box and look for a breaker that’s in the “off” position, or in a position that’s halfway between “on” and “off”. This usually indicates that the breaker has tripped.
Before resetting the breaker, it’s important to identify the cause of the overload. Unplug any appliances that were running on that circuit before the breaker tripped. This could be anything from a space heater to a hair dryer to a power strip overloaded with devices. Once you’ve unplugged the potential culprits, you can try resetting the breaker by flipping it all the way to the “off” position and then back to the “on” position.
If the breaker trips again immediately after resetting it, there’s likely a more serious problem. This could indicate a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty appliance. In this case, it’s best to call a qualified electrician to diagnose and repair the problem. Do not repeatedly try to reset the breaker, as this could damage the breaker or create a fire hazard.
Finally, a word of caution: never replace a circuit breaker with one that has a higher amperage rating. This is extremely dangerous and can overload the circuit, leading to overheating and potentially a fire. Always use a breaker with the same amperage rating as the one you’re replacing.